In the world of thermoforming, pressure forming takes center stage. This is the process of utilizing air pressure to mold heated plastic sheets, allowing for the creation of highly detailed and textured molds or parts. Selecting the right plastic material is crucial for a successful outcome. This article explores the top 10 plastic materials for pressure forming, highlighting their key properties, advantages, and ideal applications. Ranging from crystal-clear plastics to those with high impact resistance, discover the ideal material to bring your pressure forming projects to life.
1. Top 10 Plastic Materials For Pressure Forming
1.1. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
ABS excels in pressure forming due to its well-balanced properties, toughness, and formability. It can soften readily for intricate mold replication, while its strength and toughness ensure parts maintain their form. ABS can also be easily machined and finished after forming, allowing for customization and improved aesthetics.
This combination of good formability, balanced mechanical properties, and finishing options makes ABS a versatile and popular choice for pressure forming projects.
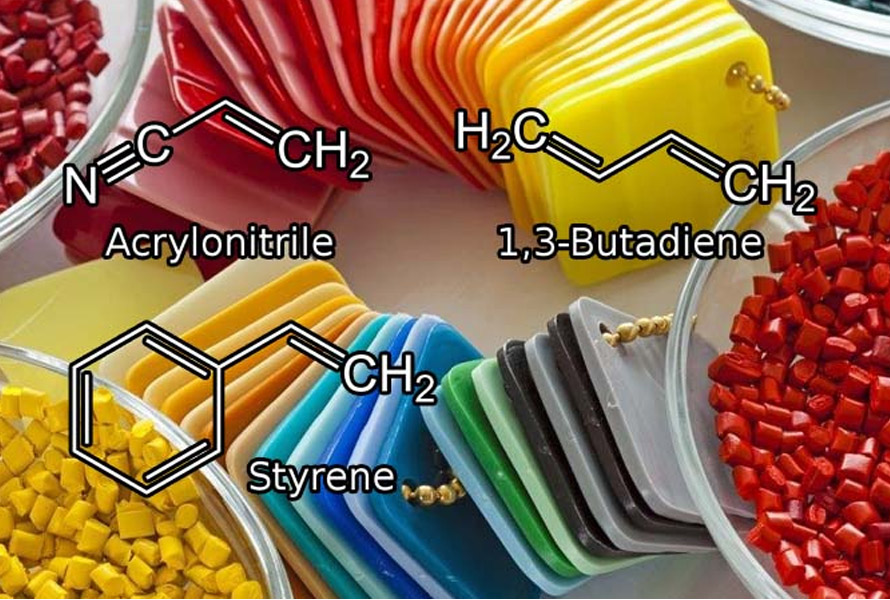
ABS plastic material can also be easily machined and finished after forming
1.2. Polycarbonate (PC)
Polycarbonate (PC) shines in pressure forming with its exceptional strength and impact resistance. This makes it ideal for parts needing to endure high stress or potential impacts. The PC also boasts excellent clarity, allowing for visually striking formed parts. Additionally, its inherent flame retardancy and good chemical resistance broaden its application range.
While PC’s formability is good, it may require slightly higher forming temperatures compared to some materials.
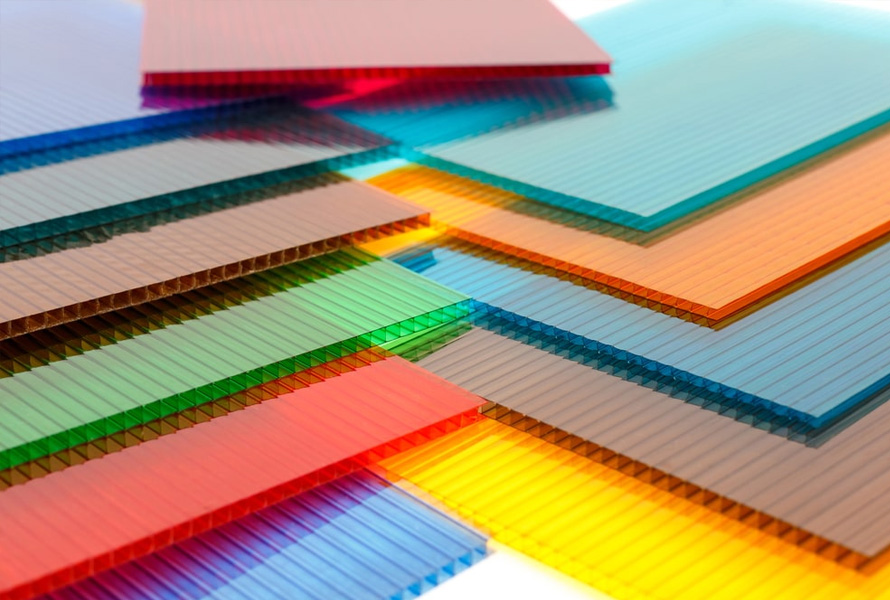

Polycarbonate (PC) plastic material requires slightly higher forming temperatures compared to some materials.
1.3. High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE)
HDPE brings a unique advantage to pressure forming is exceptional chemical resistance. This makes it the go-to choice for parts exposed to harsh chemicals or corrosive environments.
HDPE also boasts impressive impact strength, making it suitable for applications requiring durability. While its formability is adequate, achieving intricate details might be challenging compared to other materials. However, the fact that HDPE is a cost-effective material and because of its excellent chemical barrier properties makes it a strong candidate for pressure forming projects that prioritize these aspects.

HDPE plastic material brings a unique advantage to pressure forming is exceptional chemical resistance
1.4. High-Impact Polystyrene (HIPS)
High-impact polystyrene (HIPS) is known for its affordability, making it an attractive choice for cost-conscious pressure forming projects. Additionally, its good formability allows for the replication of moderate detail in the final parts.
While not the strongest material, HIPS provides adequate impact resistance for many applications. However, its clarity is not exceptional, making it less suitable for parts requiring high visual transparency. Overall, HIPS strikes a balance between affordability, formability, and impact resistance, making it a popular choice for disposable items and prototypes.

HIPS plastic material is known for its affordability
1.5. Polypropylene (PP)
The polypropylene’s lightweight nature makes it ideal for pressure forming applications where weight reduction is crucial. PP also boasts good chemical resistance, allowing it to withstand exposure to various chemicals. While not the most impact-resistant, it offers adequate formability for creating parts with moderate details. Additionally, PP’s natural moisture barrier properties make it suitable for packaging applications.

PP plastic material boasts good chemical resistance, allowing it to withstand exposure to various chemicals
1.6. Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
PVC’s versatility is available in both rigid and flexible formulations, it caters to a wide range of pressure forming applications. Its inherent flame retardancy and wearability make it suitable for outdoor use in signs and building materials. Additionally, PVC offers good chemical resistance, making it a viable option for parts exposed to harsh chemicals. While formability may be slightly lower compared to some materials, PVC’s affordability and diverse properties make it a popular pressure forming choice.

PVC plastic material is available in both rigid and flexible formulations
1.7. Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol (PETG)
PETG is a plastic material that has excellent clarity and allows for visually strikingly formed parts, making it ideal for pressure forming applications where transparency is important. PETG also boasts good impact resistance, ensuring parts can withstand some physical stress. Moreover, it offers good formability for creating intricate details, and it's even recyclable, promoting environmental responsibility.
While chemical resistance might not be its strongest point, PETG’s combination of clarity, formability, and impact resistance makes it a popular choice for packaging, displays, and point-of-purchase applications.

PETG is a plastic material that has excellent clarity and allows for visually strikingly formed parts
1.8. Acrylonitrile Styrene Acrylate (ASA)
ASA is the prime choice for pressure forming projects due to its exceptional resistance to UV rays. This also makes it the ideal choice for outdoor applications where prolonged sun exposure can degrade other plastic materials.
Acrylonitrile styrene acrylate maintains its color stability and mechanical properties even under harsh sunlight. Additionally, it boasts good formability and a smooth surface finish, allowing for the creation of detailed and visually appealing pressure-formed parts. While chemical resistance might be slightly lower than some materials, ASA’s UV resistance, durability, and aesthetics make it a top contender for outdoor signs, building materials, and automotive parts.

ASA (Acrylonitrile Styrene Acrylate) exhibits excellent UV resistance
1.9. Polylactic Acid (PLA)
Biodegradable PLA offers a unique advantage in pressure forming eco-friendliness. Derived from renewable resources, PLA caters to sustainability-focused projects. While not the strongest, it has good formality for creating moderately detailed parts. PLA’s printability makes it ideal for prototypes. However, its heat resistance limitations may require careful temperature control during pressure forming.

PLA plastic material offers a unique advantage in pressure forming eco-friendliness
1.10. Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA)
Popymethyl methacrylate plastic material, known as acrylic, takes center stage in pressure forming due to its exceptional optical properties. Its unmatched clarity allows for the creation of visually stunning, transparent parts, perfect for lenses, displays, and signage.
PMMA also boasts good formability, enabling the replication of intricate details in the final product. While not the most impact-resistant, it offers adequate strength for many applications. However, PMMA requires careful temperature control during forming due to its lower heat tolerance compared to some materials. Overall, PMMA’s exceptional clarity and formability make it a suitable choice for pressure forming projects prioritizing visual impact and intricate details.

PMMA shines with unmatched optical properties for stunning pressure formed parts
2. Factors To Consider When Choosing Plastic Materials
Plastic sheets are given vitality by pressure forming, which turns them from flat expanses into accurate, three-dimensional parts. But with a vast array of available plastic possibilities, choosing the right plastic material becomes essential to a project’s success. Here are factors to consider to help you make this suitable material choice:
2.1. Matching the requirements of your project
The ideal plastic material goes beyond just the material itself. It’s about identifying the ideal match for the particular project at hand.
Functionality: What is the pressure-formed component used for? Does it require high strength for structural applications or superior chemical resistance (e.g. for a medical device)? Narrowing down the plastic options will be easier when you determine the primary functionality.
Level of details: The complexity of the final product significantly impacts the plastic material selection. The high-intricate parts require excellent formable materials. On the other hand, more material flexibility may be available with simpler designs.
Aesthetics: For example, do you need a transparent portion for optimal visibility, or are there any requirements for color specifications? The material of choice should support the desired aesthetics of the final product.
Environment aspects: Concern over sustainability is on the rise. If eco-friendliness and sustainability are top priorities for your project, consider using recyclable or bio-based plastic materials.

Choosing plastic material match requirements of every particular project
2.2. Potential properties of plastic for pressure forming
Key plastic properties for pressure forming include:
- Formability: It reflects how easily the plastic sheet takes on the mold’s shape. Good formability allows for intricate details and complex design, creating pressure-formed parts with sharp definition. However, a less pliable material might struggle with these details, resulting in a simpler final product.
- Strength & impact resistance: Not all pressure-formed parts are built the same. Some, like phone cases, need to be tough enough to handle weight and drops. The chosen plastic material must be strong and resist impacts to handle the expected wear and tear.
- Chemical resistance: Not all plastics have chemical resistance. If your pressure-formed part requires this, choose a plastic material with superior chemical resistance. Accordingly, the part will be ensured not to weaken or degrade over time. Think of a pressure-formed container for cleaning solutions - chemical resistance is a crucial factor to prevent it from breaking down.
- Heat resistance: Pressure forming involves heat, but the story goes further. Consider the temperatures the final part will face during use. The chosen plastic needs to withstand these temperatures without warping or losing its valuable properties. Imagine a pressure-formed piece for a car’s interior - it might encounter extreme summer heat. The plastic should handle these fluctuations without compromising its shape.
- Clear or colorful cover: Do you envision a clear part or optimal visibility, or is some opacity acceptable? This significantly influences the final product’s visual appeal and functionality. Imagine a pressure-formed food container. Here, clarity is important to show the contents within.

Choosing plastic material based on their potential properties
2.3. Consider in manufacturing
Besides issues involving the plastic itself, practical considerations during pressure-forming keep an important role.
- Cost: It is necessary to account for the plastic material price and any additional processing expenses related to pressure forming. Achieving optimal equilibrium among material qualities, project needs, and budget is crucial.
- Availability: A smooth manufacturing schedule depends on the selected plastic being easily accessible in the required amount and time frame.
- Machinability: Some pressured-formed components might require further customization after forming, e.g. drilling or sanding. Choosing a plastic that allows for easy machinable processing ensures flexibility and efficiency during manufacturing.

The practical manufacture considerations during pressure-forming keep an important role for choosing the ideal plastic material
By careful close attention to these factors and aligning them with your specific project needs, you’ll be well-equipped to choose the ideal plastic material for pressure forming.
3. Conclusion
Choosing the ideal plastic for pressure forming is very important. This guide has explored 10 top plastic materials, each with its strengths. By considering factors like formability, chemical resistance, and temperature tolerance, you can find the perfect match for your project’s specific needs. Don’t forget to take careful consideration of both material properties and project requirements, you can unlock the full potential of pressure forming.
4. About EuroPlas
European Plastic Joint Stock Company, also known as EuroPlas, is a prominent global manufacturer of plastic additives, specializing in filler masterbatches These are essential additives mixed with plastic resins to enhance various properties, making them ideal for pressure forming applications. EuroPlas is headquartered in Vietnam, the company boasts a strong presence across Asia, Europe, the Middle East, and Africa.
EuroPlas focuses on developing innovative filler masterbatches that can significantly benefit pressure forming projects. Here’s how:
- Enhanced formability: Certain filler masterbatches can improve the plastic material’s ability to conform to complex mold shapes, allowing for intricate details in the final formed parts.
- Optimized strength & impact resistance: Specific filler masterbatches can increase the overall strength and impact resistance of the plastic material, creating pressure-formed parts that can withstand higher stress and potential impacts during use.
- Cost-effective solutions: Some filler masterbatches can partially replace more expensive virgin plastic resins, leading to cost reductions in pressure forming projects without compromising performance.
- Plastic material versatility: EuroPlas likely offers a range of filler masterbatches compatible with various plastic materials commonly used in pressure forming, such as ABS, PC, and HDPE. This allows for tailoring the plastic properties to specific project needs.
For more information on EuroPlas and their filler masterbatches suitable for pressure forming applications, you can visit our website or contact us here.