PS material, or polystyrene, has become one of the most indispensable components in various industries worldwide. From food packaging to advanced medical equipment, PS material’s adaptability, affordability, and customizable nature have revolutionized manufacturing and design. As modern industries continue to grow and evolve, PS material plays a key role in meeting new challenges and demands for quality, cost-efficiency, and sustainability. This article delves into the importance of PS material in today’s industries, its wide-ranging applications, and the benefits it brings, ending with a look at EuroPlas’ high-impact PS products.
1. Overview of PS Material
Polystyrene (PS) material is a versatile thermoplastic polymer with properties that make it highly useful across a broad range of industries. Derived from the styrene monomer, PS material is notable for its rigidity, clarity, and ease of processing, making it a staple in everything from household items to complex medical and construction applications. First synthesized in the early 20th century, polystyrene quickly gained popularity due to its lightweight structure and durability, establishing itself as an essential material in industrial manufacturing.
Read more: Everything you need to know about polystyrene
1.1. Key Characteristics of PS Material
PS material exhibits a range of physical and chemical characteristics that contribute to its adaptability:
Durability: PS is tough and can resist a moderate amount of impact, especially in its high-impact variant (HIPS). This durability makes it a reliable choice for products that require structural integrity.
- Transparency and Gloss: General-purpose polystyrene (GPPS) is clear and has a naturally glossy finish, which makes it ideal for items that need a polished, attractive appearance. This characteristic is especially valued in consumer goods, such as food containers and cosmetic packaging.
- Ease of Molding and Fabrication: PS material can be easily molded into complex shapes, allowing manufacturers to create detailed, customized designs. Its flexibility in processing also reduces production time and cost.
- Thermal and Electrical Insulation: PS material is an excellent insulator, with low thermal conductivity and resistance to electrical currents. This makes it ideal for packaging, construction, and electronics applications.
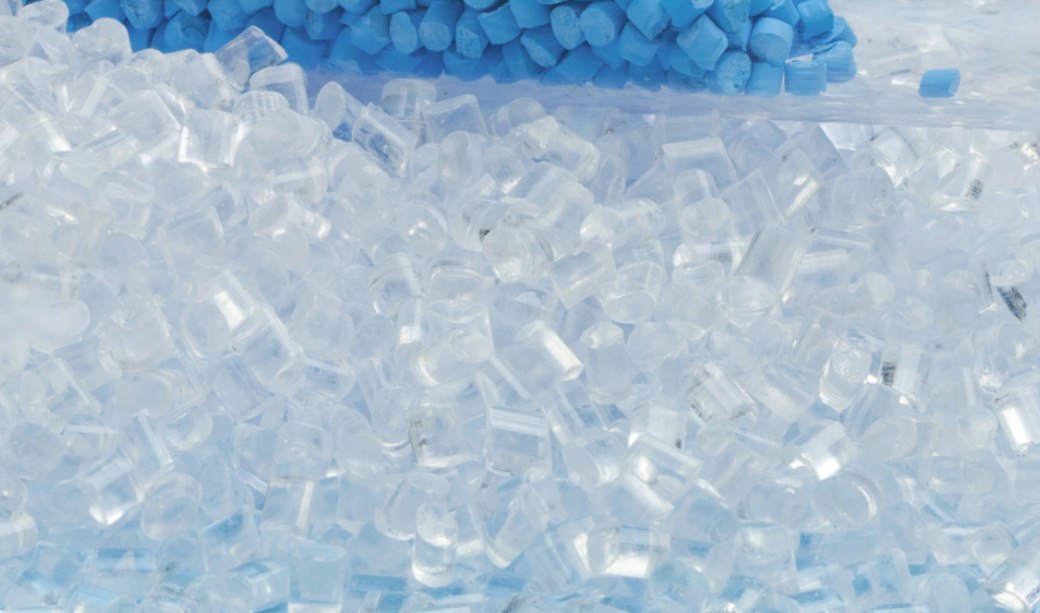

The transparency of PS material is ideal for creating beautiful products
1.2. Types of PS Material
Polystyrene material is available in several forms, each tailored to specific applications. Here’s a closer look at the main types:
- General-Purpose Polystyrene (GPPS): This type of PS material is characterized by its clarity, rigidity, and smooth surface. GPPS is widely used in transparent applications such as laboratory equipment, food packaging, and plastic utensils. Although GPPS is less impact-resistant than other forms, its strength-to-weight ratio makes it a durable and cost-effective solution for products that do not require high impact resistance.
- High-Impact Polystyrene (HIPS): HIPS is created by blending PS with rubber particles to enhance its impact resistance. This results in a strong, versatile material capable of withstanding greater mechanical stress, making it a preferred choice in electronics, automotive components, and furniture manufacturing. HIPS is also easy to print on, making it ideal for branded products, promotional materials, and retail displays.
- Expanded Polystyrene (EPS): EPS, also known as Styrofoam, is created by expanding small beads of polystyrene into a foam-like material. This type of PS material is primarily used in applications where insulation and lightweight properties are crucial, such as in packaging for fragile items, temperature-sensitive shipping containers, and construction insulation panels. EPS provides superior thermal insulation and shock absorption, making it indispensable in both the packaging and construction industries.
- Extruded Polystyrene (XPS): Similar to EPS, XPS is created by a process that results in a more uniform and denser foam structure. This form of PS material offers high compressive strength, moisture resistance, and insulation capabilities, making it ideal for construction applications, such as foundation and roof insulation. XPS is also more resistant to water absorption than EPS, which enhances its longevity in construction environments.
EPS plastic is one of the PS materials
1.3.Environmental Impact and Recent Developments
While PS material has become a cornerstone of modern industry, concerns over its environmental impact have prompted new research and development efforts focused on sustainability. Polystyrene is not biodegradable, which has led to concerns about its long-term environmental footprint. However, advancements in recycling have led to new solutions, such as mechanical and chemical recycling methods that allow post-consumer PS material to be repurposed into new products.
A growing number of companies now employ recycled PS (rPS) in their products, especially in packaging and construction, where durability is paramount. Additionally, innovations in biodegradable and bio-based alternatives to traditional PS material are emerging, allowing industries to adopt more environmentally responsible practices without sacrificing product quality.

Products from PS materials are produced with environmentally friendly methods
2. Applications of PS Material Across Industries
PS material is used in nearly every industry due to its adaptability and cost-effectiveness. Below are some of the most prominent applications of PS material across key sectors:
2.1. Electronics and Electrical Appliances
PS material is integral to the electronics industry, especially in high-impact forms such as HIPS, which provides protective, durable casings for electronics and appliances. For instance, televisions, computers, and audio systems often use PS material for their exteriors. Its insulating properties protect internal components from dust, moisture, and physical damage. Furthermore, PS material’s ability to withstand moderate heat makes it suitable for components that must endure varying temperatures without warping.

Using PS materials in the electronics industry
2.2. Packaging Industry
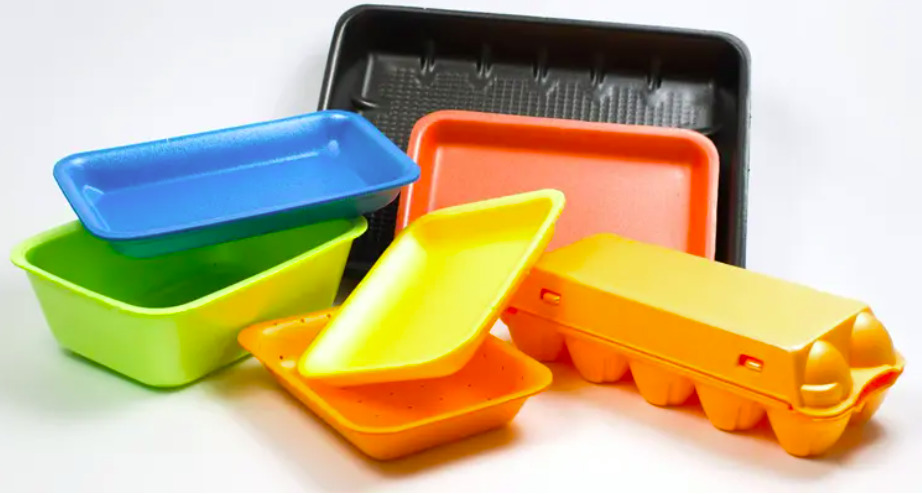
In packaging, PS material is prized for its lightweight, insulative properties. Both EPS and GPPS are widely used in the packaging of foods, pharmaceuticals, and electronics. For example, expanded polystyrene is the material of choice for temperature-sensitive packaging, which is crucial for shipping perishable foods and medical supplies. In retail, GPPS provides sturdy yet affordable packaging solutions that ensure product safety and durability without adding significant weight to the product, which is beneficial in minimizing shipping costs.

In the packaging industry, EPS and GPPS also help reduce weight significantly
2.3.Construction Sector
The construction industry relies heavily on PS material, especially in the form of EPS, for insulation purposes. EPS insulation panels are widely used in building construction to improve energy efficiency. By providing thermal insulation, EPS helps maintain indoor temperatures, leading to lower heating and cooling costs. Additionally, due to its moisture resistance, EPS can be used in areas prone to dampness without compromising structural integrity.
Polystyrene-based concrete solutions are also gaining traction, combining traditional cement with lightweight PS beads. This composite material is ideal for lightweight construction applications, offering both durability and reduced overall material weight, which eases transportation and installation challenges.
EPS insulation panels are widely used in the construction industry
2.4. Healthcare and Medical Applications
In healthcare, PS material is commonly used in disposable lab equipment, such as test tubes, petri dishes, and specimen containers. Its transparency, sterility, and ease of disposal make it ideal for medical environments. For instance, PS syringes and pipettes are widely used for one-time applications to ensure sterility. Additionally, PS material’s chemical resistance allows it to handle various substances safely, ensuring no contamination or chemical reaction occurs during medical procedures.
PS materials are also used in medicine
3. Advantages of Using PS Material
The advantages of PS material have contributed significantly to its widespread use in industries ranging from electronics and automotive to healthcare and food packaging. Here are some of the core benefits of PS material that have made it a go-to choice for manufacturers:
3.1. Lightweight and Durable
PS material’s low density is one of its most valued qualities, especially in applications that require lightweight but durable solutions. For instance, in packaging and construction, PS material minimizes the weight of the final product, which is particularly beneficial for reducing transportation costs. Despite being lightweight, PS material offers considerable strength, especially in its HIPS and XPS forms. In electronic devices, HIPS casings protect internal components from potential damage without adding excessive bulk, while in construction, XPS insulation panels offer durable, moisture-resistant solutions that withstand environmental exposure.
3.2. Versatile in Design and Easily Moldable
PS material’s ease of molding and ability to take on complex shapes is advantageous for industries requiring customized designs. It can be manufactured in both solid and foam forms, providing flexibility for a wide range of applications. The adaptability of PS material allows for intricate detailing, such as in food containers and appliance components where precision is key. Furthermore, the material’s surface is compatible with high-quality printing, making it ideal for applications that require branding or decorative finishes, such as product displays and retail packaging.

The adaptability of PS materials creates sophisticated products
3.3. Thermal and Electrical Insulation Properties
In both construction and electronics, insulation is essential for maintaining product quality and safety. PS material’s thermal insulation properties are especially useful in the construction of insulated walls and roofing systems. EPS and XPS, with their excellent resistance to heat transfer, help to regulate indoor temperatures, resulting in reduced energy consumption and lower utility costs for end users. Additionally, PS material’s ability to insulate against electrical currents makes it a safe choice for electronics casings, ensuring that electrical components are protected from both physical and thermal interference.
3.4. Cost-Effective Production and Scalability
One of the key reasons for PS material’s popularity is its cost-effectiveness. Compared to other materials like metal, glass, or certain composites, PS material is far more affordable, making it ideal for industries that require high production volumes. The availability of raw materials and relatively low manufacturing costs enable large-scale production without sacrificing profitability. For example, in the food packaging industry, where margins are often tight, PS material offers a budget-friendly alternative that meets both regulatory standards and functional requirements.
3.5. High Impact Resistance and Strength-to-Weight Ratio
HIPS, a high-impact variant of PS material, is engineered to provide exceptional impact resistance, which is crucial for applications where durability is a priority. Its resilience and strength-to-weight ratio make it ideal for products like electronic casings, children’s toys, and automotive components that must withstand daily wear and tear. For instance, HIPS can absorb moderate impacts without cracking or deforming, ensuring product longevity. This characteristic has made HIPS a preferred material in industries that prioritize both product durability and user safety.
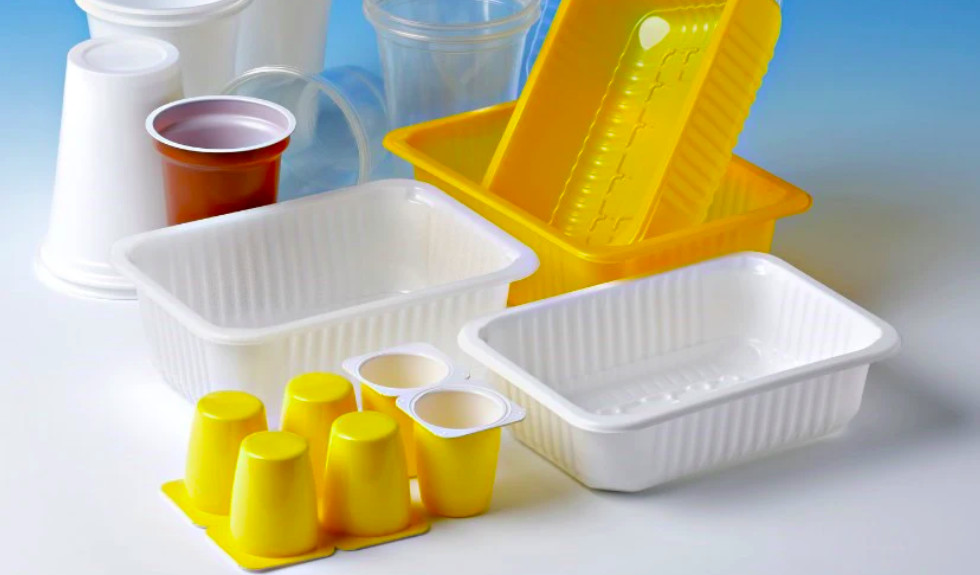

PS materials with low cost help industries produce large quantities of products
3.6. Environmental Benefits and Recyclability
While PS material has faced scrutiny over its environmental impact, recent innovations in recycling technology have improved its sustainability profile. Companies are now adopting more eco-friendly practices, such as integrating recycled PS (rPS) into their manufacturing processes, which reduces reliance on virgin polystyrene. Furthermore, chemical recycling processes now allow for the breakdown of PS material into its original monomers, enabling the production of new polystyrene without the need for additional petroleum-based resources.
In addition to recycling, bio-based alternatives are being researched, which could provide a more sustainable form of PS material in the future. These developments indicate a shift toward a circular economy, where PS material is recycled, repurposed, and continually reused, ultimately contributing to reduced waste and a more sustainable plastics industry.
4. Conclusion
PS material’s broad range of properties and types makes it indispensable across many sectors, from healthcare and packaging to construction and electronics. Its lightweight nature, thermal stability, and moldability make it an adaptable solution for modern manufacturing needs. As industries move towards more sustainable practices, advancements in PS recycling are helping make PS material an environmentally conscious choice, supporting both economic and ecological goals.
As global demand for efficient, durable, and adaptable materials grows, PS material will continue to be a vital component in modern industry. Through innovations and improvements in recycling, the use of PS material can meet evolving industry standards while minimizing environmental impact.
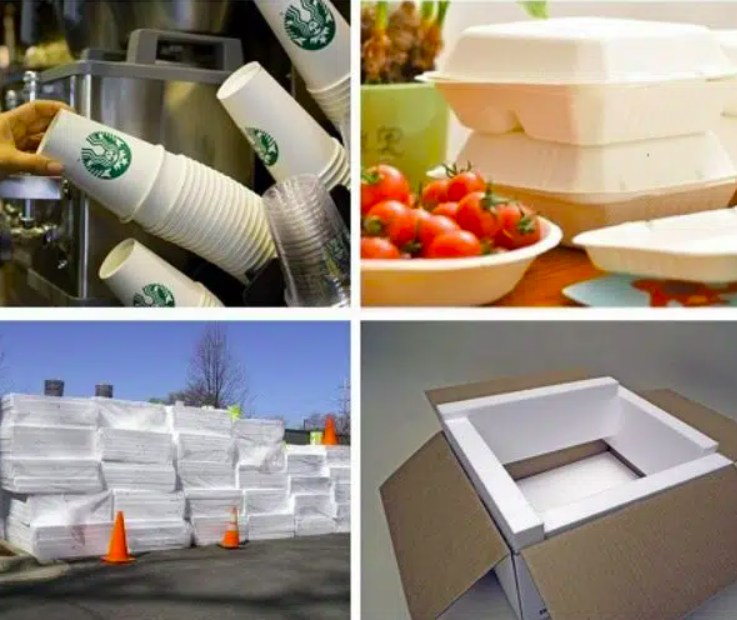

Diverse products are created from PS materials
5. About EuroPlas’ HIPS Products
EuroPlas' HIPS Filler Masterbatch is the perfect solution for enhancing sustainability and cost-effectiveness in plastic production, especially with PS material. Formulated with specialized fillers, this product improves the stiffness and impact resistance of HIPS materials, helping manufacturers reduce raw material costs without compromising the final product's quality.
EuroPlas' HIPS Filler Masterbatch is widely used across industries such as packaging, electronics, and household products. It blends easily into various plastic formulations, especially those based on PS material, optimizing production processes and boosting material performance. By using this advanced filler solution, manufacturers can increase product durability and achieve superior results.
EuroPlas is committed to providing high-quality HIPS Filler Masterbatch products as a reliable, eco-friendly solution for businesses looking to integrate sustainable, high-performance PS material into their products.
Our commitment to innovation and quality, along with a comprehensive range of HIPS products—including Filler Masterbatch, Color Masterbatch, Plastic Additives, Engineering Plastics Compounds, Bioplastic Compounds, and Bio Filler —helps businesses streamline operations, reduce production costs, and improve material properties. EuroPlas continues to be a trusted supplier in the plastics industry, providing advanced solutions that meet the diverse needs of modern manufacturing, especially with high-quality PS material.
Contact us today to learn more about our HIPS products and discover the optimal solutions for your needs. Don't forget to visit our blog for in-depth industry insights that will help you enhance your production capabilities with EuroPlas’ advanced plastic solutions.