Selecting the best production technique for plastic components can be difficult and ineffective, resulting in delays, poor quality, or lost income. Our article can help you overcome this problem by introducing two methods for producing repetitive items: rotational molding and thermoforming.
We will provide a thorough breakdown of the differences between these two techniques so that you can choose the best option for your projects. Let’s scroll down for more!
1. Overview Of Rotational Molding
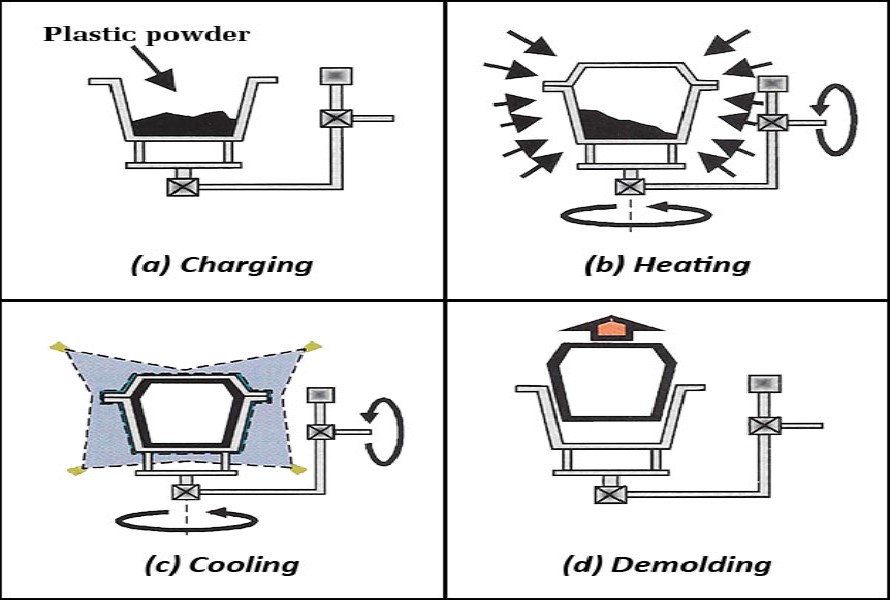 Making endless hollow plastic pieces is possible with a low-cost production method called rotational molding. It’s also often known as rotomolding or rotocasting. Reagents are added to a heated, rotated mold, and the resin is then distributed and fused on the inside surfaces. As a result, seamless pieces with consistent wall thickness are produced. They also come with additional material in corners to withstand loads and shocks .
Making endless hollow plastic pieces is possible with a low-cost production method called rotational molding. It’s also often known as rotomolding or rotocasting. Reagents are added to a heated, rotated mold, and the resin is then distributed and fused on the inside surfaces. As a result, seamless pieces with consistent wall thickness are produced. They also come with additional material in corners to withstand loads and shocks .
2. What Is Thermoforming?
Plastic thermoforming is a manufacturing technique that produces three-dimensional parts or shapes by heating thermoplastic material. This technique is adaptable and has a broad range of applications since it enables part shaping, cutting, and finishing to satisfy end-user specifications.
3. Differences Between Rotomolding and Thermoforming
Let’s take look at the table of differences between these 2 methods:
| |
Rotational molding |
Thermoforming |
| Process |
The method rotates and heats a mold that is filled with powdered resin. |
The technique includes heating a plastic sheet and shaping it against a mold. |
| Applications |
Large, hollow parts like storage tanks, playground equipment, kayaks, and fuel tanks for automobiles are common applications for rotomolding. |
Numerous things, such as packaging trays, disposable cups, car interiors, and even larger items like refrigerator liners, are made using thermoforming. |
| Design Flexibility |
Rotational molding offers excellent design flexibility and affordable tooling. Thus, intricate shapes and undercuts can be created without the need for extra assembly stages. |
Thermoforming has moderate design flexibility, making it appropriate for shallow pieces with consistent wall thickness. Intricate tooling or other processes may be required for complex geometries and sharp features. |
| Materials |
Depending on the application and the required qualities like strength, flexibility, and UV resistance, the material can be various such as nylon, polyethylene, and PVC. |
The method uses thermoplastics such as acrylics, PET, PVC, and polystyrene. The selection of materials is made according to temperature resistance, clarity, and impact resistance. |
| Production Volume |
Both small and large production runs can use rotational molding. However, it’s more ideal for custom or low to medium volume production. |
Thermoforming can be used for both small and large productions. Its fast processing speed makes larger production quantities more economical. |
4. When To Choose Rotomolding?
Rotational molding is a versatile method suitable for large-scale plastic storage tanks and containers that can be used to store a variety of materials, including chemicals, fuels, oils, and wastewater. This method creates hollow, layered pieces without the need for joining or welding, thus rendering it a great option for a variety of projects.
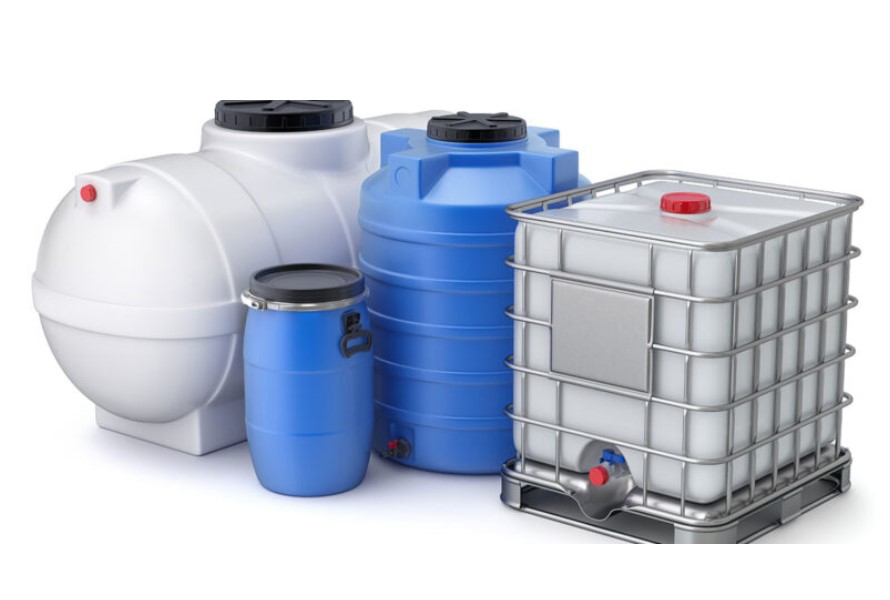

Here are some examples of its applications:
- Containers and storage tanks.
- Parts of automobiles like fenders and gasoline tanks.
- Portable barriers
- Playground equipment
- Equipment and tanks for agriculture.
- Carriers and carts
- Marine and watercraft items
- Components for containment and water treatment
- Products for garbage management
- Products for industry and material handling
5. When To Choose Thermoforming?
Compared to rotational molding, thermoforming is a more adaptable technique for forming specialized polymers, particularly for bigger projects needing intricate detail or high-color materials. It works well for operations needing variable tooling and repeat component production, making it perfect for projects that require accuracy and attention to detail.
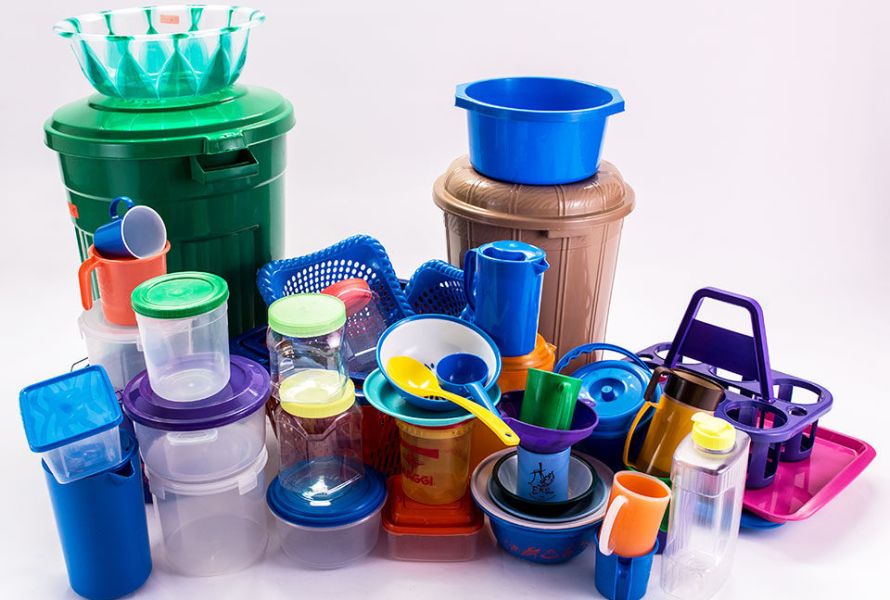

Applications of thermoforming include:
- Equipment enclosures for medical devices
- Large equipment enclosures
- Interior components of railcars: trim, paneling, window coverings, chairs, tray tables, luggage racks, etc.
- Interior and exterior paneling and coverings for industrial handling and construction vehicles
- Enclosures and fascias for POS, ATM, and kiosk applications
- Tray handling and material handling equipment
- Bedliners for pickup trucks
- Vehicle parts and equipment used in agriculture
- Components for wastewater management
6. Conclusion
Rotational molding and thermoforming are two popular plastic manufacturing processes. Depending on the requirements of products’ materials, size, complexity, and production volume, one method is chosen over the other.
While thermoforming is best suited for larger volume production of simpler shapes, rotational molding works well for custom or lower volume production. Therefore, understanding these differences help manufacturers more effectively attain desired product qualities and optimize production processes.
7. Explore EuroPlas Engineering Plastic Compound
Specialized solutions such as engineering plastic compounds are used to produce completed items with desired technical qualities. It is made up of main resin, reinforcements, and colorants to give the finished product the necessary qualities. Glass fibers, beads, conductive carbon, HIPS, POM, PBT, ABS, PC, barium sulfate, antistatic, and fireproof additives are examples of common reinforcements.

The engineering plastic compounds from EuroPlas combine all the benefits of flexibility and excellent quality into a single material. Our products include ABS antistatic compound, PC fire retardant compound, mix PA6, PA66, PBT GF-FR compound, and ABS fiberglass compound. These substances strengthen mechanical qualities, lessen shrinking, and increase thermal resistance.
Contact EuroPlas right now for more details!