Compression molding vs. Injection molding: Which one is better?
When it comes to plastic manufacturing, two popular methods come to mind: compression molding vs injection molding. Both techniques have their strengths and are suitable for various applications. In this article, we will do a comparison: compression molding vs injection molding to determine which one is better suited for different scenarios. By understanding each method, you can make an informed decision for your plastic manufacturing needs.
1. Overview of compression molding
1.1. What is compression molding?
Compression molding is a manufacturing process used to shape and form thermosetting materials, such as plastics, rubber, composites, and natural fibers. It involves applying heat and pressure to a pre-measured amount of molding material placed in a mold cavity. The material is compressed until it takes the desired shape and is cured or solidified under pressure.
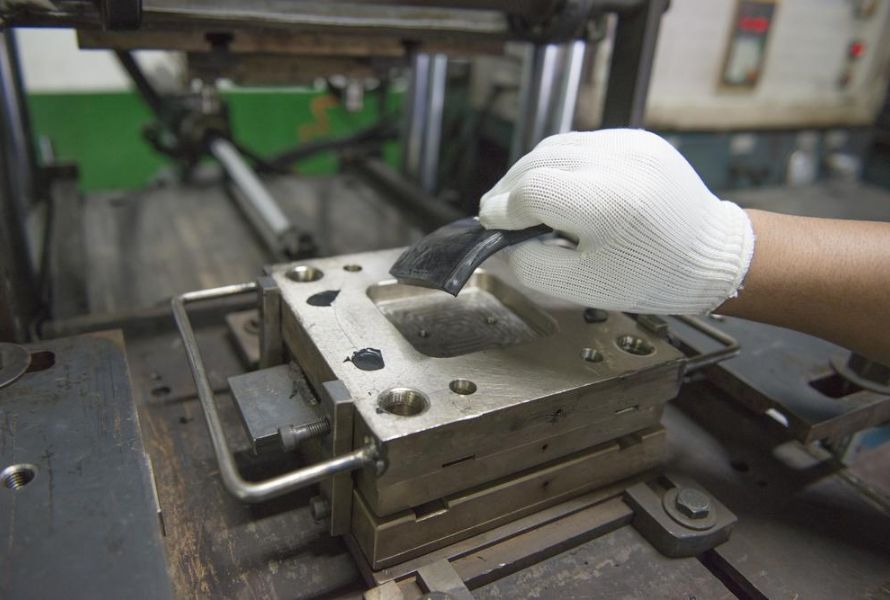

Thermosetting materials can be shaped and formed using the compression molding manufacturing process
1.2. How does compression molding work?
1.2.1. Mold preparation
The mold is prepared by coating it with a release agent to prevent the molded part from sticking to the mold surfaces. The mold may also be preheated to a specific temperature, depending on the material being used.
1.2.2. Material loading
A precise amount of molding material, in the form of powders, granules, or preforms, is weighed and placed into the mold cavity.
1.2.3. Mold closure
The mold is closed, and hydraulic or mechanical force is applied to compress the material. The pressure helps distribute the material evenly within the mold and ensures proper molding.
1.2.4. Curing or solidification
Heat is applied to the mold, causing the material to soften and flow. The combination of heat and pressure initiates a chemical reaction, often referred to as curing or cross-linking, which leads to the hardening or solidification of the material.
1.2.5. Cooling and part Removal
Once the curing process is complete, the mold is cooled to allow the part to solidify fully. The mold is then opened, and the finished part is removed.
2. Overview of injection molding
2.1. What is injection molding?
Injection molding is a widely used manufacturing process for producing plastic parts. It involves injecting molten plastic material into a mold cavity under high pressure. The molten plastic fills the mold and takes the shape of the desired part. Once the plastic cools and solidifies, the mold is opened, and the finished part is ejected.
Read more: What is injection molding? How does it work?
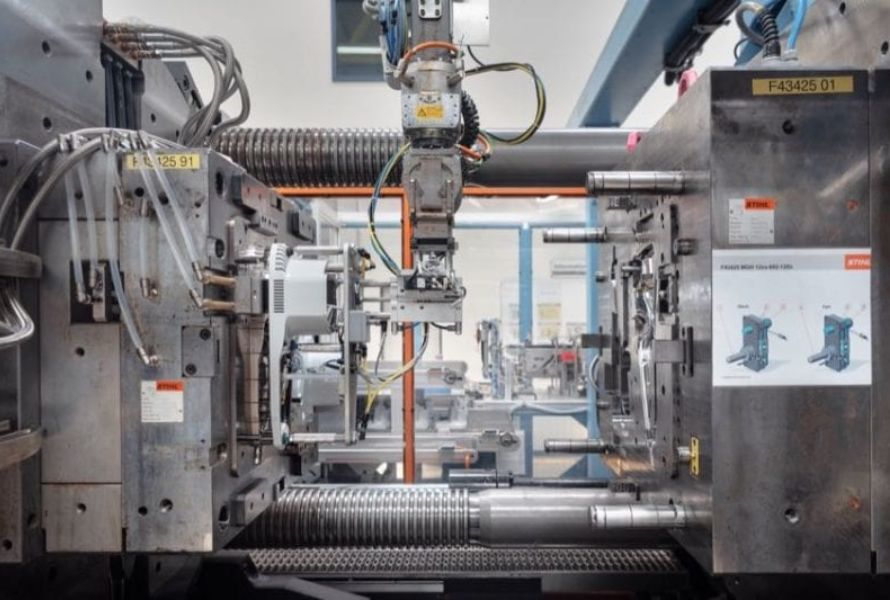

One popular method of manufacturing plastic parts is injection molding
2.2. How does injection molding work?
2.2.1. Mold preparation
The mold is prepared by ensuring it is clean and free of any debris. It may also be preheated to a specific temperature, depending on the material being used.
2.2.2. Material melting
Plastic pellets or granules are fed into a hopper and melted in an injection molding machine's heating barrel. The barrel's screw mechanism melts and homogenizes the plastic, creating a molten plastic material.
2.2.3. Injection
The molten plastic is injected into the mold cavity through a nozzle and runner system. The injection is performed under high pressure, which ensures the complete filling of the mold and the replication of intricate details.
2.2.4. Cooling and solidification
After the mold is filled, the molten plastic cools and solidifies inside the mold cavity. Cooling can be accelerated by circulating coolants through the mold.
2.2.5. Mold opening and ejection
Once the plastic has cooled and solidified, the mold is opened, and the finished part is ejected from the mold cavity. Ejection pins or mechanisms help remove the part from the mold.
3. A comparison: compression molding vs injection molding
Before getting into the details, you can take a look at the table summarizing the differences between Compression Molding vs Injection Molding as below:
| Differences: Compression molding vs Injection molding |
| Aspect |
Compression molding |
Injection molding |
| Process Overview |
Material is compressed and cured in a mold |
Molten plastic is injected into a mold cavity |
| Material Processing |
Thermosetting plastics, rubber, composites |
Thermoplastics (wide material selection) |
| Part Complexity |
Suitable for larger parts with thick walls |
Highly complex parts with intricate details |
| Production Volume |
Low to medium volume or prototype production |
High-volume production
|
| Speed and Efficiency |
Longer cycle times |
Faster production cycles |
| Tooling and Setup Costs |
Lower initial tooling costs |
Higher initial tooling costs |
| Mold Design |
Simpler |
More complex with runners, gates, and cooling channels |
| Surface Finish |
Variations possible |
Superior, smoother, and more uniform |
| Precision and Tolerances |
Good for perpendicular features |
Superior precision and tight tolerances |
3.1. Compression molding vs injection molding: Process overview
- In compression molding, pre-measured amounts of molding material are placed in a mold cavity. Heat and pressure are then applied to the material, causing it to soften and flow into the desired shape. The material is compressed until it solidifies under pressure.
- Injection molding involves melting plastic pellets or granules in an injection molding machine's heating barrel. The molten plastic is then injected into a mold cavity under high pressure. After cooling and solidification, the mold is opened, and the finished part is ejected.
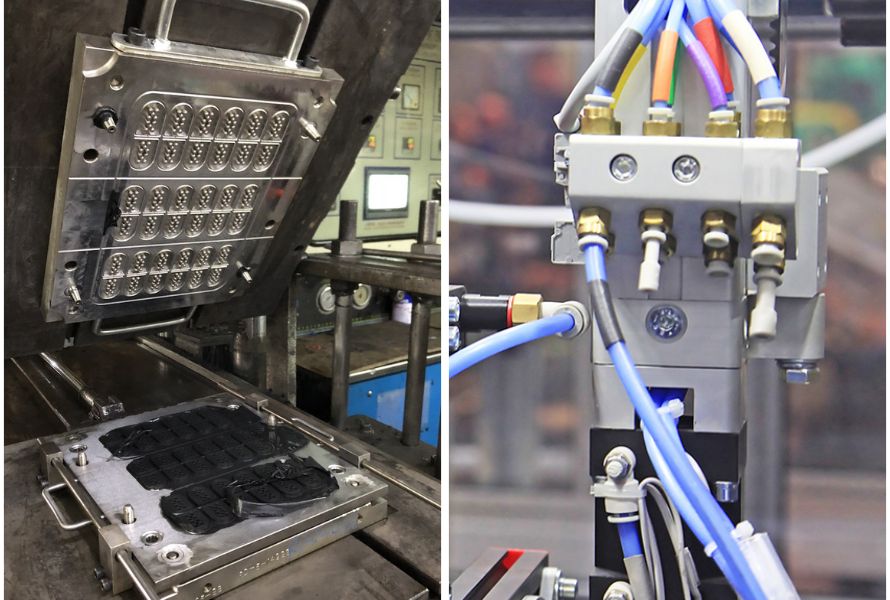
Compression Molding vs Injection Molding: One compresses and cures materials, while the other melts and injects plastic into a mold cavity
3.2. Compression molding vs injection molding: Material processing
- Compression molding can handle a wide range of materials, including thermosetting plastics, rubber, composites, and natural fibers. These materials are typically in the form of powders, granules, or preforms.
- Injection molding primarily uses thermoplastic materials, which are melted and injected into the mold cavity. It offers a vast selection of thermoplastic materials, allowing for diverse material properties.
3.3. Compression molding vs injection molding: Part complexity
- Compression molding is suitable for producing parts with larger dimensions and thicker walls. It is well-suited for applications that require robust and durable components.
- Injection molding excels in producing highly complex parts with intricate details. It allows for the replication of intricate geometries, thin walls, and precise features due to the high pressure and flow control during injection.
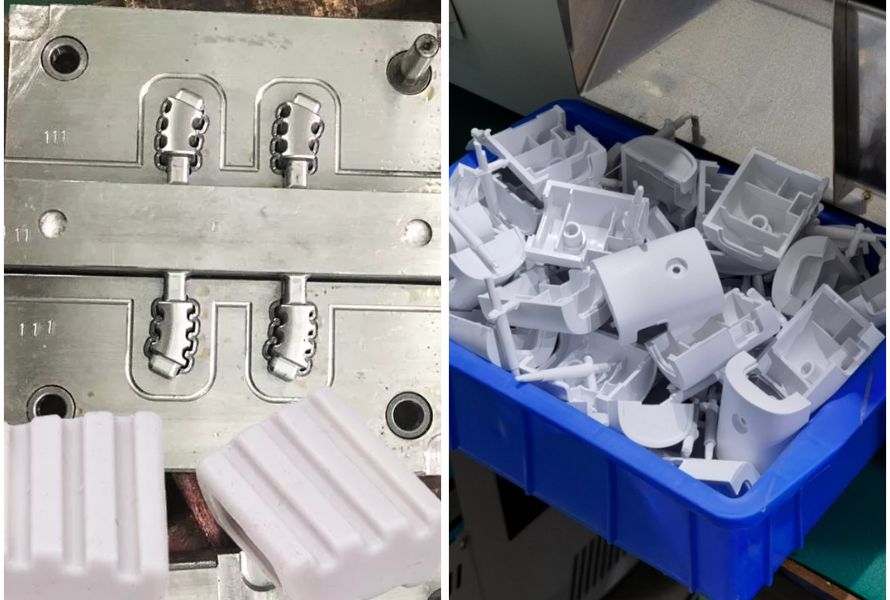

Compression Molding vs Injection Molding: One for larger parts with thicker walls, the other for intricate, complex parts
3.4. Injection molding vs compression molding: Production volume
- Injection molding is highly efficient for high-volume production runs. The process enables rapid production cycles, making it suitable for large-scale manufacturing.
- Compression molding is commonly used for low to medium volume production or prototype development. It can be cost-effective for smaller production runs due to lower tooling costs.
3.5. Compression molding vs injection molding: Speed and efficiency
- Injection molding offers faster production cycles due to its high-speed injection and cooling processes. It allows for efficient mass production and can be automated for increased productivity.
- Compression molding typically has longer cycle times compared to injection molding. The curing process and cooling time contribute to a slower overall production speed.
3.6. Injection molding vs compression molding: Tooling and setup costs
Injection molding has higher initial tooling and equipment costs. The molds used in injection molding are more complex and require precise machining, resulting in higher setup costs. However, for high-volume production, the per-unit cost can be lower than compression molding due to increased production efficiency.
The tooling costs for compression molding are generally lower compared to injection molding. The molds used in compression molding are simpler in design and construction, resulting in lower initial setup costs.
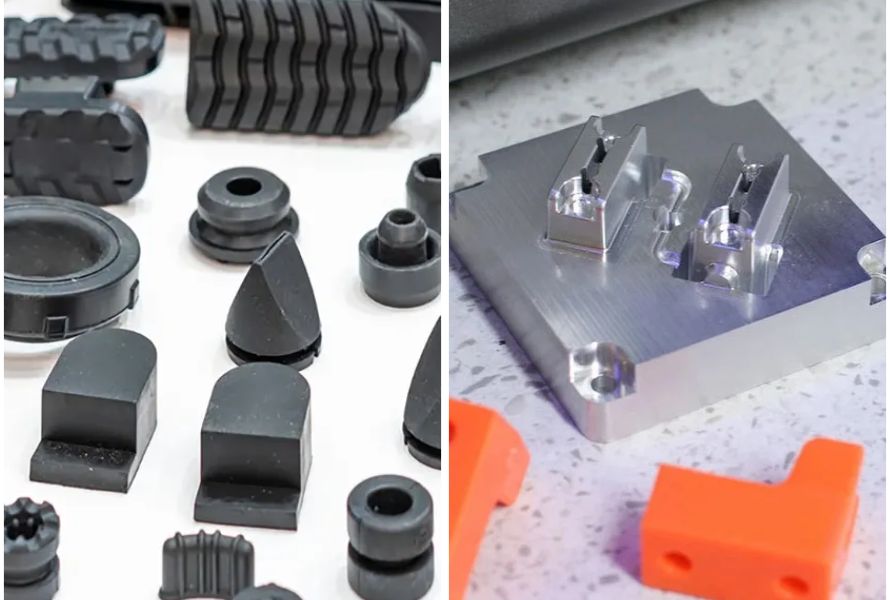

Injection Molding vs Compression Molding: One has lower costs, the other higher initial tooling and equipment costs
3.7. Compression molding vs injection molding: Material transformation
- Compression molding uses heat and pressure to transform the material, making it fluid and conform to the mold. With proper filling and consolidation, it creates rigid and chemically transformed products. It excels with thermosetting plastics, achieving complex shapes accurately.
- In contrast, injection molding melts the material and injects it into the mold. The molten material fills the mold cavity and solidifies, forming the final product. Injection molding is commonly used for thermoplastic materials, offering advantages like high production rates, intricate designs, and large quantities with consistent quality.
3.8. Compression molding vs injection molding: Mold design
Overall, the mold design for compression molding tends to be simpler compared to injection molding.
- Compression molding molds primarily focus on proper filling and uniform distribution of material during the compression process.
- Injection molding molds, on the other hand, are more complex due to the need for runners, gates, and cooling channels to facilitate material flow, control the injection process, and aid in the solidification of the material.
3.9. Injection molding vs compression molding: Surface finish
Injection molding offers superior surface finish due to precise material flow and controlled filling, resulting in smoother and more uniform surfaces. Injection molding allows for advanced surface treatments and is preferred for applications requiring high-quality aesthetics.
Meanwhile, compression molding achieves varied surface finishes influenced by mold design, material properties, and texture. It may result in some imperfections and variations in surface texture.
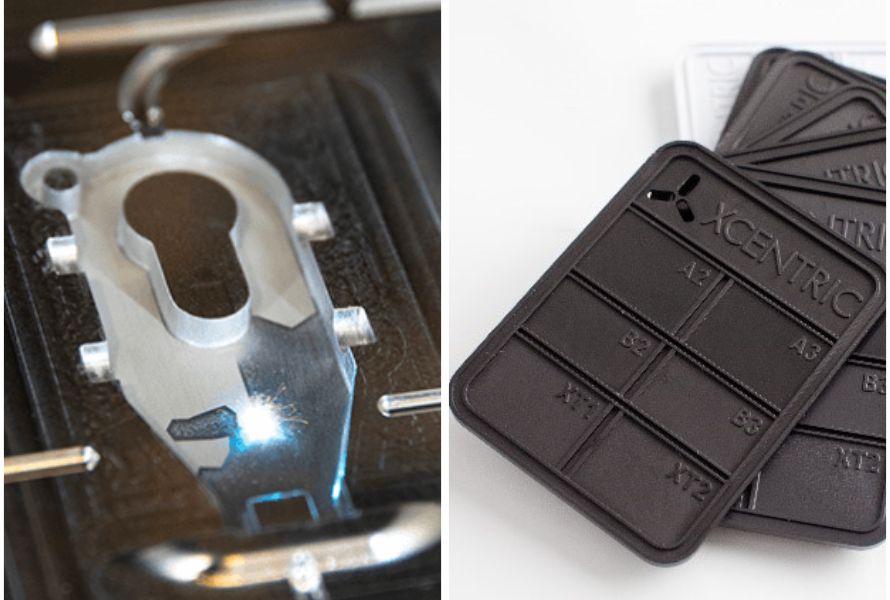

Compression Molding vs Injection Molding: One has varied surface finishes, the other offers superior surfaces
3.10. Compression molding vs injection molding: Precision and tolerances
- Compression molding offers good dimensional accuracy and can achieve tight tolerances, particularly for features perpendicular to the mold parting line. However, achieving high precision across complex geometries can be challenging.
- Injection molding excels in precision and consistently achieves tight tolerances. Advanced techniques and automated systems contribute to its accuracy.
4. Conclusion
The choice between compression molding vs injection molding depends on various factors, including cost considerations, production volume, design complexity, and material requirements. Compression molding excels in versatility and durability, making it suitable for a range of materials and large, robust parts. On the other hand, injection molding offers precision, efficiency, and design flexibility, making it ideal for high-volume production and intricate components. By evaluating your specific needs and considering these factors, you can determine which method is better suited for your plastic manufacturing requirements.
EuroPlas is among the top providers of plastic for compression molding and injection molding. With our headquarters situated in Vietnam, we have been in the business for over 15 years. Thanks to our expertise and experience, we are able to meet any need of our customers, and we never stop striving to provide the greatest products.
Our custom solutions and pre-designed products eliminate the need for you to purchase materials from other companies or worry about owning your own facility. Throughout the entire process, our passionate staff will work closely with you to make sure everything goes as smoothly as possible! If you need the most affordable plastic for compression molding vs injection molding cost for your production line, get in touch with us right now.