In a world dominated by plastics, understanding their safety is paramount. From food containers to electronics, plastics are an integral part of our lives. However, not all plastics are created equal when it comes to human health and environmental impact. With concerns over chemicals leaching into our food and the persistence of plastic pollution, it's crucial to decipher which plastics are safe choices.
This guide delves into the world of plastic safety, demystifying the Resin Identification Codes that classify various plastics. By exploring these codes and their meanings, you can equip yourself with the knowledge needed to make conscious decisions that prioritize your well-being and the planet's health. Join us as we navigate the world of safe plastics and unveil the secrets to a more informed and sustainable lifestyle!
1. The Complexities of Plastic Hazards

Plastic, an emblem of modern convenience, has forever altered the way we package, store, and consume goods. However, beneath its convenience lies a complex landscape of potential hazards to human health and the environment. The concerns are rooted in the composition of plastics, which often include additives like plasticizers, flame retardants, and colorants. These compounds can leach into the environment, impacting both terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems, and in some cases, find their way into the human food chain.
One of the most pressing concerns is the presence of chemicals like phthalates and bisphenol A (BPA), commonly found in plastic products. These chemicals are known endocrine disruptors, which means they can interfere with the body's hormonal systems, leading to a range of health issues, including developmental problems, reproductive abnormalities, and even certain cancers. Furthermore, the resilience of plastics to natural degradation has led to accumulations in the environment, contributing to the pervasive issue of plastic pollution.
2. Unveiling Safety: The Role of Resin Identification Codes
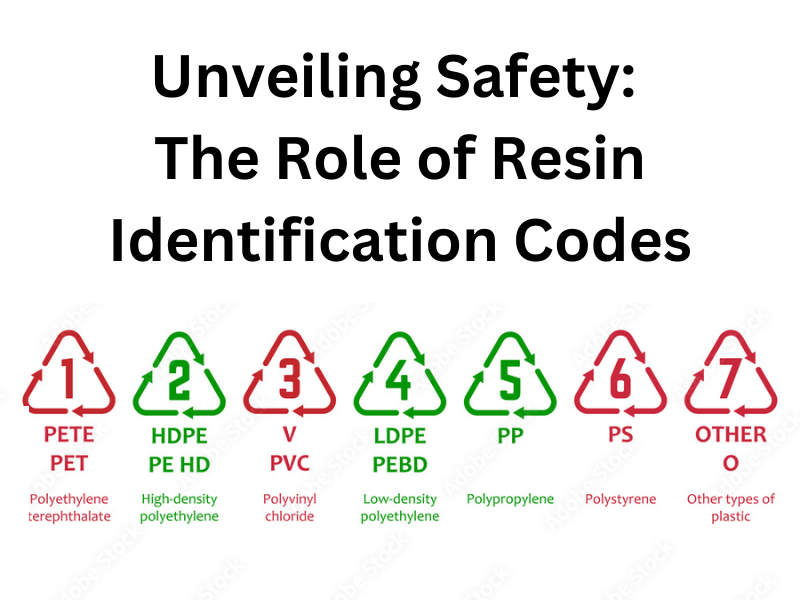
What plastics are safe? To navigate the labyrinth of plastic choices and mitigate potential risks, the plastics industry introduced Resin Identification Codes (RIC). These codes, depicted as numbers within the iconic recycling symbol, classify different types of plastic based on their chemical composition. They serve as a roadmap for consumers, helping them identify what plastics are safe and make informed choices about its usage, recycling, and disposal.
The seven RIC categories (include what number of plastic is safe and not) offer insights into the characteristics of various plastics, enabling us to discern which plastics are safer for our health and the environment and which ones to approach with caution.
2.1. What number of plastics is safe?
#5 - Polypropylene (PP):
Polypropylene, known by its code #5, is often hailed as one of the safer plastic choices. Its resistance to heat and chemicals, coupled with a low potential for leaching, make it an excellent option for food containers, bottle caps, and even medical equipment. PP's durability and stability have earned it a spot as a reliable packaging material across industries.
#1 - Polyethylene Terephthalate (PETE or PET):
Polyethylene Terephthalate, represented by #1, is prevalent in single-use beverage containers and food packaging. PET is considered safe for single use, like containing water or soft drinks. However, it's important to refrain from reusing PET containers, as repeated use can lead to bacterial growth and potential chemical leaching.
#2 - High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE):
High-Density Polyethylene, coded as #2, boasts excellent resistance to chemicals and has a low risk of leaching. This makes it a versatile and safe option for packaging a wide array of products, including milk, detergents, and cleaning agents.
#4 - Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE):
Low-Density Polyethylene, recognized by the #4 code, is renowned for its flexibility and relatively low reactivity. It's commonly used in items such as plastic wraps, squeeze bottles, and some bags. While LDPE is generally considered safe, it's advisable to avoid using it with hot foods or liquids, as elevated temperatures can lead to chemical leaching.
2.2. Cautionary plastic categories
#3 - Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC):
Polyvinyl Chloride, denoted as #3, raises significant concerns due to the presence of phthalates and the potential release of toxic chemicals throughout its lifecycle. PVC is used in a wide range of products, from pipes and shower curtains to certain food packaging. Given its potential health and environmental hazards, particularly in relation to food storage, it's advisable to minimize its use whenever possible.
#6 - Polystyrene (PS):
Polystyrene, labeled as #6, is commonly found in disposable plates, cups, and packaging materials. This plastic has the propensity to leach styrene, a substance associated with potential health risks. As such, it's recommended to limit the use of polystyrene products, especially those that come into contact with food.
#7 - Other/ Miscellaneous:
The #7 category encompasses a diverse range of plastics, including polycarbonate (PC) and bioplastics. While some #7 plastics are innocuous, others may contain bisphenol A (BPA) or other potentially harmful additives. This category demands a cautious approach, with a focus on understanding the specific type of plastic being used.
3. Utilizing Plastics Safely: A Comprehensive Approach

In a world where plastics have become nearly inseparable from our daily lives, ensuring safe usage practices is paramount. Adopting a comprehensive approach can significantly reduce our exposure to potential hazards associated with plastics:
- Mindful Microwaving: It's prudent to avoid microwaving plastic containers unless they are labeled as microwave-safe. Heat can accelerate chemical leaching, compromising the safety of the food contained within.
- Exploring Alternatives: In pursuit of a safer environment, consider transitioning to glass, stainless steel, or silicone containers for food storage and beverage consumption. These materials are known for their stability and minimal leaching potential.
- Scrutinize Packaging: Empower yourself by examining RIC symbols before purchasing plastic products. Opt for items with safer codes like #1, #2, #4, and #5, whenever feasible.
- Gentle Care: Extend the life of plastic containers by choosing to hand wash them instead of relying on dishwashers. The intense heat and potent detergents used in dishwashers can expedite plastic degradation.
- Responsible Farewell: Embrace responsible disposal practices by adhering to local recycling guidelines when discarding plastic items. Burning plastics releases harmful compounds into the atmosphere, contributing to pollution.
- Educate Others: Share your knowledge about plastic safety with friends, family, and your community. Increasing awareness can lead to more informed choices and a collective effort towards reducing plastic-related risks.
At EuroPlas, we take immense pride in being a trailblazer in the world of plastics, offering innovative solutions to customers across more than 85 countries. With over 15 years of industry expertise, we have built a reputation as a top masterbatch manufacturer in Vietnam, consistently delivering high-quality products that blend cost-efficiency with sustainability. Our commitment to shaping a better tomorrow drives us to develop cutting-edge plastic solutions tailored to a multitude of industries and applications.

One of our flagship offerings, the EuroPlas bioplastic compound, stands as a testament to our dedication to environmental responsibility. Crafted from natural starch and biodegradable additives, this unique product not only biodegrades within a year but also maintains exceptional performance standards. With applications spanning from food packaging to agricultural films and beyond, the bioplastic compound paves the way for a greener, more eco-friendly future.

EuroPlas is committed to driving change by providing eco-conscious alternatives, and our bio filler exemplifies this commitment. Comprising natural starch and biodegradable additives, the bio filler transforms plastic items into biodegradable materials within a year. This remarkable solution finds its place in food packaging, disposable tableware, and agricultural films, offering a sustainable path forward without compromising performance.
Explore our exceptional range of plastic solutions by visiting our website or reaching out to us directly. At EuroPlas, we are committed to co-creating a sustainable future through responsible plastic solutions that champion performance, innovation, and environmental stewardship. Together, let's shape a world where plastics drive progress without compromising our planet's well-being.