Silicone vs TPE are two types of materials that are widely used in various industries and applications. They have some similarities and differences in their properties and performance. In this article, we will compare and contrast Silicone vs TPE, and explain what are the advantages and disadvantages of each material. We will also introduce EuroPlas, a leading manufacturer of filler masterbatch products for plastic applications.
Table of contents
- What is TPE?
- What is silicone?
- Silicone vs TPE: What are the differences?
Temperature resistance
Chemical resistance
Recyclability
Processing method
- Conclusion
- About EuroPlas masterbatch
- FAQs
What are the main differences between Silicone vs TPE?
What are the advantages and disadvantages of using silicone or TPE?
What are the main differences between Silicone vs TPE?
1. What is TPE?
TPE stands for thermoplastic elastomer, which is a type of polymer that has both thermoplastic and elastomeric properties. Thermoplastic means that the material can be melted and reshaped by heating and cooling, while elastomeric means that the material can be stretched and return to its original shape. TPE is usually a plastic and a rubber that are physically mixed or chemically bonded together.
TPE has many advantages, such as:
- It is flexible, durable, and resilient.
- It has good resistance to water, oils, greases, and some solvents.
- It is easy to process by injection molding, extrusion, blow molding, or thermoforming.
- It is recyclable and environmentally friendly.
TPE also has some disadvantages, such as:
- It has low resistance to heat, abrasion, and UV radiation.
- It has low resistance to strong acids, bases, or oxidizing agents.
- It has low dimensional stability and creep resistance.
Some examples of TPE products are:
- Automotive parts such as bumpers, seals, gaskets, hoses, or mats.
- Medical devices such as catheters, syringes, gloves, or implants.
- Consumer products such as toys, sports equipment, footwear, or phone cases.

TPE stands for thermoplastic elastomer, which is a type of polymer that has both thermoplastic and elastomeric properties
2. What is silicone?
Silicone is a type of synthetic polymer that has a silicon-oxygen backbone with organic groups attached to the silicon atoms. It is usually colorless, oil-like, or rubber-like, and has various applications in sealants, adhesives, lubricants, medicine, cooking utensils, insulation, and more.
Silicone has many advantages, such as:
- It has high resistance to heat and does not have a melting point.
- It has high resistance to water, oxidation, ozone, and most chemicals.
- It has high electrical insulation and low thermal conductivity.
- It has good biocompatibility and low toxicity.
Silicone also has some disadvantages, such as:
- It is expensive and difficult to recycle.
- It requires curing agents and high temperatures to form its shape.
- It is not resistant to steam, hydrocarbon fuels, alkalis, acids, trichloroethylene, or aromatic hydrocarbons.
Some examples of silicone products are:
- Sealants and adhesives for construction, aerospace, or electronics.
- Lubricants for industrial or medical applications.
- Medical devices such as implants, prosthetics, valves, or tubing.
- Cooking utensils such as bakeware, spatulas, or molds.

Silicone is a type of synthetic polymer that has a silicon-oxygen backbone with organic groups attached to the silicon atoms
3. Silicone vs TPE: What are the differences?
Now that we have learned what Silicone vs TPE are, let us compare and contrast them in terms of their temperature resistance, chemical resistance, recyclability, and processing method.
3.1. Temperature resistance
One of the main differences between TPE vs silicone is their temperature resistance. Silicone has a high resistance to heat and does not have a melting point. It can withstand temperatures up to 200-450°C without losing its mechanical properties. This makes silicone suitable for applications that require high temperature stability, such as sealants, adhesives, or lubricants for aerospace or electronics.
TPE has a lower resistance to heat and has a melting point of 260-320°C. It can be reprocessed by heating and cooling. This makes TPE suitable for applications that require flexibility and recyclability, such as automotive parts, medical devices, or consumer products.
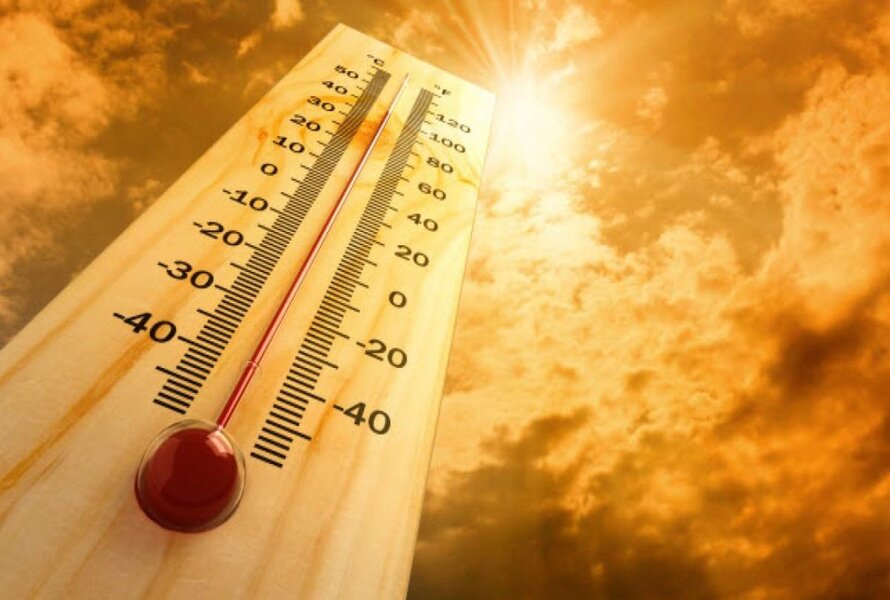

One of the main differences between TPE vs silicone is their temperature resistance
3.2. Chemical resistance
Another difference between Silicone vs TPE is their chemical resistance. Silicone is resistant to water, oxidation, ozone, and most chemicals. It is not resistant to steam, hydrocarbon fuels, alkalis, acids, trichloroethylene, or aromatic hydrocarbons. This makes silicone suitable for applications that require high chemical stability, such as medical devices, cooking utensils, or insulation.
TPE is resistant to water, oils, greases, and some solvents. It is not resistant to strong acids, bases, or oxidizing agents. This makes TPE suitable for applications that require moderate chemical stability, such as automotive parts, consumer products, or sports equipment.

Another difference between Silicone vs TPE is their chemical resistance
3.3. Recyclability
A third difference between Silicone vs TPE is their recyclability. Silicone is not easily recyclable because it requires high temperatures and special catalysts to break down its bonds. This makes silicone less environmentally friendly and more costly to dispose of.
TPE is easily recyclable because it can be melted and reshaped multiple times without losing its quality. This makes TPE more environmentally friendly and more economical to reuse.

A third difference between Silicone vs TPE is their recyclability
3.4. Processing method
A fourth difference between Silicone vs TPE is their processing method. Silicone can be processed by injection molding, extrusion, compression molding, or liquid injection molding. It requires curing agents and high temperatures to form its shape. This makes silicone more complex and expensive to process.
TPE can be processed by injection molding, extrusion, blow molding, or thermoforming. It does not require curing agents or high temperatures to form its shape. This makes TPE more simple and cheap to process.
A fourth difference between Silicone vs TPE is their processing method
4. Conclusion
In conclusion, Silicone vs TPE are two types of materials that have some similarities and differences in their properties and applications. Silicone has high resistance to heat and chemicals but low recyclability and complex processing methods. TPE has low resistance to heat and chemicals but high recyclability and simple processing method. Depending on your needs and preferences, you can choose the best material for your project.
We hope this article has helped you understand the differences between Silicone vs TPE. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to leave them below. Thank you for reading!
5. About EuroPlas masterbatch
EuroPlas masterbatch is a leading manufacturer of filler masterbatch products in Vietnam. Filler masterbatch is a type of additive that can enhance the properties and performance of plastic materials such as TPE vs silicon.
EuroPlas masterbatch offers a wide range of filler masterbatch products for silicone vs TPE materials, such as:
- Calcium carbonate filler masterbatch: This product can improve the stiffness, strength, heat resistance, and dimensional stability of silicone vs TPE materials. It can also reduce the cost and weight of the final products.
- Transparent filler masterbatch: This product can improve the transparency, glossiness, smoothness, and scratch resistance of silicone vs TPE materials. It can also reduce the yellowing effect and increase the light transmission of the final products.
- Color masterbatch: This product can provide various colors and effects for silicone vs TPE materials. It can also improve the color consistency, dispersion, and fastness of the final products.
EuroPlas masterbatch has many advantages and applications for silicone vs TPE materials, such as:
- High quality: EuroPlas masterbatch uses advanced technology and equipment to produce high-quality filler masterbatch products that meet international standards and customer requirements.
- Competitive price: EuroPlas masterbatch offers competitive prices for its filler masterbatch products that can help customers save costs and increase profits.
- Customized service: EuroPlas masterbatch provides customized service for its filler masterbatch products that can meet customer specifications and expectations.
One of the successful cases of EuroPlas masterbatch is the cooperation with a leading manufacturer of medical devices in Vietnam. The customer needed a filler masterbatch product that could improve the properties and performance of their silicone catheters. EuroPlas masterbatch provided a transparent filler masterbatch product that met the customer’s needs. The customer was satisfied with the results and continued to order from EuroPlas masterbatch.
If you are looking for a reputable and quality supplier of filler masterbatch products for your plastic applications, you can contact EuroPlas at europlas.com.vn/en-us/contact-us.
EuroPlas masterbatch is a leading manufacturer of filler masterbatch products in Vietnam
6. FAQs
What are the main differences between Silicone vs TPE?
Silicone vs TPE are both types of synthetic polymers that have rubber-like properties, but they have some differences in their chemical structure, temperature resistance, chemical resistance, recyclability, and processing method. Silicone has a silicon-oxygen backbone with organic groups attached to the silicon atoms, while TPE is a copolymer or a physical mix of polymers that have both thermoplastic and elastomeric properties. Silicone has a high resistance to heat and does not have a melting point, while TPE has a lower resistance to heat and has a melting point of 260-320°C. Silicone is resistant to water, oxidation, ozone, and most chemicals, while TPE is resistant to water, oils, greases, and some solvents. Silicone is not easily recyclable because it requires high temperatures and special catalysts to break down its bonds, while TPE is easily recyclable because it can be melted and reshaped multiple times without losing its quality. Silicone can be processed by injection molding, extrusion, compression molding, or liquid injection molding, while TPE can be processed by injection molding, extrusion, blow molding, or thermoforming.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of using silicone or TPE?
The advantages and disadvantages of using silicone vs TPE depend on the specific application and requirements of the product. Generally speaking, silicone has the advantages of high temperature stability, high chemical stability, high electrical insulation, low thermal conductivity, good biocompatibility, and low toxicity. However, silicone also has the disadvantages of being expensive and difficult to recycle, requiring curing agents and high temperatures to form its shape, and being not resistant to steam, hydrocarbon fuels, alkalis, acids, trichloroethylene, or aromatic hydrocarbons. TPE has the advantages of being flexible, durable, resilient, water-resistant, oil-resistant, grease-resistant, solvent-resistant, easy to process by various methods, recyclable and environmentally friendly. However, TPE also has the disadvantages of having low resistance to heat, abrasion, UV radiation, strong acids, bases, oxidizing agents.
What are the main differences between Silicone vs TPE?
Silicone vs TPE have some differences in their temperature resistance, chemical resistance, recyclability, and processing method. Silicone has a high resistance to heat and does not have a melting point, while TPE has a lower resistance to heat and has a melting point of 260-320°C. Silicone is resistant to water, oxidation, ozone, and most chemicals, while TPE is resistant to water, oils, greases, and some solvents. Silicone is not easily recyclable because it requires high temperatures and special catalysts to break down its bonds, while TPE is easily recyclable because it can be melted and reshaped multiple times without losing its quality. Silicone can be processed by injection molding, extrusion, compression molding, or liquid injection molding, while TPE can be processed by injection molding, extrusion, blow molding, or thermoforming .