Thermoplastic Vulcanizate (TPV) stands at the forefront of modern polymer technology, seamlessly combining the flexibility of thermoplastics with the durability of vulcanized rubber. This innovative material, known for its exceptional heat resistance, elasticity, and chemical stability, has found its way into diverse industries.
From automotive components to consumer goods, TPV's adaptability and cost-effectiveness make it a compelling choice. In this blog, we delve into the key properties that set TPV material apart and explore its myriad applications across sectors, showcasing how this blend of thermoplastic and rubber transforms ideas into reality. Let’s get started!
1. What is Thermoplastic Vulcanizate (TPV)?

Thermoplastic vulcanizate (TPV) or TPV material is a versatile and innovative class of materials that combines the characteristics of thermoplastics and elastomers. This unique blend results in a material with exceptional mechanical properties, making it suitable for a wide range of applications across various industries.
1.1. Definition
TPV is a type of thermoplastic elastomer (TPE) that undergoes a vulcanization process during its manufacturing, imparting elastomeric properties to the final product. Vulcanization involves the cross-linking of polymer chains, leading to increased strength, durability, and flexibility. Unlike traditional vulcanized rubbers, TPVs can be melted and reprocessed multiple times, thanks to their thermoplastic nature.
1.2. Components
TPVs are typically composed of a blend of thermoplastic and elastomeric phases. The key components include:
Thermoplastic matrix:
The thermoplastic matrix in TPVs provides structural integrity and processability. Common thermoplastics used include polypropylene (PP), polyethylene (PE), and ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM). The choice of thermoplastic matrix influences the overall performance and processing characteristics of the TPV material.
Elastomeric phase:
The elastomeric phase, often based on EPDM rubber, contributes to the elastomeric properties of TPV. EPDM is known for its excellent weather resistance, heat resistance, and low-temperature flexibility. The elastomeric phase plays a crucial role in enhancing the material's elasticity, impact resistance, and fatigue resistance.
Vulcanizing agents:
During the manufacturing process, vulcanizing agents are added to initiate cross-linking between the thermoplastic and elastomeric phases. This cross-linking is essential for achieving the desired balance of properties, including enhanced tensile strength, elongation, and tear resistance.
Additives:
Various additives such as stabilizers, antioxidants, and processing aids are incorporated to improve the overall performance and processability of TPVs. Stabilizers protect the material from degradation caused by exposure to heat and UV radiation, while antioxidants enhance the material's resistance to oxidative degradation.
2. Properties of Thermoplastic Vulcanizate (TPV)

Thermoplastic vulcanizate (TPV) exhibits a unique set of properties, blending the advantages of thermoplastics and elastomers. These characteristics make TPV material an attractive material for a wide range of applications. Here are the key properties of TPV:
2.1. Flexibility and elongation:
TPV inherits the elastomeric nature of its rubber component, providing exceptional flexibility and elongation properties. This flexibility allows TPV material to withstand repeated deformation and recover its original shape, making it suitable for applications requiring resilience and durability.
2.2. Tensile strength:
The vulcanization process in TPV enhances its tensile strength, making it a robust material that can withstand significant mechanical stress. This property is crucial in applications where the material is subjected to stretching forces, ensuring long-term structural integrity.
2.3. Impact resistance:
TPV's ability to absorb and dissipate impact energy is a valuable property in applications where resistance to sudden shocks or collisions is essential. This impact resistance makes TPV an ideal choice for automotive components, protective equipment, and other impact-prone applications.
2.4. Chemical resistance:
The thermoplastic matrix in TPV, often based on materials like polypropylene or polyethylene, provides resistance to various chemicals. This makes TPV material suitable for applications where exposure to oils, solvents, and other chemicals is a concern, such as automotive under-the-hood components.
2.5. Weather resistance:
TPV's elastomeric phase, commonly derived from EPDM rubber, imparts excellent weather resistance. This property makes TPV material resistant to environmental factors such as UV radiation, ozone, and extreme temperatures, expanding its applicability in outdoor and harsh weather conditions.
2.6. Compression resistance:
TPV exhibits resistance to compression, meaning it can maintain its shape and elasticity even after prolonged periods of compression. This property is crucial in applications where the material is subjected to constant pressure or deformation.
2.7. Thermal stability:
The thermoplastic nature of TPV allows it to be processed through various molding techniques while maintaining its thermal stability. This property is essential for applications requiring intricate shapes and complex designs.
2.8. Recyclability:
One of the significant advantages of TPV is its recyclability. The material can be melted and reprocessed multiple times without significant degradation in its properties, contributing to sustainable manufacturing practices.
3. Applications of Thermoplastic vulcanizate (TPV)
Thermoplastic vulcanizate (TPV) has gained widespread acceptance across diverse industries due to its unique combination of properties, making it a preferred material for various applications. Here are some notable applications where TPV material demonstrates exceptional performance:
3.1. Automotive components:
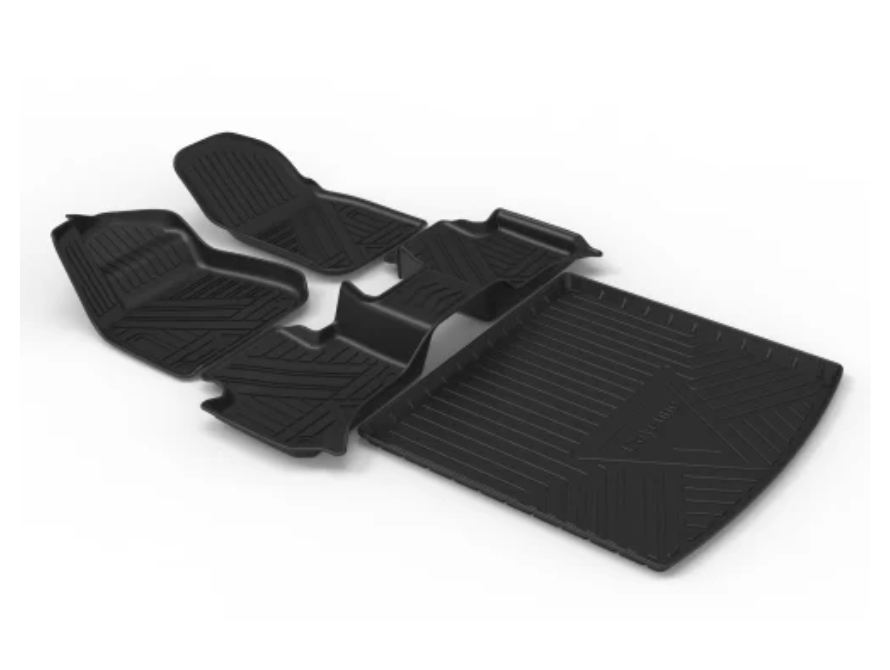

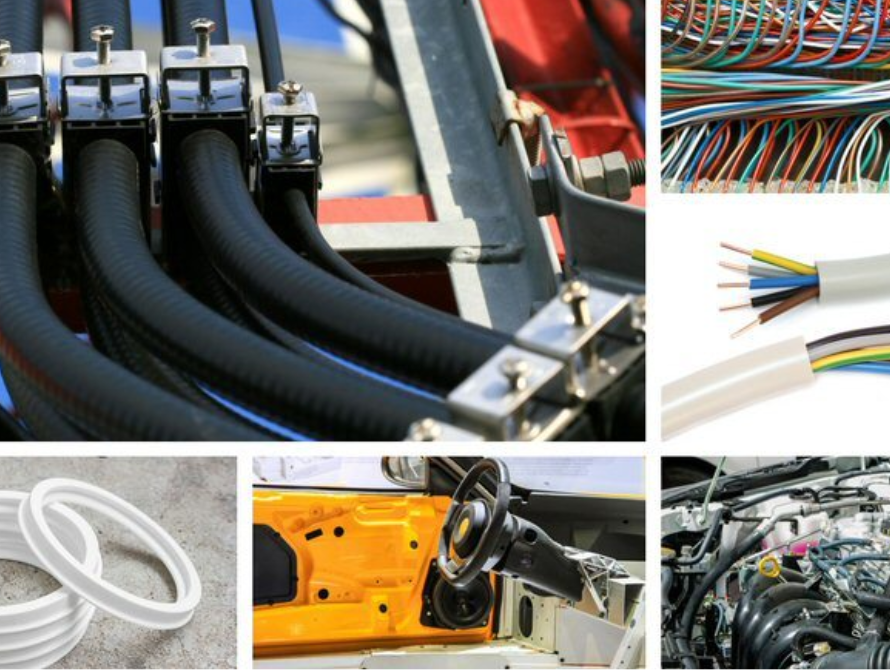
TPV is extensively used in automotive applications for manufacturing weather seals, gaskets, and other sealing components. Its weather resistance, flexibility, and durability make it suitable for withstanding the challenging conditions in automotive environments.
3.2. Wire and cable insulation:
TPV's excellent electrical insulation properties, combined with its flexibility, make it an ideal choice for wire and cable insulation. It provides protection against environmental factors and mechanical stress in electrical applications.
3.3. Consumer goods:

TPV is employed in the production of various consumer goods such as grips, handles, and overmolded components. Its tactile feel, impact resistance, and aesthetic flexibility make it valuable in enhancing the ergonomics and durability of everyday items.
3.4. Industrial seals and gaskets:

The elastomeric properties of TPV, coupled with its resistance to chemicals and compression set, make it well-suited for industrial seals and gaskets. It ensures a reliable and long-lasting seal in machinery and equipment.
3.5. Sporting goods:

TPV's combination of flexibility, impact resistance, and weather resistance finds applications in sporting goods. It is used in the manufacturing of grips, handles, and protective components for sports equipment.
3.6. Medical devices:
In the medical field, TPV is utilized for manufacturing components of medical devices that require a balance of flexibility, sterilization resistance, and durability. Its biocompatibility and ease of processing make it suitable for various healthcare applications.
3.7. Construction materials:

TPV is employed in the construction industry for seals, gaskets, and weatherstripping due to its weather resistance and long-term durability. It is also used in architectural profiles and other building components.
3.8. Footwear:

TPV's elastic properties make it a valuable material for footwear applications. It is used in the production of shoe soles, providing comfort, flexibility, and wear resistance.
3.9. HVAC systems:

TPV is chosen for applications in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems. It can be found in components such as grommets, seals, and insulation due to its ability to withstand temperature variations and exposure to environmental elements.
3.10. Appliance components:

TPV is utilized in the manufacturing of various appliance components, including handles, gaskets, and seals. Its resistance to heat, chemicals, and mechanical stress contributes to the longevity and reliability of these components.
4. Conclusion
In the dynamic landscape of material science, Thermoplastic Vulcanizate (TPV) stands as a resilient and adaptable solution, bridging the gap between flexibility and strength. From automotive advancements to consumer goods, TPV's unique properties continue to redefine possibilities.
As industries increasingly turn to sustainable and versatile materials, TPV's role is set to expand, promising a future where innovation meets durability. Embrace the potential of TPV – a material that not only withstands the test of time but shapes the way we engineer solutions for a multitude of applications.