Polyethylene (PE) is a key material in modern manufacturing and industrial applications. Known for its versatility and cost-effectiveness, PE is one of the most widely used plastics, appearing in a range of everyday items and industrial products. However, understanding the different types of polyethylene and their specific melting points is essential for optimizing production processes and ensuring product performance.
This guide will explore the melting point of PE, specifically LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene), HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene), LLDPE (Linear Low-Density Polyethylene), UHMWPE (Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene), and MDPE (Medium-Density Polyethylene). We will discuss their unique melting points, the importance of these temperatures in manufacturing, and how to choose the right PE type for your needs. Additionally, we will highlight how EuroPlas’ PE products and additives can improve your production efficiency.
For more details, you can read our article on the Temperature ranges for different plastic materials.
1. Why Is The Melting Point Of PE So Important?
The melting point of PE is crucial for several reasons, impacting both manufacturing processes and the final product performance:
- Manufacturing Process: The melting point determines the temperature at which different types of polyethylene can be processed. Accurate control of this temperature is essential for processes like extrusion, injection molding, and blow molding. Operating at the correct temperature ensures that the polymer, whether it is LDPE, HDPE, LLDPE, UHMWPE, or MDPE, flows properly, fills molds efficiently, and cools correctly, resulting in high-quality products.
- Material Properties: The melting point of PE affects the physical properties of the final product. Higher melting points in types of polyethylene generally correspond to increased strength, stiffness, and resistance to deformation under heat. For applications where durability and performance are critical, selecting the right type of polyethylene with an appropriate melting point is essential for ensuring that the product meets its performance requirements.
- Application Suitability: Different applications require specific melting point of PE to ensure optimal performance. For example, packaging materials often need to be processed at lower temperatures for efficiency, while structural components require higher melting points for added strength and durability. Understanding the melting points of various types of polyethylene helps in selecting the right type for each application.
- Cost Efficiency: Optimizing the processing temperature of different types of polyethylene can lead to cost savings in manufacturing. Efficiently controlling the melting temperature reduces energy consumption and improves production efficiency. This can lower production costs and enhance the overall economic viability of the manufacturing process.
2. What Is The Melting Point Of PE?
The melting point of PE is a critical property that influences its processing and end-use applications. Understanding the melting points of various types of polyethylene is essential for selecting the appropriate material for different applications. Here’s a closer look at the melting points for several key types of polyethylene:
- LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene): LDPE typically melts at temperatures ranging from 105-115°C (221-239°F). The lower melting point of LDPE is attributed to its highly branched molecular structure, which creates a less dense material with a lower thermal threshold. This makes LDPE easy to process at lower temperatures, which is advantageous for manufacturing applications that require softer and more flexible materials. LDPE's lower melting point is a significant factor when considering the types of polyethylene for applications needing high flexibility.
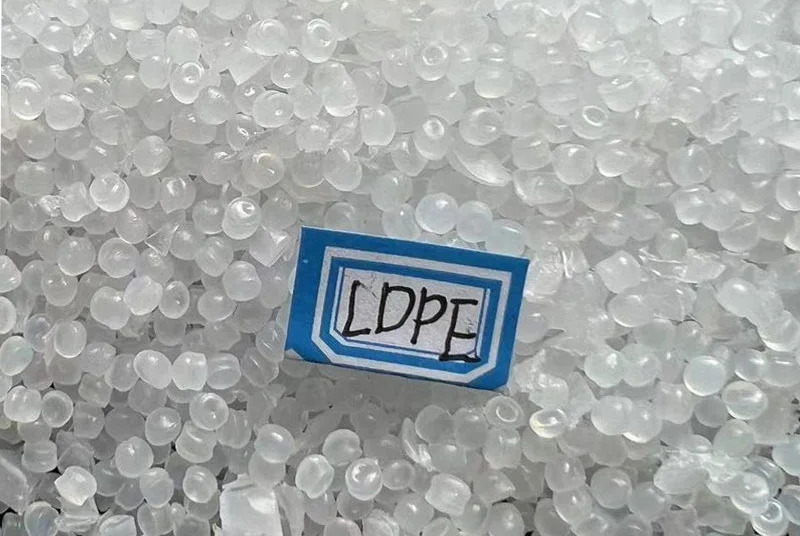

LDPE typically melts at temperatures ranging from 105-115°C (221-239°F).
- HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene): HDPE has a higher melting point, generally between 130-140°C (266-284°F). The linear and closely packed polymer chains in HDPE contribute to its higher melting point, allowing it to withstand more demanding conditions and maintain its strength and rigidity. This higher melting point is beneficial for applications that require materials to retain their properties under heat and stress. When evaluating types of polyethylene for durability and structural integrity, HDPE’s higher melting point is a crucial consideration.

HDPE melting point is generally between 130-140°C (266-284°F).
- LLDPE (Linear Low-Density Polyethylene): The melting point of LLDPE ranges from 120-130°C (248-266°F). This melting point is higher than that of LDPE but lower than HDPE, reflecting LLDPE’s balance between flexibility and strength. The linear structure with short branches provides a good compromise, making LLDPE suitable for a wide range of applications where both flexibility and strength are needed. Understanding LLDPE’s melting point helps in selecting the right types of polyethylene for applications that require a balance of these properties.
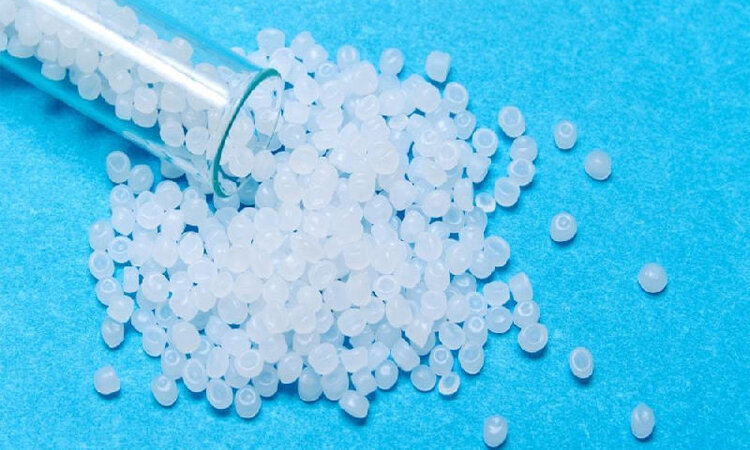

The melting point of LLDPE ranges from 120-130°C (248-266°F).
- UHMWPE (Ultra-High-Molecular-Weight Polyethylene): UHMWPE exhibits a high melting point, approximately 130-136°C (266-277°F). The high melting point is a result of its long polymer chains and high molecular weight, which contribute to its superior thermal stability. This makes UHMWPE suitable for high-performance applications where maintaining material properties under extreme conditions is essential. UHMWPE’s melting point is a key factor when choosing types of polyethylene for high-strength and high-performance needs.
UHMWPE exhibits a high melting point, approximately 130-136°C (266-277°F)
- MDPE (Medium-Density Polyethylene): MDPE melts at around 120-130°C (248-266°F), similar to LLDPE. The intermediate melting point of MDPE reflects its position between LDPE and HDPE in terms of density and strength, providing a versatile option for various applications. MDPE’s melting point plays a role in determining its suitability among the types of polyethylene for applications requiring a balance between flexibility and strength.
By understanding the melting points of these different types of polyethylene, manufacturers can better choose the material that meets their specific needs and conditions. This knowledge helps in optimizing the processing and performance of polyethylene-based products.
3. Conclusion
Understanding the melting point of PE is vital for optimizing production processes and ensuring product performance. Each type of polyethylene, from LDPE to UHMWPE, offers unique properties that cater to specific needs. By comprehending these properties and their implications, manufacturers can make informed decisions, achieve better production outcomes, and improve the quality of their products.
Polyethylene’s versatility and wide range of applications make it a crucial material in modern industry. Knowing the melting point of PE and their effects on different types of polyethylene allows manufacturers to leverage polyethylene’s full potential, ensuring that each application benefits from the material’s optimal characteristics.
4. About EuroPlas’ PE Products
EuroPlas is a leading provider of high-quality plastic additives, offering a range of products designed to enhance the performance of polyethylene. Our product lineup includes:
- PE Filler Masterbatch: Made from a combination of PE resin and CaCO3, our PE filler masterbatch helps reduce production costs while improving impact resistance, heat resistance, surface hardness, strength endurance, and ductility. It is ideal for use in various applications, including injection molding, blown film, and food packaging. The addition of CaCO3 and other additives helps improve the overall performance of the finished products, making them more cost-effective and durable.
- Specialty Additives: EuroPlas offers a diverse range of additives to meet specific needs, including anti-odor, flame retardant, anti-aging, processing aids, anti-static, UV stabilizers, and clarity enhancers. These additives help tailor the properties of polyethylene to suit various applications, improving functionality and performance.
With 18 years of experience in the industry, EuroPlas is committed to providing high-quality and cost-effective solutions to plastic manufacturers worldwide. Our expertise ensures that you receive the best products and support for optimizing your production processes. For more information about our PE filler masterbatch and other additives, visit our blog and stay updated with the latest news and advancements in plastic technology.
Contact EuroPlas today to discover how our products can enhance your manufacturing processes and help you achieve your production goals.