In the intricate tapestry of modern manufacturing, plastic pellets stand as the unsung heroes, transitioning from raw materials to the diverse array of products that fill our daily lives. Originating from refined hydrocarbons like crude oil and natural gas, these tiny yet powerful pellets undergo a metamorphosis through polymerization and pelletization processes. As the backbone of plastic production, they embark on a journey enhanced by additives and masterbatch compounds, shaping the future of materials engineering.
From injection molding to extrusion, the manufacturing phase breathes life into these pellets, transforming them into ubiquitous items - packaging materials, consumer goods, automotive components, and more. Our comprehensive blog will be an exploration of this dynamic journey, delving into the nuances that make plastic pellets a vital force in the contemporary world of production and consumption. Let’s get started!
1. Overview of plastic pellets

1.1. Definition
Plastic pellets, also known as resin pellets, represent the foundational building blocks in the intricate process of plastic production. These small, cylindrical entities serve as the raw material that undergoes various transformations, ultimately culminating in an extensive array of plastic products.
The journey from plastic pellets to finished goods involves a series of meticulous steps, including melting, molding, and shaping, each contributing to the unique properties of the end product.
1.2. Components
The composition of plastic pellets is primarily centered around polymers, long chains of repeating molecular units that characterize the plastic's fundamental nature. The choice of polymer significantly influences the physical and chemical attributes of the resulting plastic product.
Common polymers found in plastic pellets encompass polyethylene, polypropylene, polyvinyl chloride (PVC), and polystyrene. In addition to polymers, various additives—such as stabilizers, colorants, and reinforcing agents—might be introduced to the pellets, further refining and enhancing specific properties.
Read more: https://europlas.com.vn/blog/phu-gia-nhua-pvc-thong-tin-huu-ich-can-biet
1.3. Benefits of using plastic pellets
a. Versatility
One of the key advantages of utilizing plastic pellets lies in their exceptional versatility. Manufacturers can tailor these pellets to meet precise specifications, enabling the production of an extensive range of products with diverse shapes, sizes, and functionalities. This adaptability positions plastic pellets as a fundamental component in industries spanning packaging, automotive, medical, and construction.
b. Cost-effectiveness
The production of plastic pellets is an inherently cost-effective process. The raw materials required for their creation are often abundant and economically accessible, contributing to the widespread adoption of plastic pellets in the manufacturing sector. This cost efficiency is a driving force behind the pivotal role plastic pellets play in the global plastics industry.
c. Lightweight and durable
Plastic pellets offer a remarkable combination of being lightweight yet exceptionally durable. This characteristic is particularly advantageous in industries where weight considerations are critical, such as transportation. Furthermore, the durability of plastic products originating from pellets ensures an extended lifespan and resistance to degradation, further solidifying their utility in various applications.
d. Recycling potential
A crucial aspect of the plastic pellet lifecycle is its recyclability. Many plastic pellets are recyclable, contributing significantly to sustainability efforts in waste management. The recycling of plastic pellets into new products minimizes the environmental impact of plastic waste, fostering a more circular economy and aligning with contemporary efforts to address environmental concerns.
e. Customizable properties
Plastic pellets offer a canvas for customization, allowing manufacturers to imbue the end products with specific properties. Through the incorporation of additives such as stabilizers, colorants, and reinforcing agents, the physical, chemical, and aesthetic attributes of the plastic can be finely tuned. This adaptability ensures that plastic pellets can meet the exacting requirements of diverse industries and applications.
f. Longevity and resistance
Products derived from plastic pellets often boast an extended lifespan and resistance to degradation. This durability factor contributes to the longevity of plastic goods, reducing the need for frequent replacements. In applications ranging from consumer goods to industrial components, the robust nature of plastic products derived from pellets enhances their overall value proposition.
2. The journey of plastic pellets: from raw materials to products
.png)
The intricate journey of plastic pellets from their origins as raw materials to the creation of diverse, everyday products is a captivating process that traverses multiple stages. This comprehensive evolution, encompassing various chemical and manufacturing processes, plays a pivotal role in determining the characteristics and applications of the final plastic goods.
2.1. Raw material selection
The journey initiates with a critical decision: the selection of raw materials. The choice of polymers is paramount and depends on the desired attributes of the end product. Whether it is the malleability of polyethylene, the robustness of polypropylene, or the versatility of PVC, this initial selection sets the foundation for subsequent manufacturing steps.
2.2. Polymerization
Following raw material selection, the polymerization process unfolds. This entails chemically bonding monomers to form extensive chains, creating the polymers that will constitute the basis of the plastic. The resulting polymers are then meticulously processed into small, uniform pellets, setting the stage for the subsequent manufacturing phases.
2.3. Extrusion or injection molding
The pivotal stage in the journey of plastic pellets involves the choice between extrusion and injection molding processes. Each method brings its unique advantages, catering to specific product requirements.
Injection molding pellets take center stage in a precise and efficient manufacturing process. These pellets, precisely melted and injected into molds, allow for the creation of intricate and custom-designed plastic products. The injection molding method is ideal for producing high-volume, uniform items with complex geometries, ensuring a seamless and cost-effective production cycle. It is a go-to choice for industries seeking precision and consistency in their final products.
On the other hand, extrusion grade pellets undergo a slightly different journey. In the extrusion process, these pellets are melted and shaped into a continuous form, which is then cooled and cut into the desired length. This method is particularly advantageous for products that require a consistent cross-sectional profile, such as pipes, tubing, and certain types of packaging materials. Extrusion grade pellets offer versatility in creating long, uniform shapes with efficiency.
2.4. Shaping and cooling
Post-molding, the plastic products undergo shaping and cooling processes. The cooling phase is critical for solidifying the plastic into its final structure, ensuring that it retains the intended shape and possesses the requisite properties. This phase significantly influences the product's structural integrity and overall quality.
2.5. Finishing touches
The journey continues with potential additional processes for finishing touches. These may include surface treatments, coatings, or any enhancements required to meet specific quality standards or cater to aesthetic preferences. These refinements contribute to the product's final appearance and functionality.
2.6. Quality control
Throughout the entire journey, rigorous quality control measures are implemented. These measures involve thorough testing for structural integrity, dimensional accuracy, and other performance factors. Stringent quality control is imperative to ensure that the final plastic products meet the required standards and adhere to the specifications set during the design and development phases.
2.7. Packaging and distribution
With the manufacturing process complete, the plastic products enter the packaging phase. Thoughtful and efficient packaging not only safeguards the products during transit but also plays a pivotal role in minimizing the environmental impact. Sustainable packaging practices are increasingly emphasized, aligning with global efforts to reduce the ecological footprint of plastic products.
2.8. End-use and life cycle
The final stage of the journey sees the plastic products finding applications across a spectrum of industries. From packaging and construction to healthcare and electronics, the versatility of plastics ensures their presence in diverse fields. Understanding the end-use applications is indispensable for comprehending the complete life cycle of plastic products, including potential recycling or disposal considerations.
3. EuroPlas: The supreme manufacturer for superior plastic pellets
When it comes to sourcing top-tier plastic solutions that embody both exceptional performance and unwavering sustainability, EuroPlas emerges as a global industry leader. With an impressive legacy spanning over 15 years, EuroPlas has carved out a sterling reputation for delivering innovative and eco-conscious products to customers across more than 85 countries.
Headquartered in Vietnam, EuroPlas stands as a masterbatch manufacturer with a commitment to excellence. Our state-of-the-art facilities, coupled with unique natural resources and cutting-edge technology, position us at the forefront of the industry. These assets empower us to tailor products that cater to a diverse array of industries and applications, showcasing our versatility and commitment to meeting the evolving needs of our global clientele.
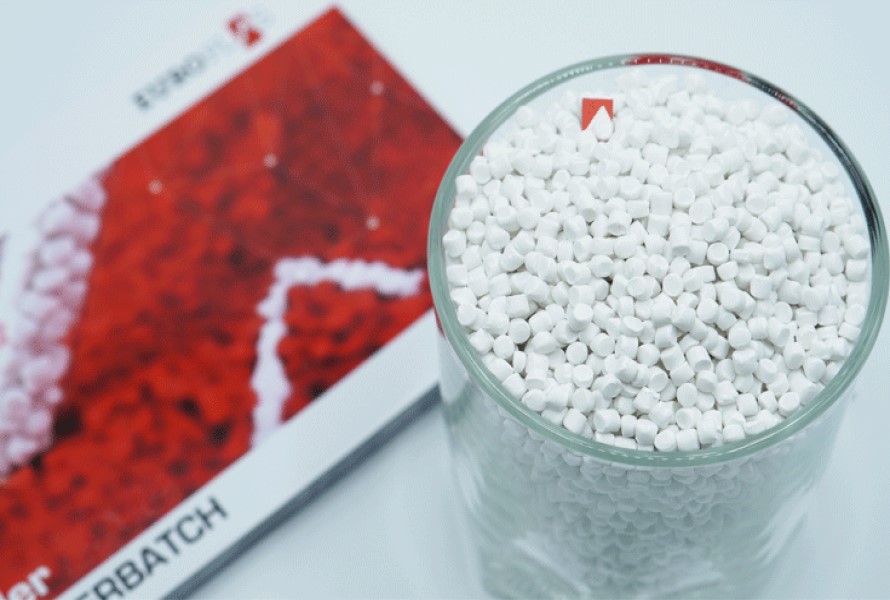

EuroPlas' Filler Masterbatch stands as a game-changer for industries aiming to reduce production costs while enhancing the properties of plastic products. By substituting a portion of virgin resin with filler materials like calcium carbonate or talc, this product improves stiffness, heat resistance, opacity, and printability. Its versatility spans applications in blowing films, injection molding, extrusion, and thermoforming, making it indispensable across various sectors.
At EuroPlas, we recognize the significance of aesthetics. Our Color Masterbatch offers precise and consistent colors for toys, household appliances, cosmetics, and more. Utilizing high-quality pigments and additives that can be blended with various resins, we ensure that your products showcase vibrant and captivating designs that perfectly align with market demands.
EuroPlas stands as your steadfast partner in embracing the future of plastic materials—a future defined by excellence in performance and a profound commitment to environmental responsibility. With a diverse product range and unwavering dedication, EuroPlas eagerly anticipates the opportunity to serve your plastic needs and be a catalyst in your journey towards a more sustainable tomorrow. Contact us now for more information!