The Polyethylene furanoate market is estimated to reach 2 kilotons by the end of this year. It is expected to reach 5 kilotons in the next 5 years, with a projected CAGR of over 20.11% during the forecast period.
Key factors driving the market include the increasing demand for polyethylene furanoate for bottle production and the growing demand from the fiber segment. Additionally, the rising need for the application of bio-plastics and plastic recycling in various industries presents ample opportunities for the growth of the PEF market.
This EuroPlas article will provide you with a comprehensive understanding of PEF market trends, the level of competitiveness, and practical applications in manufacturing and industry.
1. What is PEF - polyethylene furanoate?
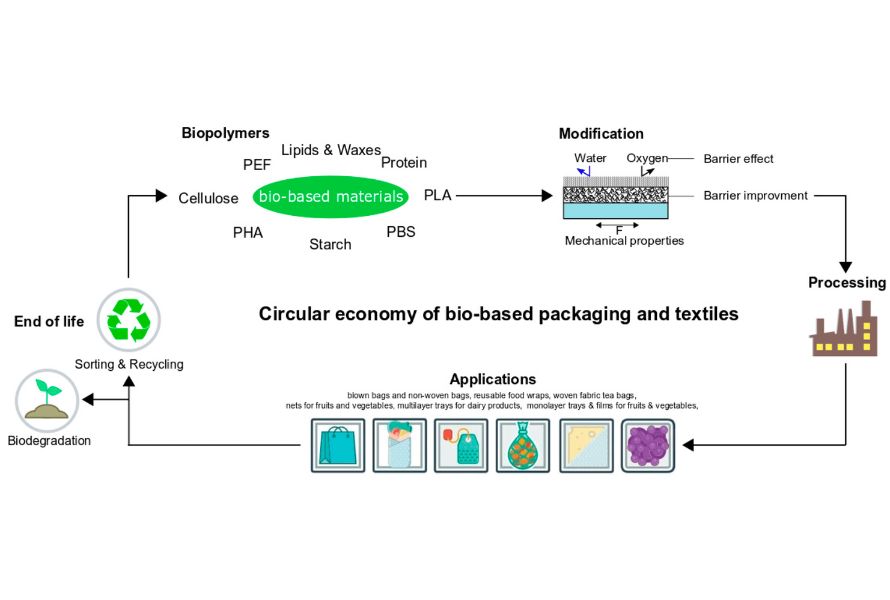
Polyethylene furanoate, abbreviated as PEF or PEF plastic, is a biopolymer with 100% recyclability. It is produced from renewable raw materials, primarily derived from plants, with the main source being sugar. PEF is considered the next-generation polyester with significant potential to replace polyethylene terephthalate (PET), a polymer dependent on traditional synthetic sources. Compared to PET, PEF offers numerous advantages, including:
- Superior performance and mechanical properties, as well as a higher melting temperature.
- Higher glass transition temperature and lower melting point.
- Recyclability, which helps reduce carbon emissions.
- Cost competitiveness on an industrial scale.
Additionally, PEF enhances the sustainability of packaging products, as it is produced from FDCA (furandicarboxylic acid) sourced entirely from bio-based origins when using monoethylene glycol (MEG), which is also bio-based. PEF is created through the polymerization of furan dicarboxylic acid (FDCA) in combination with ethylene glycol.
At the production level, the synthesis process for PEF is similar to the PET production process, but it substitutes terephthalic acid with 2,5-furan dicarboxylic acid (FDCA).
.jpg)
What is PEF - polyethylene furanoate?
2. PEF market trends
The Polyethylene Furanoate (PEF) market trends are experiencing robust growth, especially in the PEF bottle segment. The increased adoption of PEF in bottle applications is attributed to its exceptional durability, puncture resistance, and excellent heat resistance. Moreover, PEF enhances its oxygen and carbon dioxide barrier properties, preventing the oxidation of food products. This has led to a growing demand for PEF in the food and beverage sector, driving market growth.
The food and beverage sector is one of the most crucial manufacturing industries in Europe, and it is also a primary consumer of various packaging types, including bottles. According to FoodDrinkEurope, in the fourth quarter of 2022, the revenue of the food and beverage industry increased by 2.3% compared to the previous quarter and grew by 19.2% compared to the same period the previous year, as of the fourth quarter of 2021.
Furthermore, the export value of food and beverages in the European Union reached 48.3 billion EUR (~50.9 billion USD) in the fourth quarter of 2022, marking a 17.5% increase compared to the fourth quarter of 2021. This strong growth in food and beverage exports has had an impact on the demand for bottles and containers within the industry.
According to the Department for Environment, Food & Rural Affairs in the United Kingdom, there are a total of 1,610 beverage manufacturing businesses, including both small and medium-sized enterprises, along with 30 large companies. With the growth of these companies, the demand for bottles made from sustainable materials is also expected to rise, positively affecting the PEF market.
Therefore, the increasing demand for beverage packaging such as water, soft drinks, fruit juices, and alcoholic beverages is expected to contribute to the development of the Polyethylene Furanoate market in the forecast period.
.jpg)
PEF market trends
3. Can PEF compete with other bio-plastics?
PEF is a synthetic plastic, whereas other bioplastics like PLA and PHA are made from bio-based sources. Therefore, PEF can compete with other bioplastics in terms of durability and resistance.
However, bio-plastics may have sustainability advantages since they are made from renewable sources and can undergo biodegradation. Hence, the competition between PEF and other bio-plastics will depend on consumer demand for sustainable products.
Here are some insights from market and pricing experts regarding PEF:
- Hideo Nishimura, President and CEO of Idemitsu Kosan, stated: "We believe that PEF will be an important plastic in the future, given its superior properties over PET and other plastics. We are investing in the development of new PEF production technologies to reduce manufacturing costs and expand the market for PEF."
- Mark Miles, CEO of DuPont Packaging & Industrial Polymers, mentioned: "We believe that PEF has the potential to replace PET in some food and beverage packaging applications. We are collaborating with customers to develop new applications for PEF."
- Kevin McCarthy, CEO of Eastman Chemical, said: "We believe that PEF can compete with other bio-plastics in terms of durability and resistance. We are developing new PEF production technologies to reduce manufacturing costs and expand the market for PEF."
Overall, the PEF market is rapidly evolving. With its superior properties and support from policies and regulations, PEF has the potential to become a significant plastic in the future.
Can PEF compete with other bio-plastics?
4. Which type of polyethylene furanoate is consumed the most?
Based on its origin, the market is divided into plant-based, bio-based, and other types. Bio-based Polyethylene Furanoate occupies a significant portion of the global market.
The demand for beverage packaging is on the rise, the use of bio-plastics is increasing, and the demand for recyclable products is growing, along with changes in consumer preferences towards environmentally friendly options.
All of these factors are predicted to drive the demand for bio-based polyethylene furanoate. The increase in consumption of food and beverage products worldwide is boosting the sales volume of bio-based polyethylene furanoate.
5. Which PEF application is expected to dominate the market?
Polyethylene furanoate (PEF) fibers hold a 47.2% global market share of PEF and continue to lead over other applications such as bottles and films. PEF fibers exhibit superior properties and have the potential to replace PET fibers.
They can be recycled from PEF bottles and are also used to produce 100% bio-based textiles.
Moreover, these fibers find application in wrapping industrial products like fertilizers, pesticides, and cement. They also appear in carpets, clothing, and sports equipment.
.jpg)
Which pef application is expected to dominate the market?
6. Polyethylene furanoate recycling
PEF recycling is the process of transforming used PEF plastic into new products. PEF is a thermoplastic resin widely used in applications such as water bottles, food packaging, and fibers. Recycling PEF can help reduce environmental pollution and conserve natural resources.
There are two primary methods for recycling PEF:
- Mechanical Method: PEF plastic is ground into small pieces, then melted and formed into new products. This method is often used to produce lower-quality items, such as carpets and insulation materials.
- Chemical Method: PEF plastic is broken down into smaller molecules and then recombined into new products. This method is typically employed to manufacture higher-quality items, such as water bottles and food packaging.
PEF recycling is still in its developmental stages, but it is becoming increasingly popular. Some companies are investing in new technologies to enhance the efficiency of PEF recycling. There are several benefits of recycling PEF:
- Environmental Pollution Reduction: PEF recycling helps minimize the amount of plastic waste that ends up in the environment. PEF plastic can persist in the environment for hundreds of years and can cause soil, water, and air pollution.
- Conservation of Natural Resources: PEF recycling contributes to conserving natural resources. PEF is made from petroleum, a non-renewable resource. Recycling PEF reduces the need for new petroleum consumption.
- Creation of New Products: PEF recycling results in the creation of new products. PEF plastic can be recycled into high-quality items, such as water bottles and food packaging.
To promote PEF recycling, cooperation among government agencies, businesses, and consumers is essential. Government agencies should enact policies that support PEF recycling. Businesses should invest in PEF recycling technologies. Consumers should be conscious of segregating and recycling PEF plastic waste.
.jpg)
Polyethylene furanoate recycling
7. Related questions
What is the current price of polyethylene furanoate (PEF)?
The price of PEF varies depending on several factors, including quality, application, and purchase volume. According to
ChemOrbis, the average PEF price in Europe in September 2023 is approximately $12,000 per ton.
What is the projected market value of polyethylene furanoate (PEF) in 2032?
The global market for polyethylene furanoate is expected to reach $76.7 million by 2032.
What factors are driving the PEF market?
Increasing demand for sustainable and environmentally friendly materials. PEF is a bio-plastic, meaning it is produced from renewable sources.
Advancements in PEF production technology. Manufacturers are continually improving the PEF production process to make it more efficient and cost-effective.
What is the market share of the leading PEF manufacturers?
According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global PEF market is projected to reach $1.2 billion by 2027, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12.5% during the period 2022-2027. The current market share of leading PEF manufacturers is as follows:
- Idemitsu Kosan (Japan): 35%
- Mitsui Chemical (Japan): 25%
- DuPont (USA): 20%
- Eastman Chemical (USA): 10%
- LyondellBasell (USA): 10%
Can PEF replace PET in food and beverage packaging applications?
PEF has several superior properties over PET, including higher strength, better oxygen barrier properties, and improved gas barrier properties. Therefore, PEF has the potential to replace PET in some food and beverage packaging applications, such as bottled water, carbonated beverages, and fresh foods.
However, PEF is still a relatively new plastic, and production costs are currently higher than PET. Therefore, the substitution of PEF for PET in food and beverage packaging applications will require time and the support of policies and regulations.