Polybutylene succinate (PBS) plastic is a biodegradable thermoplastic polymer that offers promising solutions to industries seeking sustainable alternatives for traditional plastics. Produced from renewable or petroleum-based feedstocks, PBS combines environmental benefits with reliable mechanical properties. Its applications span sectors such as packaging, agriculture, and automotive, where functionality and sustainability are increasingly demanded. PBS exhibits excellent thermal stability, processability, and compostability, making it a preferred choice in innovative manufacturing.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of PBS plastic, detailing its chemical composition, unique properties, and industrial applications, equipping professionals with the knowledge to leverage PBS in environmentally responsible production processes.
PBS plastic is a biodegradable polymer offering sustainable, versatile solutions for multiple industries.
1. What Makes PBS An Emerging Bioplastic?
As bioplastics gain traction, PBS (polybutylene succinate) is emerging as a frontrunner of the bioplastics market for its compatibility with current manufacturing processes and commitment to sustainability. Made from plant-based compositions including bio-derived succinic acid and 1,4-butanediol, this polymer mimics the processing properties of traditional plastics, making it compatible with existing industrial systems.
PBS plastic supports a wide range of applications, from packaging to agriculture, while enabling sustainable end-of-life options like recycling and composting.
Its ability to cater to diverse industries and support eco-friendly practices at all stages—from production to end-of-life—positions it as a cornerstone of sustainable material strategies.
Read more: What are bioplastics made from? Materials to make bioplastics

PBS plastic is a sustainable bioplastic compatible with industrial systems, advancing eco-friendly manufacturing.
2. Properties of PBS Plastic
PBS plastic owns a unique combination of properties that make it a compelling alternative to traditional plastics, including:
- Biodegradability: Exhibits excellent biodegradability under specific environmental conditions, contributing to a more sustainable plastic lifecycle. This property makes PBS plastic ideal for applications where composting or controlled biodegradation is desired at the end-of-life stage.
- Good Mechanical Properties: PBS plastic showcases good tensile strength, impact resistance, and flexibility, making it suitable for a wide range of applications requiring moderate mechanical performance.Exhibits strong tensile and flexural strength comparable to synthetic plastics like polypropylene.
- Processability: PBS exhibits good processing compatibility with existing plastic processing techniques, including extrusion, injection molding, and blow molding. This facilitates a smooth transition from conventional plastics for manufacturers.
- Thermal Stability: PBS possesses good thermal stability, with its melting temperature around 180-190°C, allowing it to withstand moderate processing temperatures and maintain its structural integrity during use in various applications.
- Crystallinity: Exhibits semi-crystalline behavior, offering PBS plastic a balance between rigidity and flexibility. This property can be tailored by adjusting processing parameters to achieve desired characteristics for specific applications.
- Chemical Resistance: Resistant to hydrolysis and oxidative degradation, extending product durability
- Water Resistance: PBS demonstrates good water resistance compared to some biodegradable alternatives. While not water-proof, it offers sufficient performance for applications where moisture management is crucial.
- Gas Barrier Properties: Although not as effective as some traditional plastics, PBS possesses moderate gas barrier properties suitable for certain packaging applications. This allows it to extend shelf life of products susceptible to degradation by oxygen or other gas.
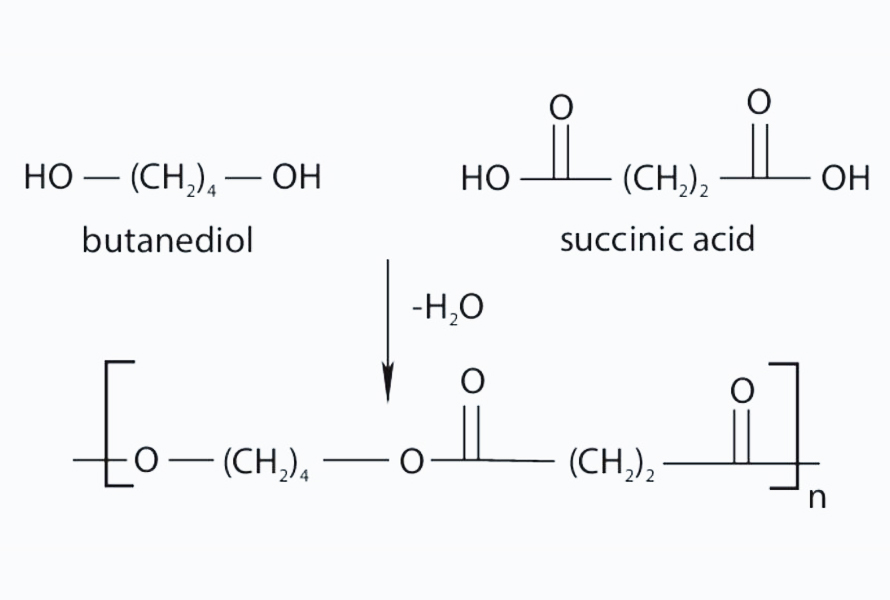
PBS plastic owns a unique combination of properties that make it a compelling alternative to traditional plastics
3. Applications of PBS Plastic
The unique combination of biodegradability, biocompatibility, and good mechanical properties makes PBS plastic a promising material across various industries.
3.1 Sustainable Packaging Solutions
- Food Packaging: Biodegradable films for wrapping fruits, vegetables, and baked goods, extending shelf life while minimizing waste.
- Compostable Bags: Biodegradable alternatives to traditional plastic bags for grocery shopping and food waste collection.
- Agricultural Mulch Films: PBS films promote crop growth and suppress weeds, with the benefit of biodegrading in the field at the end of the season.
Packaging for Industrial Goods: Biodegradable wrapping or cushioning materials for heavy-duty products.
3.2. Biocompatible Medical Devices
- Sutures: Biodegradable sutures minimize the risk of infection and eliminate the need for a second surgery to remove them.
- Medical Packaging: Syringes, medication pouches, and catheters
- Wound Dressings: Provide safe biodegradation for infection control.
3.3 Durable Consumer Goods
- Electronics Casings: PBS offers a sustainable alternative to traditional plastics for electronic devices, while maintaining good mechanical properties.
- Toys for Children: Biodegradable toys made from PBS ensure safety and minimize environmental impact.
- Bottles and Food Containers: Reusable bottles and containers made from PBS can contribute to a circular economy.
3.4. Agriculture
- UV-resistant plant pots and weather-protective mulch films.
- Eco-friendly fishing nets for sustainable aquaculture.
3.5. Industrial Uses
- Automotive Components: Durable and lightweight interior trims, dashboards, and paneling.
- Electronic Casings: Biodegradable housings for devices like remote controls or small appliances.
- 3D Printing Filaments: Used in prototyping and manufacturing eco-friendly models
3.6. Construction
- Wall Panels and Flooring Materials: Durable yet compostable wall and flooring panels
- Insulation Sheets: Eco-friendly thermal or acoustic insulation solutions.
- Structural Components: Reinforced blends of PBS used in formworks or other non-load-bearing structures.

PBS plastic offers biodegradability, biocompatibility, and durability, making it valuable for diverse industries.
4. Benefits and Limitations of PBS Plastic
PBS plastic is gaining recognition as a sustainable alternative to traditional plastics, offering both environmental and functional advantages. However, like any material, PBS comes with certain trade-offs, making it essential to evaluate its benefits and limitations before applying.
Benefits
- Environmental Sustainability: PBS is biodegradable and breaks down within months under industrial composting, significantly reducing environmental impact.
- Mechanical Properties: Comparable tensile strength to polyethylene, with good thermal stability across diverse industries.
- Regulatory Compliance: PBS often meets FDA, REACH, and ISO standards for food, medical, and industrial applications.
- Thermal Adaptability: Operates across a wide temperature range, outperforming some traditional plastics.
- Customizable: Easily blended for specific applications in packaging, agriculture, and electronics.
Limitations
- High Costs: Costs remain higher than traditional plastics, conventional counterparts like polypropylene and polyethylene.
- Limited Availability: Market penetration and bulk purchasing options remain restricted compared to conventional materials.
- Specialized Applications: May require blending for applications needing specific advanced properties.
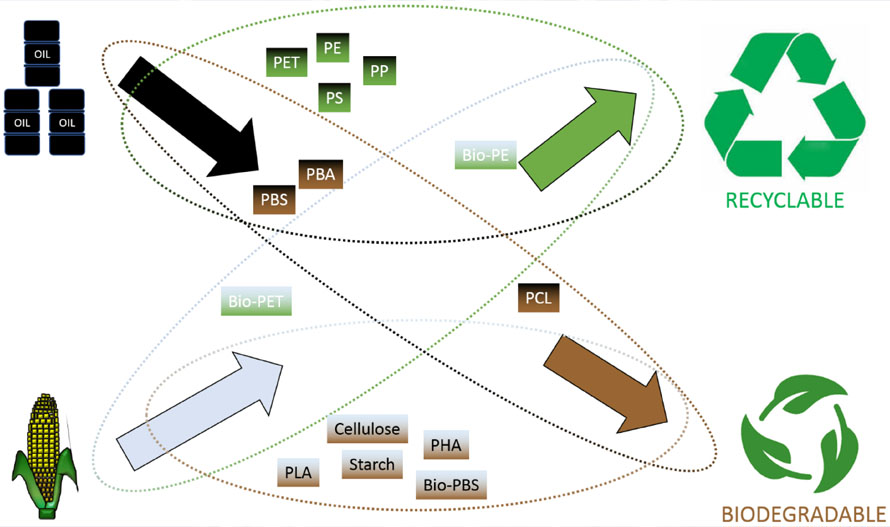
PBS plastic provides sustainable advantages over traditional plastics, balancing environmental benefits and limitations.
5. Conclusion
PBS plastic combines ecological benefits with versatile mechanical properties, positioning it as a key material for sustainable applications. From food packaging to agricultural films, its functionality spans diverse industries, contributing to reduced plastic waste. Despite hurdles like higher costs and market constraints, PBS is a viable solution for industries aiming to meet environmental goals. Its expanding role, driven by innovation and demand, underscores the importance of bioplastics in creating a sustainable future.
6. About EuroPlas’ Bioplastics
EuroPlas’ BiONext bioplastic compounds are a revolutionary advancement in sustainable materials. Crafted from renewable resources like polylactic acid (PLA), Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA), and PBS plastic in combination with PBAT, BiONext ensures exceptional biodegradability. These compounds decompose into water, CO₂, and biomass within 12 months, promoting an eco-friendly lifecycle and creating opportunities for agricultural reuse.

EuroPlas’ BiONext bioplastics, made from renewable materials, decompose into eco-friendly byproducts within 12 months.
BiONext’s unique blend offers remarkable mechanical properties, including high hardness, excellent impact resistance, and a glossy finish. This versatility makes it ideal for products like biodegradable packaging, agricultural mulch films, food containers, and disposable utensils. The material's adaptability to processes like injection molding, extrusion, and film blowing ensures both functionality and aesthetic appeal.
By reducing reliance on fossil fuels, BiONext addresses global environmental challenges while delivering high-performance solutions. Exclusively developed by EuroPlas, this innovation is a cornerstone in the shift toward green manufacturing, aligning with the company’s mission of environmental stewardship. Through meticulous production standards, EuroPlas ensures consistent quality, enabling industries to adopt sustainable practices without compromising on material excellence.
EuroPlas’ BiONext bioplastics reflect a commitment to innovation and sustainability, offering an efficient, eco-conscious alternative to traditional plastics. By integrating PBS plastic into its formulations, it provides a pathway for industries to support a greener future.
To learn more about our bioplastic solutions or discuss collaboration opportunities, contact us today!