Environment factors including temperature, humidity, impurities, irradiation, microorganisms… is the main reason accelerating the degradation of plastics. Therefore, plastic products exposed to the weather require additives like UV absorbers and light stabilizers to avoid the loss of their useful functions. In this blog, we’ll discover the effects of UV lights on plastics and how to mitigate the problem. Let’s get started!
Read more: What are plastic additives? 8 most common plastic additives in plastic industry
1. Does plastic block UV lights?
Normally, the photodegradation of plastics is caused by sunlight, UV rays, heat, and reaction with oxygen. That means plastic itself can’t avoid the damage of ultraviolet lights. People assess the UV degradation of plastics according to components as followings:
- Change in chemical structure: the oxidative degradation process will produce hydroperoxy, hydroxy, carbonyl groups, and cross-linking that affect the properties of plastics.
- Change on the surface: when oxidative degradation takes place, the surface of plastics is the part that suffers the most. Normally, it causes a brittle outer layer that can be observed from SEM or optical microscopy.
- Embrittlement: embrittlement is unavoidable, we can easily test it by hand, especially when plastics are exposed to hot weather for a long period.
- Generation of free radicals: the degradation processes are free radical reactions and generate various types of free radicals.
- Change in molecular weight: reduction in molecular weight happens due to chain scission processes.
- Loss in mechanical properties: the reaction with UV lights causes the loss in mechanical properties of a degraded polymeric material.
- Impairment of transparency: this is due to the formation of different morphology on polymer degradation. This results in heterogeneity in the bulk of a polymeric material, which scares incident light rather than transmitting it. Therefore, plastics lose their transparency.
2. Methods to protect plastics from the effect of UV lights
2.1. Use UV absorbers
Nowadays, the most common method to protect plastics from UV lights is UV absorbers. Depending on the manufacturing purposes, people will use either inorganic compounds (Carbon Black, TiO2, ZnO,…) or organic compounds (Benzophenone, Benzotriazole, Triazine) of UV absorbers.
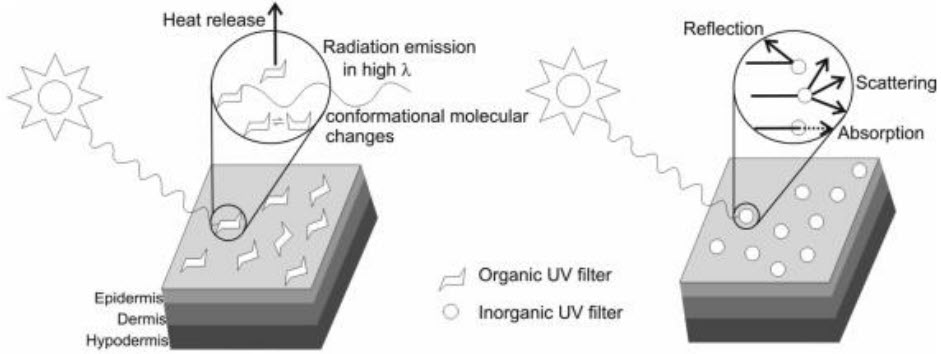
Inorganic compounds
- Main feature: colored inorganic solid, not being affected by the working environment.
- Mechanism: absorbing and filtering UV lights.
- Advantage: long-lasting protection, not being affected by the environment.
- Disadvantages: low level of protection (except the black color)
+ TiO2: Only work with Rutile, Anatase has the ability to absorb water, creating OH- ions that cause rapid destruction of plastic.
+ CB: the application is more limited due to the black color.
Organic compounds
- Main feature: yellow color, low melting point, solid or liquid.
- Mechanism: absorbs UV and releases visible light energy
- Advantage: Does not affect the color of the product, easy to process, works effectively in the UV range (under 400nm); can retain the transparency of the film. Protect the quality of the product contained in the packaging.
- Disadvantages: affected by oxidation, leaching, especially chlorine-containing compounds, and pH<6 environments; only protect the product for a short time and the level of protection is weak.
2.2. Use antioxidants when processing plastic products
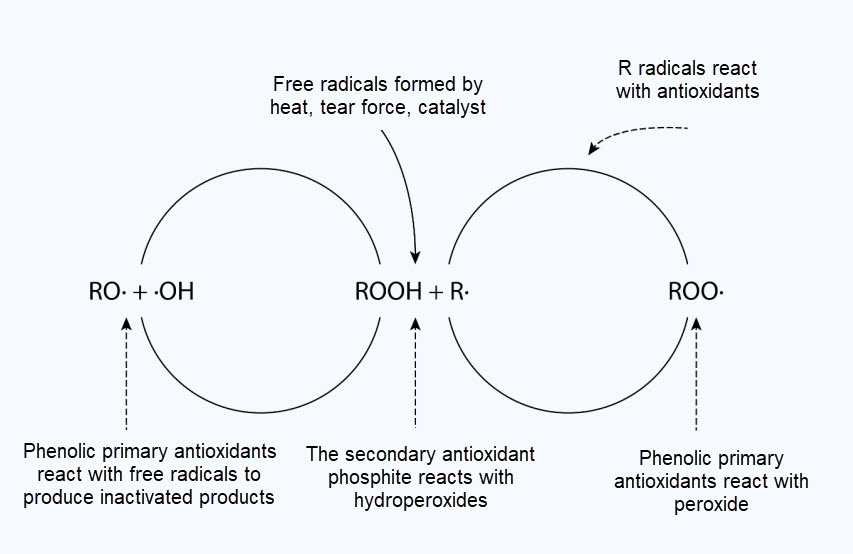
This method will use antioxidant compounds to prevent oxidation when processing and using. When combined with HALS, it also prevents circuit cutting when plastic exposes to UV lights and impurities.
Advantage: effectively blocks thermal oxidation when processing.
Disadvantage: poor reproducibility, less effective when used outdoors
2.3. Hindered Amine Light Stabilizer (HALS)
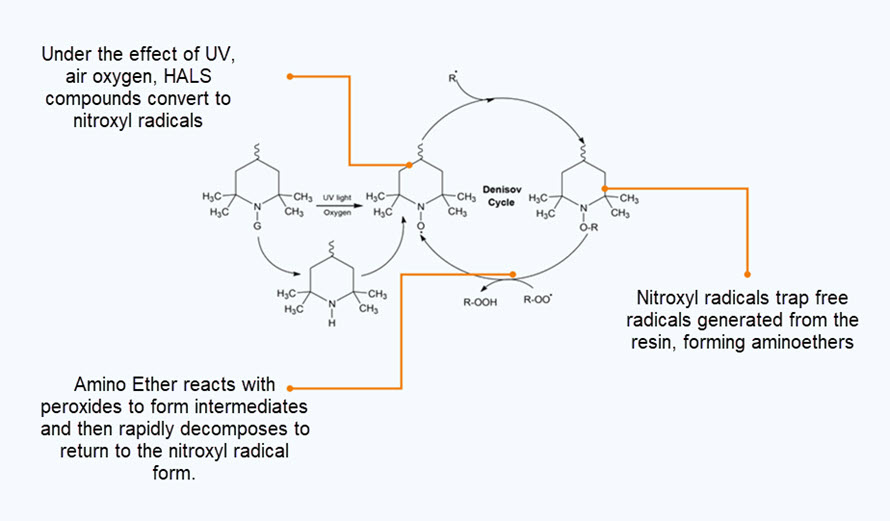
This method will use Hindered Amine Light Stabilizer (HALS) to form inactive peroxide compounds that inactivate free radicals.
Advantages: high protection effect, long protection time, good reproducibility
Disadvantages: can not prevent thermal oxidation when processing
Some types of HALS and their application:
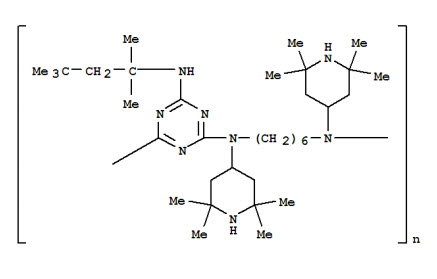
- Suitable for thin PE and PP film application
- Application in greenhouse film
- Improved heat and light resistance
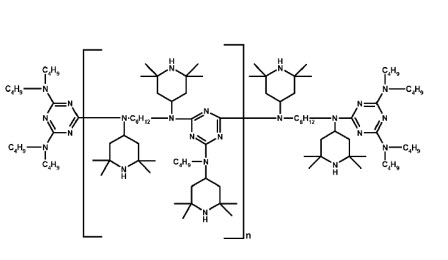
- Suitable for PP, PE, and EVA plastic application
- Enhance temperature resistance for thick PP products.
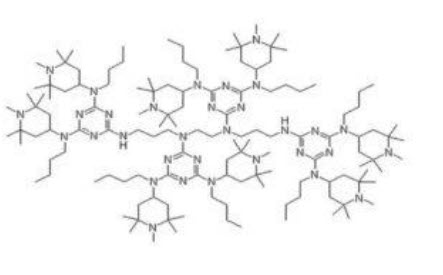
- Suitable for PE film application
- Effective when applied to greenhouse films with medium to high pesticide exposure
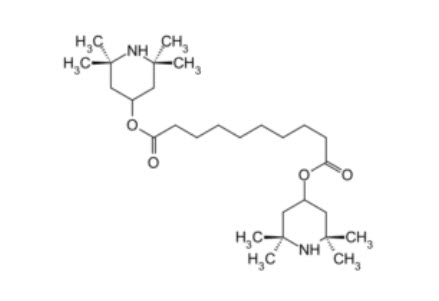
- Suitable for applications using PP, ABS, etc.
- Improves UV resistance and effective anti-oxidation
“So which is the most optimal solution?” - you may ask. The answer is that you should combine all of them to make the most out of their function and enhance your product properties.
3. Where can I buy anti-UV additives for plastics?

European Plastic Company (EuP) is the world’s largest filler masterbatch manufacturer located in Vietnam. Our anti-UV additives are quality-proven products that satisfied thousands of customers in +85 countries all around the world. This product is a perfect solution to minimize and prevent the degradative impacts of UV lights on end-products:
- Prevent UV light's negative impacts on end-products
- Maintain end-products mechanical properties and improve end products durability
- Great dispersion without spots
- Strongly absorb organic UV lights
- Permanent effectiveness
If you want to get more details about our products, please fill in this form or contact us via email/phone number. We are more than happy to help!