Polypropylene vs PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) are two widely used thermoplastic polymers, each with unique characteristics and applications. Understanding their differences is crucial for making informed decisions in various industries. The article below will give you some information to distinguish between them.
1. What is Polypropylene (PP)?
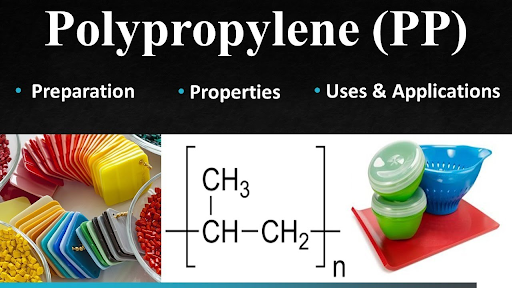
Some information about Polypropylene (PP)
Polypropylene (PP) is a versatile thermoplastic polymer widely used in various industries. It is a synthetic resin made from the polymerization of propylene monomers. PP is known for its exceptional chemical resistance, durability, and high melting point. It is lightweight, yet strong, making it ideal for applications requiring both flexibility and strength.
PP has a wide range of uses, including packaging materials, textiles, automotive components, medical devices, and laboratory equipment. Its resistance to moisture, acids, and bases makes it suitable for containers and products that come into contact with different substances. PP is also popular in the food industry due to its non-toxic nature and ability to withstand high temperatures, making it suitable for food containers and microwave-safe products.
Additionally, PP is known for its recyclability, making it an environmentally friendly choice in the plastic industry. It can be easily recycled and used in the production of various plastic products, contributing to sustainability efforts.
Read more: PP Plastic: Everything you need to know
2. What is PVC?

PVC is used to produce plastic pipes
Polyvinyl Chloride, commonly known as PVC, is a versatile and widely used thermoplastic polymer. It is made from vinyl chloride monomers through polymerization. PVC is known for its excellent durability, chemical resistance, and versatility.
PVC is inherently flame-resistant and has good electrical insulation properties, making it valuable in construction, electrical, and plumbing applications. It is commonly used for pipes, cable insulation, vinyl flooring, window frames, and medical tubing. PVC's rigidity and stability make it suitable for structural applications, while its resistance to moisture and chemicals enhances its longevity.
One of PVC's key advantages is its cost-effectiveness; it is generally more affordable than other materials with similar properties. However, its production and disposal can raise environmental concerns due to the release of chlorine gas and the persistence of PVC in the environment. Recycled PVC is increasingly used to mitigate these concerns, promoting a more sustainable approach to its use.
Read more: What is PVC Plastic? All Information About PVC Plastic
3. Polypropylene vs PVC: What are the differences?

Distinguish between PVC and PP
Polypropylene (PP) and Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) are two commonly used thermoplastic polymers, each with distinct characteristics and applications. Here’s a comparison to help you understand the differences between them:
- Flexibility: PP is more flexible than PVC, making it suitable for applications requiring bending and flexibility.
- Chemical resistance: Both materials offer good chemical resistance, but PP is better suited for certain chemicals and solvents.
- Temperature resistance: PP has a higher melting point than PVC, making it more heat-resistant.
- Density: PVC is denser than PP, providing better structural support in certain applications.
- Cost: PP is generally more affordable than PVC, making it a cost-effective choice for many applications.
- Applications: Polypropylene is commonly used in packaging, textiles, automotive components, medical devices, and laboratory equipment. Meanwhile, PVC is used to make pipes, cable insulation, vinyl flooring, signage, and inflatable structures.
4. Conclusion
In summary, the choice between Polypropylene and PVC depends on the specific requirements of the application. PP offers flexibility and chemical resistance, while PVC provides durability and stability. Evaluating the unique properties of each material is essential to selecting the most suitable option for your project, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
5. PP products of EuroPlas

PP flame retardant compound at EuroPlas
PP flame retardant compound consists of polypropylene (PP) resin and halogen/non-halogen flame retardant. Available in UL94-standard ratings 5VA, 5VB, V0, V1, and V2, it's used in electronics, fireproof components, etc. At EuroPlas, our PP flame retardant compound offers all-in-one functionality, direct processing, customization depending on requirements, and fire prevention on plastic surfaces.

PP conductive compound at EuroPlas
PP conductive compound comprises PP resin and carbon black, making it lightweight and easy to use in injection molding. It finds applications in electronic components, cable jackets, and electrical housings. EuroPlas' PP conductive compound has some outstanding features such as all-in-one functionality, direct processing, customization according to needs, enhanced stability, and improved electrical conductivity.

PP BaSO4 compound at EuroPlas
EuroPlas' PP BaSO4 compound is formulated by treating polypropylene with BaSO4, reducing shrinkage, enhancing formability and improving heat resistance, chemical resistance and impact resistance, limiting deformation at high temperatures. The advantages of the PP BaSO4 compound render it ideal for a variety of applications in which maintaining dimensional stability and longevity is of utmost importance. Such applications include the manufacture of sanitary equipment, household appliances, and water filtration equipment. Utilizing EuroPlas PP BaSO4 compound enhances mechanical properties and reduces final product costs.

PP talc compound at EuroPlas
PP talc compound combines talc powder with specific additives based on end-product needs. Talc, a natural mineral composed of magnesium, silicon, oxygen, and hydrogen, enhances stiffness, flexural modulus, and strength in thermoplastics. It reduces creep in high-temperature settings and improves heat distortion temperature and dimensional stability due to its unique properties.

PP glass bead compound at EuroPlas
PP glass bead compound blends PP resin, glass beads, and additives to enhance product stiffness, transparency, compression resistance, and thermal stability. This material finds extensive applications in car interiors, home decor, and household appliances due to its superior properties.

PP glass fiber compound at EuroPlas
PP glass fiber compound, containing PP base resin, glass fiber, and additives, enhances the final products' flexural modulus and tensile strength. EuroPlas offers diverse PP glass fiber compounds like ECP PP 10GF, ECP PP 20GF, ECP PP 30GF, ECP PP 40GF, and ECP PP 50GF, varying in glass fiber density.
EuroPlas ensures extensive research and development for all plastic compounds before their introduction and delivery to clients. Our PP plastic products are trusted globally as a result of meticulous research processes. Connect with us now to look for more information about our diverse product range and find the perfect plastic solution for your company.