
PET vs HDPE uses
The utilization of High Density Polyethylene (HDPE) and Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) plastic materials in manufacturing fields has long been no stranger. Especially in the industries of health care, food packaging, agricultural packaging, freight transportation, etc., PET vs HDPE are always top considerations. Although sharing the same advantages of flexibility, compact design, cost efficiency, and remarkable durability, PET vs HDPE plastic still has its own characteristics and performance. Analyzing and understanding the properties of PET vs HDPE is very important to optimize product performance and investment costs. The shares below will provide some comparisons between PET vs HDPE to assist readers in choosing materials suitable for production needs.
1. What is PET plastic?

Bottles made of PET plastic
PET plastic's full chemical name is polyethylene terephthalate. One of the most commonly used plastics in many different industries. PET has transparent properties and belongs to the most popular thermoplastic group in polyester. To obtain PET, people use ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid to combine together. This compound forms polymer chains that are then cut into small plastic beads. PET plastic pellets are then heated and molded into shapes according to production needs. The melting point of PET plastic is 145°F. PET plastic can be recycled but requires careful cleaning.
In addition, PET possesses excellent technical parameters. Typically, PET has high durability, good resistance to mechanical damage, and is very safe for consumers' health because it does not contain phthalate and BPA. According to FDA certification, PET plastic is completely safe to use to make products that come into direct contact with food and drinks such as water bottles, food packaging, and food containers. Besides its top position in the food packaging field, PET plastic is also widely used in the production of clothing fibers, chemical bottles, and product protective films.
Read more: What is Polyethylene terephthalate (PET)?
2. What is HDPE plastic?

Bottles made of HDPE plastic
HDPE plastic is one of the types of plastic that is safe for humans and has very diverse uses. To create HDPE, people collect and heat ethane (from ethylene gas). Ethane is mixed with benzene, which is exposed directly to UV radiation. After this chemical reaction, the compound is heat treated to remove oxygen and molded into sheets. At this point, we obtain HDPE, known as high-density polyethylene plastic. HDPE is a thermoplastic with a melting point higher than many other plastics with an index of up to 160°F. However, when melted, HDPE is very easy to bend, mold or re-shape and will be very sturdy when cooled.
Besides, HDPE plastic also possesses extremely valuable properties such as high durability, impact resistance, water resistance, and high antibacterial properties. The moisture absorption rate of HDPE is very low, they can resist organic solvents such as salts, bases, acids, and some other corrosive chemicals. Because of its durability and lack of damage, HDPE is often used in the production of plastic containers, agricultural packaging, plastic containers for chemicals, etc. Thanks to its antimicrobial properties, HDPE is also very safe for human health. Specifically, it is used to produce water bottles, water bottles, and food containers.
Read more: HDPE (High density polyethylene) - What is it? Properties & common uses
3. Physical properties comparison
3.1 PET physical properties

PET plastic beads
-
Density : 1.3 – 1.4 g/cm3
- Gamma Radiation Resistance: Good
- UV Light Resistance: Fair
- Water Absorption 24 hours: 0.1%- 0.2%
- HDT @0.46 Mpa (67 psi): 75°C – 115°C
- HDT @1.8 Mpa (264 psi): 65°C – 80°C
- Coefficient of Linear Thermal Expansion x 10-5: 6 – 8°C
- Strength at Break (Tensile): 45 – 70MPa
3.2 HDPE physical properties

HDPE plastic beads
-
Density: 0.94 – 0.97 g/cm3
-
Gamma Radiation Resistance: Fair
-
UV Light Resistance: Poor
-
Water Absorption 24 hours: 0.005%- 0.01%
-
HDT @0.46 Mpa (67 psi): 60°C – 90°C
-
HDT @1.8 Mpa (264 psi): 45°C – 60°C
-
Coefficient of Linear Thermal Expansion x 10-5: 6 – 11°C
-
Strength at Break (Tensile): 25 – 45MPa
4. Temperature range comparison: PET vs HDPE

PET melting point is 145°F
Both PET and HDPE have quite good heat resistance, but HDPE has a higher melting point of 160°F and PET is 145°F. In terms of cold resistance, HDPE has a lower cold brittle temperature than PET at -50°F and PET at -40°F.
In general, PET vs HDPE does not have a big difference in temperature range and are both considered good temperature resistant materials. However, depending on production needs and usage environment, investors can consider the type of plastic suitable for temperature and climate conditions.
5. Resistance to stress cracking comparison: PET vs HDPE

Barrels made of HDPE plastic
Environmental stress is one of the common causes of internal and external cracks in plastic materials caused by tensile stress. This may affect the products they contain. Considering HDPE plastic, they often crack due to chemical attacks on the semi-crystalline plastic material. For PET, the molecular density of PET is higher than HDPE, so it somewhat improves its resistance to cracking from environmental stress.
6. Recyclability comparison: PET vs HDPE
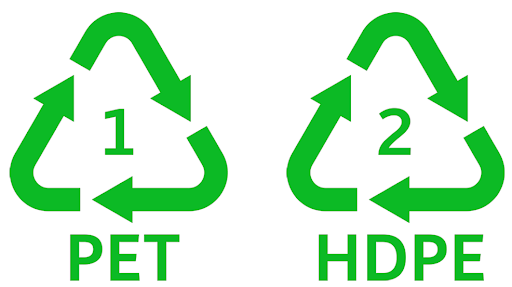
PET vs HDPE Recyclability comparison
As mentioned above, PET vs HDPE both belong to the group of recyclable thermoplastics. However, each type will have a different recycling process to facilitate the decomposition and reconstitution of elements because they have different structures. For PET plastic, the recyclability rating is 1. This means that PET plastic indicates that PET's recyclability is not very good. Consumers should thoroughly clean PET plastic before intending to recycle it and reuse it only once before disposing of it. Regarding HDPE plastic, it has a recycling rating of 2. This means that HDPE plastic has a safer recycling level than PET with about 10 times more recycling before disposal.
7. Conclusion

HDPE bottle and PET bottle
In general, PET and HDPE are both plastics with diverse applications. Besides, PET vs HDPE is also a material that brings economic benefits to investors because the price is cheaper than other metal materials. Depending on the purpose, environment, usage needs and business plan, investors can consider the properties of PET and HDPE to choose the appropriate material for their project. For example, if you need a material for food wrap you can choose PET. If you need to produce drums or barrels, you can consider HDPE. Read more useful articles at EuroPlas to update more useful information about material selection trends on the market today!