Plastic, a ubiquitous material in modern life, plays an indispensable role in fulfilling a diverse range of needs. Its remarkable properties including versatility, affordability, and ease of processing have provided us with immense benefits, significantly enhancing our quality of life. In tandem with advancements in science and technology, numerous innovative plastic processing methods have emerged, each with its distinct advantages, limitations, and applications. Embark on a journey to uncover the boundless potential of plastic and the ingenious methods that transform ideas into tangible realities.
1. Prevalent Plastic Processing Techniques in Modern Times
Driven by the ever-expanding and multifaceted demands of the market, plastic processing techniques have undergone continuous refinement and innovation. Each method boasts a unique set of advantages and finds applications across a wide spectrum of industries, from manufacturing and healthcare to consumer goods production. Delve into the realm of plastic processing as we explore four of the most prevalent methods employed today:
1.1. Injection Molding
Injection molding stands as a frontrunner among plastic processing techniques, renowned for its widespread adoption and remarkable effectiveness. This method reigns supreme in the mass production of intricate plastic products that demand high precision and consistent replication.

The injection molding process commences with the melting of raw plastic within a heated cylinder. Subsequently, this molten plastic is injected into a mold under immense pressure. As the plastic cools and solidifies, it takes on the desired shape, forming the final product. Injection molds can be meticulously crafted to produce items with intricate details, ranging from minuscule electronic components to sizable automotive parts.
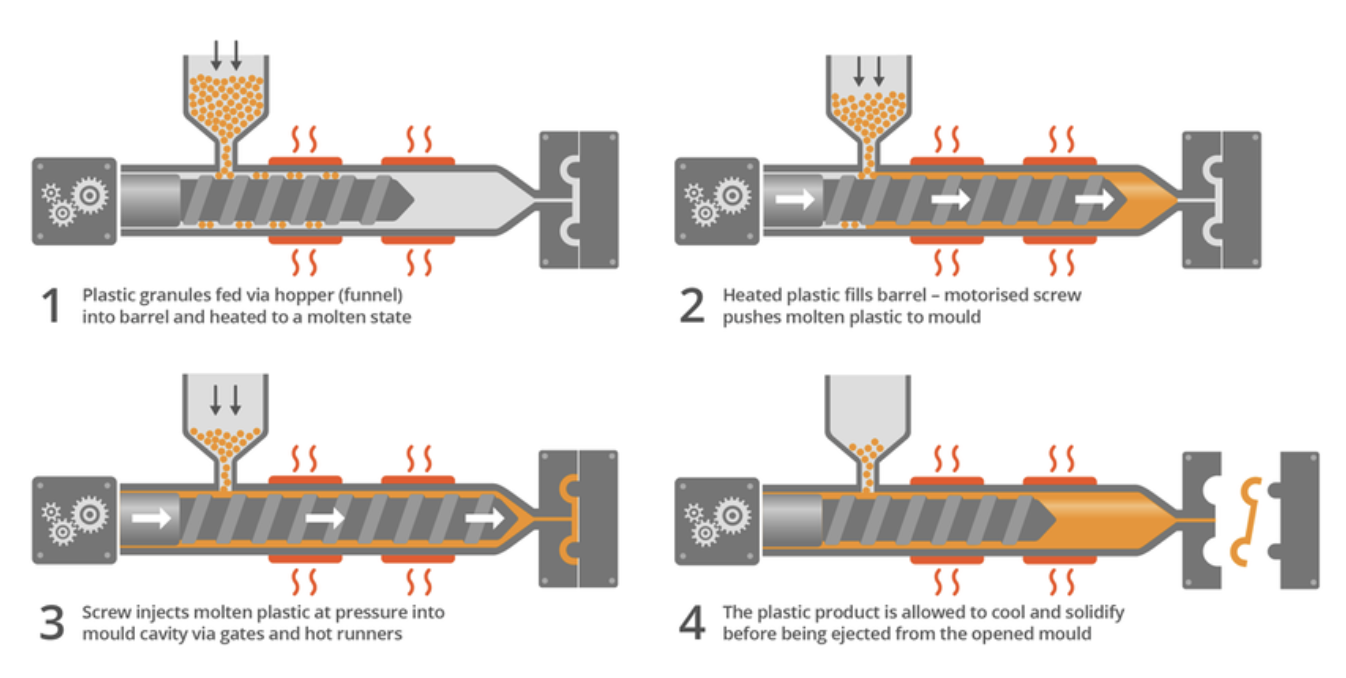
Diverse Applications of Injection Molding in Plastic Processing:
- Packaging: Crafting bottle caps, containers, and various packaging solutions;
- Medical: Manufacturing medical devices and equipment components;
- Electronics: Creating casings, connectors, and components for electronic devices;
- Consumer Goods: Producing household appliances, utensils, toys, and packaging;
- Industrial: Manufacturing components, spare parts, and industrial tools and equipment;
- Automotive: Producing interior and exterior components such as door panels, bumpers, dashboards, and more.
Injection molding not only excels in delivering high-quality products but also optimizes production time and costs. This method proves ideal for large-scale manufacturing, ensuring consistency in product quality. Furthermore, with advancements in technology, injection molding is becoming increasingly versatile, capable of producing plastic products in a diverse range of colors and materials.
In conclusion, injection molding emerges as an exceptional choice for manufacturers seeking to streamline their plastic processing operations, guarantee product quality, and effectively cater to market demands.
For a more in-depth exploration of injection molding, refer to the following article:
- What is injection molding? How does it work?
- Injection molding troubleshooting.
1.2. Extrusion Molding
Extrusion molding, a technique with a rich history spanning centuries, has established itself as a cornerstone in the production of continuous-length plastic products with consistent cross-sectional profiles, such as pipes, rods, or sheets. This method hinges on the utilization of dies to shape the molten plastic into the desired form.

The extrusion molding process commences with feeding raw plastic into an extruder, where it is melted and subsequently forced through a die, shaping it into the specific profile required for the final product. Imagine squeezing toothpaste from a tube; the emerging shape mirrors the die's design. Extrusion molding finds widespread application in industries like plastics, metals, and food processing.

Diverse Applications of Extrusion Molding in Plastic Processing:
- Electronics: Crafting enclosures for cables and electronic components;
- Construction: Producing pipes, plastic rods for panels and windows;
- Automotive: Manufacturing plastic car components such as trim panels or fuel lines;
- Consumer Goods: Creating food wrapping films, straws, and various household items.
Extrusion molding excels in continuous production of uniform-shaped products, optimizing productivity. Compared to other plastic processing methods, extrusion boasts lower operational costs and material savings. This method not only delivers high production efficiency but also ensures the quality of plastic products. With its versatility and extensive applications, extrusion molding remains a frontrunner in the realm of modern plastic processing.
1.3. Injection Blow Molding
Injection blow molding, also known as extrusion blow molding, stands as a prevalent plastic processing technique widely employed in the fabrication of three-dimensional products with thin, hollow walls, such as bottles, flasks, containers, toys, and uniquely shaped plastic items.

The injection blow molding process commences with melting raw plastic and extruding it into a preform, which resembles a tube. This preform is then placed within a mold, and compressed air is injected into it, forcing the plastic to expand and conform to the mold's shape, creating the final product.

Diverse Applications of Injection Blow Molding in Plastic Processing:
- Medical: Producing pharmaceutical bottles, containers, and medical devices;
- Industrial: Manufacturing containers, tanks, and other storage solutions;
- Consumer Goods: Creating products like spray bottles, cosmetic containers, and toys;
- Packaging: Producing beverage bottles, chemical containers, and various food packaging.
Injection blow molding proves cost-effective for high volumes of identical products, and the required tooling is generally simpler compared to injection molding. This method not only delivers high-quality products but also optimizes production processes and reduces costs. With its versatility and extensive applications, blow molding stands as one of the most prevalent and efficient plastic processing techniques currently employed. However, it is important to note that this method may not always offer the same level of detail and precision as other techniques, and it is less suitable for solid, complex products.
1.4. Thermoforming
Thermoforming, a cutting-edge plastic processing technique, has gained widespread adoption in the production of intricate products demanding high accuracy. This method harnesses the heat-induced malleability of plastic to mold it into the desired form.

The thermoforming process commences with the heating of raw plastic to a molten state. This molten plastic is then forced into a mold and cooled to solidify, forming the final product.
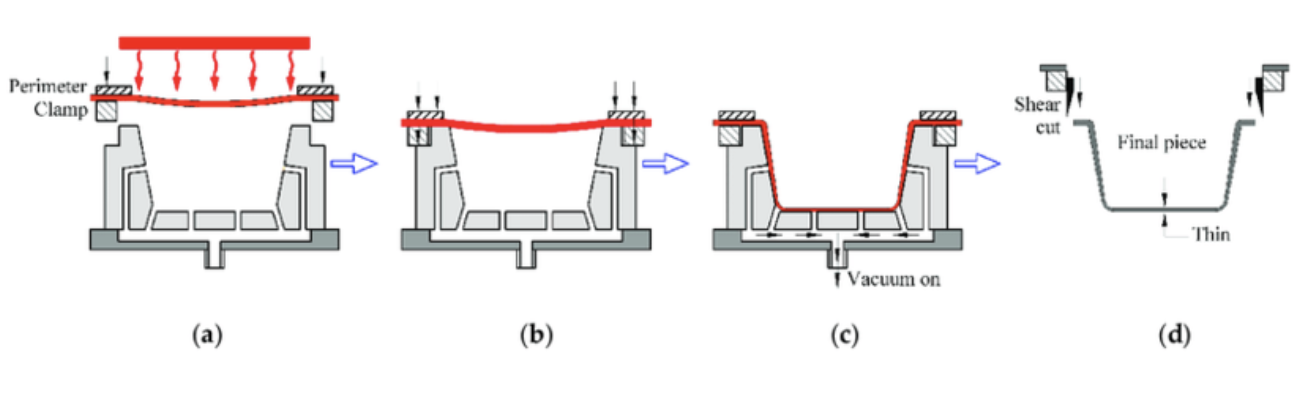
Diverse Applications of Thermoforming in Plastic Processing:
- Medical: Crafting medical materials such as medical implants and surgical instruments;
- Industrial: Producing industrial components and parts;
- Automotive: Manufacturing vehicle interior and exterior components;
- Household Goods: Creating household products like plumbing pipes, conduits, and domestic utensils.
Thermoforming not only delivers exceptional precision and durability to plastic products but also streamlines the production process. This method proves particularly suitable for applications demanding intricate details and consistent product quality.
2. Exploring Diverse Plastic Processing Techniques

The realm of plastic processing extends far beyond the widely recognized methods of injection molding, extrusion molding, injection blow molding, and thermoforming. A multitude of alternative techniques exist, each offering unique advantages and applications across a broad spectrum of industries. Embark on a journey to uncover some of these prevalent plastic processing methods:
2.1. Rotational Molding
In the realm of plastic processing, rotational molding stands as a unique technique, excelling in the creation of hollow, one-piece plastic products. Storage tanks, large containers, and children's toys are prime examples of its capabilities. The rotational molding process commences with the introduction of plastic powder or liquid plastic into a mold. Subsequently, the mold is rotated and heated, ensuring an even distribution of plastic and shaping it into the desired product form.
2.2. Casting
Casting, a versatile plastic processing technique, encompasses a range of methods that transform liquid plastic into desired shapes. Open casting involves pouring plastic into a mold, while pressure casting forces the molten plastic into the mold under pressure, enhancing product quality. Applications abound, from intricate figurines to durable machine parts.
2.3. Compression Molding
Compression molding, a traditional plastic processing method, finds its niche in the production of flat or simple-shaped plastic products such as sheets and panels. The compression molding process begins with placing raw plastic into a mold. Subsequently, the mold is closed, and the plastic is subjected to high pressure to form the final product.
2.4. Foamed Plastic Molding
Foamed plastic molding, a specialized technique, is often employed in the fabrication of insulation and soundproofing materials, resulting in lightweight yet durable products. The process commences with mixing plastic with foaming agents and then injecting it into a mold to create a product with a foamed structure.
2.5. Thermoset Resin Casting
Thermoset resin casting, a plastic processing technique utilizing thermoset resins, is commonly employed in the production of high-strength, heat-resistant plastic products, such as electronic components and industrial plastic items. The thermoset resin casting process begins by pouring the thermoset resin into a mold, followed by heating to cure the resin and solidify the product.
3. Conclusion
The realm of plastic processing is a diverse and dynamic landscape, encompassing a multitude of techniques that cater to a vast array of applications. From the widely recognized methods of injection molding, extrusion molding, blow molding, and thermoforming to specialized techniques like rotational molding, transfer molding, compression molding, foamed plastic molding, and thermoset resin casting, each method brings its unique strengths and advantages to the table.
The choice of plastic processing method hinges on the specific characteristics and requirements of the product at hand. Each method, with its unique capabilities, contributes to the vast tapestry of plastic processing, empowering innovation and shaping the world around us.
4. EuroPlas: Your Partner in Filler Masterbatch
EuroPlas, a frontrunner in the production of filler masterbatch, stands as a trusted partner. With years of expertise and cutting-edge technology, EuroPlas is committed to providing customers with effective filler masterbatch solutions that meet the most demanding industry standards.
At EuroPlas, innovation is at the heart of our endeavors. We continuously strive to refine and advance, to ensure our customers receive the highest quality products and services. Our team of dedicated professionals is committed to providing expert guidance and tailored solutions to address every plastic processing need.
Whether you seek consultation on the most suitable filler masterbatch for your product or require assistance in selecting the appropriate filler masterbatch, EuroPlas is here to support you. Reach out to our team of experts via email or phone, or leave your contact details through our online form, and experience the EuroPlas difference.