1. Different Ways To Distinguish Between PE And HDPE Film
PE and HDPE film play a crucial role in the packaging and construction industries. While PE film are known for their flexibility and softness, making them perfect for food packaging and plastic bags, HDPE film provide greater stiffness and durability, catering to high-strength applications. By understanding the distinct characteristics of these materials presented in this article, businesses can make informed decisions to enhance both product quality and economic efficiency.
Distinguishing between PE (Polyethylene) and HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) films is crucial in the packaging industry. Each film type has unique characteristics that affect their performance and applications. Here are several methods to help you easily recognize the differences between these two types of films.
1.1. Density And Structure
Density is a key differentiator between PE and HDPE film. PE typically has a lower density, which contributes to its flexibility and softness, making it suitable for applications like plastic bags and food packaging. In contrast, HDPE has a higher density, ranging from 930 to 970 kg/m³, which results in increased stiffness and durability, ideal for high-strength products such as bottles and piping.
The structure of these materials also varies significantly. PE can exist in various forms, including low-density and high-density versions, depending on its molecular arrangement and branching. HDPE, on the other hand, has a linear structure with minimal branching, leading to stronger intermolecular forces and higher tensile strength. This structural difference allows HDPE to maintain its rigidity and withstand heavier loads compared to other polyethylene types.

Read more: HDPE (High density polyethylene) - What is it? Properties & common uses
1.2. Transparency And Clarity
Transparency of PE is generally higher than that of HDPE film, allowing light to pass through more easily. This makes PE a popular choice for applications requiring aesthetic appeal, such as food packaging and plastic bags, where visibility of the product inside is important. PE films can be clear or opaque, depending on the application requirements.
In contrast, HDPE typically has lower transparency, with a more opaque surface and a cloudy appearance. This makes HDPE an ideal choice for products that need greater strength and protection, such as plastic bottles and piping. Although HDPE is not as transparent as PE, it offers better resistance to environmental impacts, such as UV rays and chemicals, helping to protect the product inside.

1.3. Strength And Durability
HDPE has a tensile strength of approximately 38 MPa, while regular PE has a tensile strength around 21 MPa. This difference in strength is largely due to HDPE's linear molecular structure, which allows for stronger intermolecular forces, resulting in greater overall strength.
In terms of durability, HDPE film exhibits superior resistance to impacts and environmental factors compared to PE film. HDPE can withstand higher temperatures (up to 120°C for short periods) and offers better resistance to chemicals and UV radiation. This makes HDPE a preferred choice for applications requiring long-lasting performance, such as packaging, piping, and construction materials.
.jpg)
1.4. Chemical Composition
HDPE is a high-density, linear polymer produced by polymerizing ethylene into long chains with minimal branching. This linear structure allows HDPE molecules to pack tightly, resulting in high strength and durability, with a general chemical formula of (C2H4)n.
In contrast, PE is a low-density polymer characterized by a branched structure. The branching occurs during polymerization, creating side chains off the main backbone, which results in a less dense material with lower tensile strength. This branching weakens intermolecular forces, making PE more flexible but less strong than HDPE.
Read more: HDPE Plastic Recycling - Its Possibility and Benefits
1.5. Properties
Below is a comparison table of the properties of Polyethylene (PE) and HDPE . This table provides detailed information about density, hardness, tensile strength, elongation, modulus of elasticity, and many other properties, helping you better understand the differences between these two types of materials.
| Property |
HDPE Value (metric) |
PE Value (metric) |
| Hardness, Shore D |
55 - 69 |
42 - 56 |
| Density |
0.933 - 1.27 g/cm³ |
0.915 - 0.96 g/cm³ |
| Tensile Strength, Ultimate |
15.2 - 45 MPa |
8.96 - 54 MPa |
| Elongation at Break |
3 - 1900% |
226 - 650% |
| Tensile Strength, Yield |
2.69 - 200 MPa |
7.6 - 14 MPa |
| Modulus of Elasticity |
0.483 - 1.45 MPa |
0.152 - 0.29 MPa |
| Dielectric Constant |
2.0 - 2.6 |
2.27 - 2.29 |
| Flexural Modulus |
0.5 - 4.83 MPa |
0.07 - 0.276 MPa |
| Flexural Yield Strength |
16.5 - 91 MPa |
14 - 21 MPa |
| Melting Point |
120 - 130 °C |
102 - 113 °C |
| Max Service Temperature |
80 - 120 °C |
80 - 100 °C |
1.6. Cost Difference
HDPE is an affordable material produced in large quantities, typically priced around $8.50 per kg for virgin material and $2.50 per kg for recycled versions. In contrast, Polyethylene (PE) is generally cheaper, with granules selling for approximately $0.90 to $1.10 per kg. Recycled clear PE is available at a similar or slightly lower cost and is often blended with virgin material in a ratio of 10 - 20%, providing some cost savings per kg.
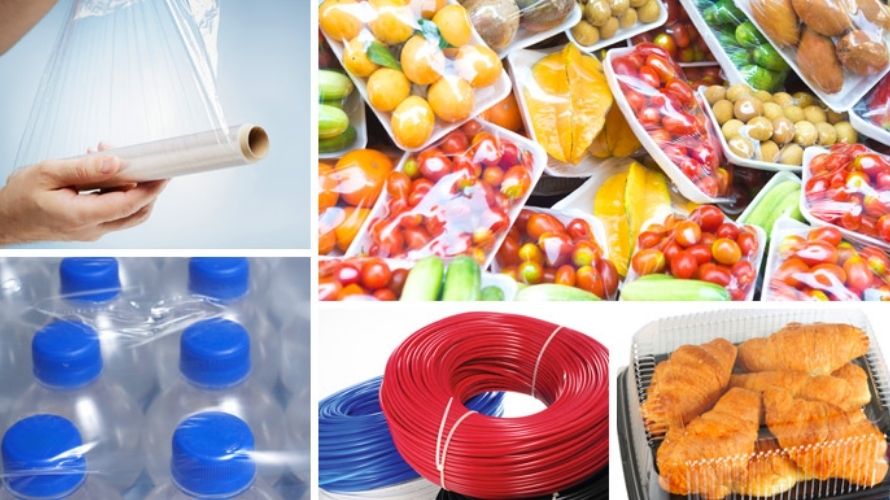
2. Common Applications Of PE And HDPE Film
HDPE Applications:
- Packaging: Commonly used for crates, trays, milk bottles, caps for PET bottles, fuel cans, drums, and industrial fluid containers.
- Consumer Goods: Includes trash bins, garden equipment, furniture, storage bins, children's toys, and playground equipment.
- Fibers and Textiles: Due to its high tensile strength, HDPE is utilized in agricultural applications like ropes, fishing nets, and sports goal nets.
- Plumbing: Employed in pipes and fittings for LPG gas supply, water supply, sewage handling, drainage, and septic tanks.
- Automotive: Used for fuel tanks, cable insulation, cable ties, and body-mounted clips.
Polyethylene Applications:
- Packaging: Widely used for pharmaceutical, household chemical, and food packaging, including squeeze bottles, caps, and tamper-evident closures.
- Pipes and Fittings: Suitable for water pipes, garden hoses, and food production piping due to its plasticity and low risk of tainting.
- Various Goods: Found in kitchenware, toys, agricultural films, wiring sheaths, and insulators.

Read more: Common problems during PE film blowing process
3. Conclusion
In summary, HDPE and PE are two distinct plastic materials with notable differences. HDPE film is denser and more durable, offering superior resistance to wear, tear, and chemicals. It is commonly utilized in applications such as pipes, liners, sheets, and films. Conversely, PE is primarily used for shopping bags, packaging films, and agricultural films. Both materials are recyclable, but HDPE has a higher recycling rate and is more frequently recycled compared to PE.
4. About EuroPlas’ PE Products
If you are looking for a quality source to produce PE films,
EuroPlas is an excellent choice. EuroPlas is the world's leading company in the production and supply of filler masterbatch. With 15 years of development, EuroPlas takes pride in offering a cost-effective solution for plastic manufacturers. Here are the key features of EuroPlas's
PE filler masterbatch:
- Cost savings in production: Helps reduce overall costs in the manufacturing process.
- Improvement of various product properties: Includes brightness, opacity, and shrinkage reduction.
- Energy savings: Thanks to the excellent thermal transmission capability of CaCO3.
- Increased stability in the manufacturing process: Ensures a smoother and more efficient production process.
EuroPlas is committed to providing high-quality products and optimal solutions for your needs.

Let EuroPlas accompany you on your journey to find the perfect products! If you want to explore our high-quality solutions or have any questions, don’t hesitate to visit the Contact Us page. We are always ready to assist you and provide the necessary information. Click the button now to start this amazing experience!