Nylon 66, a versatile synthetic polymer, has gained immense popularity in various industries due to its exceptional properties and wide range of applications. As one of the most commonly used engineering plastics, Nylon 6:6 has revolutionized numerous fields, offering unparalleled strength, durability, and versatility. In this article, EuroPlas will delve into the world of Nylon 6.6, exploring its composition, properties, notable benefits, and diverse applications.
.jpg)
Nylon 66: What is it? Properties, benefits and applications
1. What is nylon 66?
Nylon 66, also known as nylon 6-6, nylon 6/6, nylon 6.6, or nylon 6:6, is a type of nylon polyamide (polyamide 6 6) or nylon. It is one of the most commonly used materials in the textile and plastic industries, alongside nylon 6.
Nylon 6:6 derives its name from the two monomers it comprises, namely hexamethylenediamine and adipic acid, each containing 6 carbon atoms. Apart from its outstanding physical properties, nylon 6-6 is favored due to the low cost of its precursors.
The synthesis of nylon 66 involves the polycondensation of hexamethylenediamine and adipic acid. Equal amounts of these two monomers are combined in water. In the original method, the resulting salt, composed of ammonium and carboxylate, is isolated. And then heated, either in batches or continuously, to initiate polycondensation.
The removal of water promotes polymerization by facilitating the formation of amide bonds between the acid and amine groups. This polymerization can occur in a concentrated aqueous mixture containing hexamethylenediamine and adipic acid.
At this stage, the resulting product can be extruded and granulated or directly spun into fibers through a process called extrusion. The polymer is forced through a spinneret, which is a small metal plate with fine holes, and then cooled to form filaments.
.jpg)
What is nylon 66?
2. Nylon 66 material properties
Nylon 6:6 possesses several notable material properties that make it highly desirable in many applications. These properties of nylon 6/6 material properties include:
2.1. Nylon 6 6 structure
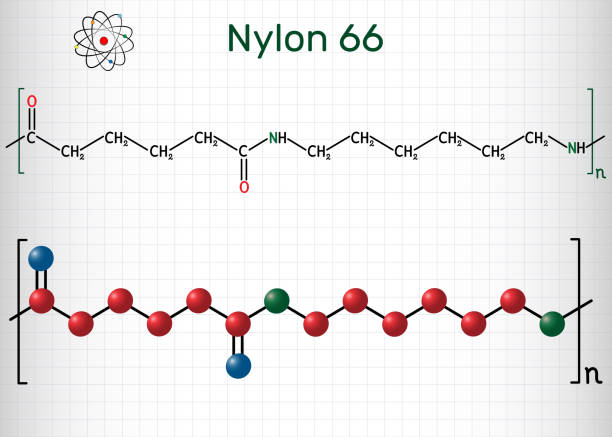
Nylon 6.6 is formed through the condensation polymerization of hexamethylenediamine and adipic acid. This results in a repeating unit composed of six carbon atoms (hexamethylene) linked by amide groups. The chemical formula for nylon 66 is (NH-(CH2)6-NH-CO-(CH2)4-CO-)n, where n represents the number of repeating units in the polymer chain.
Chemical Structure
- Monomer 1: Hexamethylenediamine (C₆H₁₆N₂)
- Monomer 2: Adipic acid (C₆H₁₀O₄)
Condensation Process
Nylon 6,6 is formed through the condensation reaction between hexamethylenediamine and adipic acid, with the removal of a water molecule at each bond.
Molecular Structure
- Straight Chain: Nylon 6,6 has a straight chain structure with amide (-CONH-) bonds connecting the methylene (-CH₂-) groups together.
- Hydrogen Bonding: The amide groups in Nylon 6,6 are capable of forming hydrogen bonds between the polymer chains, which enhances mechanical properties such as strength and heat resistance.
Characteristics of Nylon 6,6
- High mechanical strength: Nylon 6,6 has good tensile strength and abrasion resistance, commonly used in applications such as textile fibers, carpets, cables, and engineering components.
- Heat resistance: Nylon 6,6 has high temperature resistance, with a melting point of about 265°C.
- Chemical resistance: Nylon 6,6 is resistant to a wide range of chemicals, including oils and organic solvents, however, it can be attacked by strong acids and alkalis.
2.2. Nylon 6 6 molecular weight
The molecular weight of nylon 6:6 can vary depending on the manufacturing process and desired nylon 66 properties. On average, the molecular weight of nylon 6:6 ranges from 20,000 to 50,000 grams per mole. This relatively high molecular weight contributes to the material's strength and durability.
The molecular weight of 66 nylon is an important factor that affects its mechanical and thermal properties. Higher molecular weight generally results in increased tensile strength, impact resistance, and heat resistance. It also affects other characteristics of nylon 6:6, such as crystallinity, melting point, and viscosity.
The molecular weight of nylon 6:6 can vary depending on the manufacturing process and desired nylon 66 properties.
2.3. Nylon 66 density
The density of nylon 6:6 is typically around 1.14 to 1.15 grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³). This makes it a moderately dense material. Nylon 6/6 density contributes to its lightweight nature, which is advantageous in applications where weight reduction is important, such as in the automotive and aerospace industries.
2.4. Nylon 66 melting point
Nylon 6-6 has a relatively high melting point compared to other thermoplastics. The melting point of nylon 6:6 typically ranges from 255 to 265 degrees Celsius (491 to 509 degrees Fahrenheit). This high melting point enables nylon 66 to withstand elevated temperatures without losing its structural integrity. It also allows for various processing techniques, including injection molding and extrusion.
The combination of moderate density and high melting point makes nylon 6/6 suitable for a wide range of applications. Its density provides strength and durability while maintaining a lightweight profile. The high nylon 6/6 melting point ensures stability and resistance to deformation under high-temperature conditions.
.jpg)
Nylon 66 material properties
3. Advantages of using nylon 66
Nylon 6-6, a type of polyamide (polyamide 66), is a versatile and widely used synthetic material with various applications across industries. Its unique nylon-6 6 properties make it an advantageous choice for numerous purposes.
- Strength and Durability: Nylon 6:6 exhibits excellent tensile strength and durability, making it ideal for demanding applications. It can withstand high mechanical stress, making it suitable for use in heavy-duty components, automotive parts, and industrial machinery.
- Heat Resistance: Nylon 6:6 has exceptional heat resistance properties, allowing it to maintain its structural integrity at elevated temperatures. This feature makes it a preferred choice in applications that involve exposure to high temperatures, such as engine parts, electrical connectors, and cookware handles.
- Chemical Resistance: Nylon 6:6 possesses excellent resistance to various chemicals, including oils, greases, fuels, and solvents. This makes it suitable for use in industries where exposure to corrosive substances is common, such as automotives, chemical processing, and oil and gas industries.
- Moisture Absorption: Nylon 6:6 has a lower moisture absorption rate compared to other nylon materials. This characteristic ensures that the material retains its dimensional stability even in high-humidity environments.
Consequently, Nylon 66 finds applications in outdoor equipment, sports gear, and components exposed to moisture.
- Wear Resistance: Nylon 6:6 exhibits excellent wear resistance properties, enabling it to withstand friction and abrasion. This makes it suitable for applications involving sliding or rotating components, such as bearings, gears, and conveyor belts.
- Electrical Insulation: Nylon 6:6 possesses good electrical insulation properties, making it suitable for electrical and electronic applications. It is commonly used in wire insulation, connectors, and circuit board components.
- Ease of Processing: Nylon 6:6 can be easily processed using techniques like injection molding, extrusion, and blow molding. Its versatility in processing methods enables manufacturers to create complex shapes and designs, resulting in cost-effective production.
- Lightweight: Nylon 6:6 offers a favorable strength-to-weight ratio, making it an attractive option in industries that require lightweight materials without compromising structural integrity. It finds applications in automotive components, consumer goods, and aerospace industries.
.jpg)
Advantages of using nylon 66
4. Common applications of nylon 66
Nylon 6:6 has exceptional strength, durability, and resistance to wear and tear, making it a popular choice for a wide range of products.
- Textiles: 6 6 nylon is extensively used in the textile industry to create clothing, sportswear, and outerwear fabrics. It's high tensile strength and abrasion resistance make it ideal for applications that require durability, such as backpacks, luggage, and heavy-duty workwear.
- Automotive Industry: Nylon 66 is widely used for various components in the automotive sector. It is commonly found in engine components, fuel systems, electrical connectors, and under-the-hood parts due to its excellent resistance to heat, chemicals, and mechanical stress.
- Electrical and Electronics: The industry relies on Nylon 6/6 for its insulating properties and high dielectric strength. It is commonly used in wire and cable insulation, electrical connectors, circuit breakers, and electronic housings.
- Consumer Goods: 6 6 nylon is found in a plethora of consumer products. It is commonly used to manufacture household items such as toothbrushes, combs, brushes, zippers, buttons, and fasteners. Its lightweight nature and chemical resistance make it suitable for applications in the kitchen and bathroom.
- Industrial Applications: 66 nylon is extensively employed in various industrial applications. It is used in the production of conveyor belts, hoses, seals, gaskets, and bearings due to its excellent mechanical properties and abrasion resistance. Nylon 6/6 is also utilized to manufacture industrial machinery components and tools.
- Sports and Recreation: Nylon 66's strength and durability make it ideal for sports and recreational equipment. It is commonly used to produce tennis racket strings, fishing lines, camping gear, hiking backpacks, and protective gear such as helmets and knee pads.
- Medical Field: Nylon 6-6 is employed in medical devices and equipment due to its biocompatibility and resistance to sterilization processes. It is used in surgical sutures, catheters, dental floss, and orthopedic implants.
.jpg)
Common applications of nylon 66
5. Introduction of EuroPlas PA66 (nylon66) engineering plastic compound
PA66 Compound - EuroPlas PA66 (Nylon 66) engineering plastic compound refers to a mixture or blend of Polyamide 66 (PA66) resin with various additives and reinforcing agents to enhance its properties and processability. PA66 is a thermoplastic material known for its high strength, durability, and excellent mechanical properties.
The engineering plastic PA66 compound typically includes additives such as plasticizers, stabilizers, reinforcements, flame retardants, lubricants, and reinforcing agents. These additives are mixed with the PA66 resin during the compounding process to achieve specific performance characteristics, such as improved impact resistance, heat resistance, chemical resistance, dimensional stability, and reduced friction.

PA66 & PA6 Glass Fiber Compound - a product of EuroPlas
One of the significant advantages of engineering plastic PA66 compound is its exceptional mechanical strength. It exhibits excellent tensile and flexural strength, making it suitable for applications requiring structural integrity and load-bearing capacity. This strength allows PA66 compounds to withstand heavy loads, impacts, and vibrations, making them ideal for automotive components, industrial machinery, and structural parts.
Additionally, the engineering plastic PA66 compound possesses excellent heat resistance. It can withstand high temperatures without significant deformation, making it suitable for applications exposed to elevated temperatures, such as engine components and electrical enclosures.
Due to its exceptional properties, engineering plastic PA66 compound finds extensive applications across multiple industries. In the automotive sector, it is used for manufacturing engine components, fuel system parts, electrical connectors, and various interior and exterior components.
In electrical and electronics, it is employed for switches, connectors, and insulating parts. Industrial machinery utilizes PA66 compounds for gears, bearings, rollers, and conveyor parts. Additionally, consumer goods such as sports equipment, appliances, and power tools benefit from the strength and durability of the PA66 compound.
Engineering plastic PA66 compound is a highly versatile material that offers exceptional mechanical strength, heat resistance, chemical resistance, dimensional stability, and ease of processing. Its wide range of applications across industries highlights its suitability for demanding environments and the manufacturing of high-performance components. As technology continues to advance, the demand for PA66 compounds is expected to grow, driven by the need for reliable, durable, and innovative solutions in various sectors.
Read more about the products here: PA66 & PA6 Glass Fiber Compound
If you would like to know more details about our filler masterbatch product in particular, as well as our other masterbatches, please fill out this form or contact us via email/phone number. We are happy to answer all your product questions and concerns!