3D printing has revolutionized the manufacturing industry, offering endless possibilities to hobbyists and industrialists alike. Among the many materials available, 3D printing with ABS plastic stands out for its durability, affordability, and versatility. Known for its resilience, ABS plastic is often used in automotive parts, consumer products, and even toys. In this article, we explore why ABS plastic is a preferred material for 3D printing, provide a comprehensive guide on how to print with it, discuss common challenges, and examine some alternatives. We’ll also take a closer look at how EuroPlas can support your plastic manufacturing needs.
1. Why 3D Printing with ABS Plastic is the Better Choice

3D Printing With ABS Plastic
3D printing with ABS plastic offers several unique benefits that make it an optimal choice for both beginners and seasoned professionals:
- High Impact Resistance: ABS is known for its impact resilience, making it ideal for functional parts that must withstand frequent handling or mechanical stress. This strength makes ABS highly suitable for structural and load-bearing components.
- Thermal Stability: Compared to other popular 3D printing materials like PLA, ABS can tolerate higher temperatures, making it ideal for environments where heat resistance is critical. ABS doesn’t deform easily under moderate heat, a quality that enhances its performance in automotive and electronic applications.
- Smooth Surface Finish: ABS offers a polished finish when printed, making it a great option for projects that require post-processing. This quality is advantageous for creating visually appealing products that may need further finishing, such as sanding or painting.
- Ease of Recycling: ABS is a recyclable material, which aligns well with sustainability efforts. Recycling ABS can reduce plastic waste, making it a responsible choice for environmentally conscious makers.
- Cost-Effective: ABS provides excellent value for the quality it offers, making it accessible for both hobbyists and industries. Compared to specialty materials, ABS allows users to achieve high-quality prints without a significant cost increase.
These advantages have made 3D printing with ABS plastic the preferred choice for many industrial applications, including automotive parts, consumer electronics, and even toy manufacturing. However, while ABS is highly versatile, it requires specific handling and conditions to yield the best results.
2. How to 3D Print with ABS Plastic

3D Printing With ABS Plastic
To achieve successful 3D printing with ABS plastic, following certain best practices can greatly enhance the quality of your prints. Here’s a step-by-step guide to working with ABS effectively:
- Use a Heated Bed: ABS is prone to warping, especially during cooling. A heated bed set to around 100°C is essential to prevent the bottom layers from lifting. This will help maintain stability and reduce warping.
- Print in an Enclosed Chamber: ABS printing emits fumes that can be irritating to inhale. Printing in an enclosed space not only protects the user but also keeps the temperature stable, which reduces the risk of warping and cracking.
- Optimize Bed Adhesion: Bed adhesion is crucial for ABS. Using adhesives like ABS slurry, painter’s tape, or specialty adhesive solutions can help the base layer stick more effectively, ensuring a smooth start for your print.
- Control Cooling: Rapid cooling can lead to cracks and layer separation. Avoid direct airflow to the printed object, and consider using a slow-cooling setup to maintain uniformity.
- Adjust Printer Settings for ABS: Generally, ABS filament requires nozzle temperatures between 230-250°C. It’s essential to fine-tune these settings, as different brands of ABS filaments may respond differently. Experiment with your printer’s temperature settings to find the ideal balance for strength, detail, and layer bonding.
Other useful tips for printing ABS include printing with thicker walls to improve strength and setting infill levels to optimize durability while minimizing filament usage. It’s also advisable to store ABS filaments in a dry place, as ABS is sensitive to moisture, which can impact print quality.
3. Challenges When 3D Printing with ABS Plastic
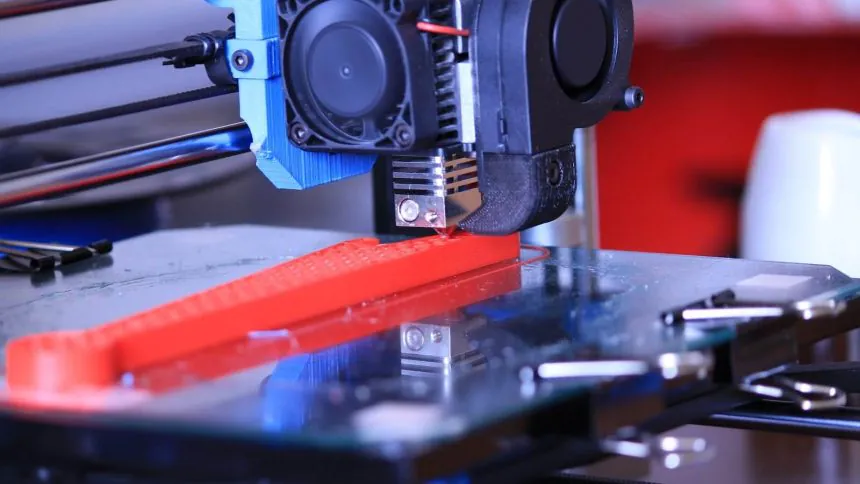
Challenges When 3D Printing with ABS Plastic
While 3D printing with ABS plastic offers many benefits, it also presents specific challenges that need to be managed for optimal results:
- Warping and Cracking: ABS tends to contract as it cools, which can lead to warping or cracking if the print bed temperature fluctuates. A heated enclosure and stable environment are crucial to prevent these issues.
- Emission of Fumes: When ABS is heated, it releases fumes that can be unpleasant and potentially harmful with prolonged exposure. Printing in a well-ventilated area or using an enclosed setup with an air filter is recommended to mitigate this.
- Bed Adhesion Issues: Due to its tendency to warp, ABS often struggles with bed adhesion, particularly on non-heated beds. Without proper adhesion, prints can lift at the edges, causing failed prints and wasted material.
- Surface Imperfections: ABS prints may show visible layer lines or small gaps, especially if print settings aren’t optimized. Post-processing techniques like sanding, acetone vapor smoothing, or painting may be needed to achieve a polished finish.
Understanding and addressing these challenges will help you make the most out of 3D printing with ABS plastic, especially for complex or high-precision projects.
4. Common Applications for 3D Printed ABS Parts

3D Printing With ABS Plastic
Thanks to its strength, impact resistance, and affordability, ABS is commonly used for applications that require durability and resistance to wear. Some typical applications include:
- Prototyping: ABS’s cost-effectiveness and durability make it an ideal material for prototyping, allowing engineers to test designs without incurring high material costs.
- Automotive Industry: ABS is widely used in automotive components, from dashboard parts to interior panels, due to its ability to withstand temperature changes and physical stress.
- Consumer Electronics: The electronics industry uses ABS extensively for housing units and casings due to its electrical insulation properties and smooth finish.
- Toys and Educational Models: Popular toy brands, including LEGO, use ABS for its resilience and non-toxic nature, making it ideal for products intended for children.
- Household Items and Fixtures: ABS is used to create household goods like tool handles, storage containers, and kitchenware due to its durability and ease of cleaning.
With these applications, 3D printing with ABS plastic has become a mainstay in industries requiring durable, aesthetically pleasing components.
5. Alternatives to ABS for 3D Printing

PLA as an alternative to 3D printing with ABS plastic
While ABS is highly versatile, there are times when alternative materials might better suit specific needs. Here are some alternatives for consideration:
- PLA (Polylactic Acid): PLA is known for its ease of use and minimal warping, making it a popular choice for beginners. However, it is less heat-resistant and durable than ABS.
- PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol): PETG combines some properties of PLA and ABS, providing both strength and flexibility with minimal warping. It’s a popular choice for parts that need durability without the challenges associated with ABS.
- Nylon: Known for its exceptional strength and wear resistance, nylon is ideal for mechanical parts. However, it’s more challenging to print and requires specialized printing conditions.
- Polycarbonate (PC): PC is among the strongest 3D printing materials, offering superior heat resistance and impact strength, making it suitable for high-stress environments.
Each material offers distinct advantages, so understanding their strengths and limitations will help you select the best fit for your project.
6. Conclusion
3D printing with ABS plastic offers an effective solution for projects requiring durability, impact resistance, and a high-quality finish. While the material presents some challenges, such as warping and fume emissions, following best practices can mitigate these issues. ABS remains a cost-effective choice, suited to a wide range of applications from prototypes to consumer electronics and automotive parts. With its combination of strength, affordability, and recyclability, ABS plastic continues to be a versatile option for 3D printing enthusiasts and professionals alike.
7. About EuroPlas
.png)
EuroPlas - No. 1 3D printing material manufacturer
EuroPlas (EuP) is the world’s leading filler masterbatch manufacturer, committed to providing innovative and high-quality plastic solutions to elevate the competitiveness of businesses worldwide. With a strong focus on ABS compounds and other essential 3D printing materials, EuroPlas is a trusted partner for industries looking to improve efficiency and sustainability.
EuP operates seven factories across Vietnam, spanning dozens of hectares, and produces up to 0.8 million tons annually. This extensive manufacturing capacity enables EuP to fulfill large-scale orders for clients in over 95 countries. With state-of-the-art equipment, such as extruders and injection molding machines, EuP guarantees products that meet the highest standards of quality and consistency.
What’s the wait? Visit our Contact Us page to learn how EuroPlas can help your business thrive.