An injection molding machine is essential for the injection molding method to guarantee top-notch processes and final goods. These machines are available in a variety of configurations, each with unique functions and advantages.
A successful injection molding process requires an awareness of the functionality of several injection molding machines on the market. Thus, this article will include a full list to help you comprehend and choose the proper machine for your production. Let's delve in!
Read more: What is injection molding? How does it work?
1. What is an Injection Molding Machine?
An injection molding machine is essential for the production of large quantities of plastic parts for use in the aerospace, automotive, medical, and consumer goods industries. The equipment forms the required part shape by injecting melted plastic pellets into a mold cavity. The component is then cooled and removed from the mold.
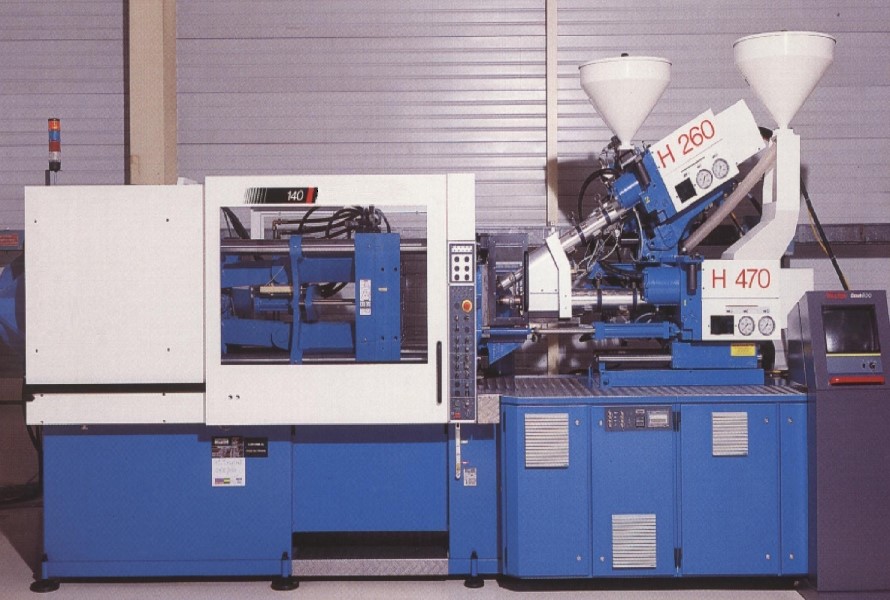

The main parts of these machines are the clamping unit and injection device. While the clamping unit moves the mold and supplies the force required for closing, clamping, and other activities, the injection unit warms the pellets. Using an injection molding machine has the benefits of rapid processing and low total cost.
2. All Types Of Injection Molding Machines
There are criteria dividing the machine into different types:
2.1. According to Drive Methods
- Hydraulic injection molding machines
The earliest injection molding machines in use today were hydraulic models created in the early 1900s. The hydraulic drives bind the mold halves together and push the melted plastic into the mold cavity. These machines are the most affordable, robust, and accessible on the market.
They are perfect for larger molds and provide unmatched clamping forces. They do, however, require higher temperatures and more infrastructure. They also make more noise and run the danger of leaking hydraulic fluid.
Their price ranges from $3,000 to more than $100,000, with yearly maintenance and infrastructure requirements of about $17,000. If properly maintained, this injection molding machine can survive up to seven or ten years; however, if improperly cared for, the hydraulic systems may limit its lifespan.
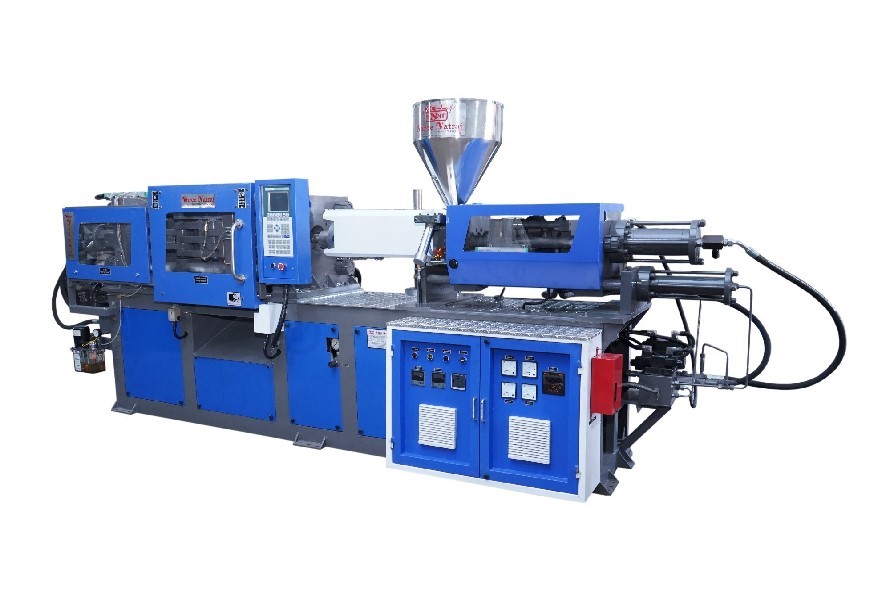

- Electric injection molding machines
Developed in Japan in the 1980s, these machines are an advancement over hydraulic machines. They can save up to 75% on power requirements by precisely controlling injection, extrusion, clamping, and ejecting with digitally controlled servo motors.
This type of injection molding machine is perfect for cleanroom applications since it is simple to use, maintain, allowing for a faster, repeatable, more precise, and energy-efficient operation. However, compared to hydraulic ones, it is more expensive, more difficult to fix, and has less clamping force.
The price varies based on size and features, from $5,000 to more than $200,000. These machines are mostly utilized in cleanroom applications for tiny to medium-sized parts in the pharmaceutical, medical, and biochemical industries. With regular maintenance, they can endure for more than 20 years.
- Hybrid injection molding machines
Hybrid injection molding machines combine the advantages of electric and hydraulic injection molding machines to create a machine that is strong, precise, and energy-efficient. Compared to completely hydraulic devices, they use a servo motor-based reciprocating screw, circulating oil for hydraulic pressure, and servo motor pumps for hydraulic fluid. This results in lower energy expenditures.
The benefits of this injection molding machine type are reduced maintenance and downtime, energy efficiency, responsiveness, and affordability. They do, however, have certain drawbacks, including the requirement for technicians to be competent with both electric and hydraulic machinery and variations in design depending on the manufacturer or model.
Yet, in comparison to all-electric or all-hydraulic machines, hybrid models are typically more affordable, with fewer maintenance costs and a quicker payback period. They are appropriate for heavy industrial items, parts with varying wall thicknesses, and high-volume components used in the medical industry.
2.2. According to Trends of Switching Mode
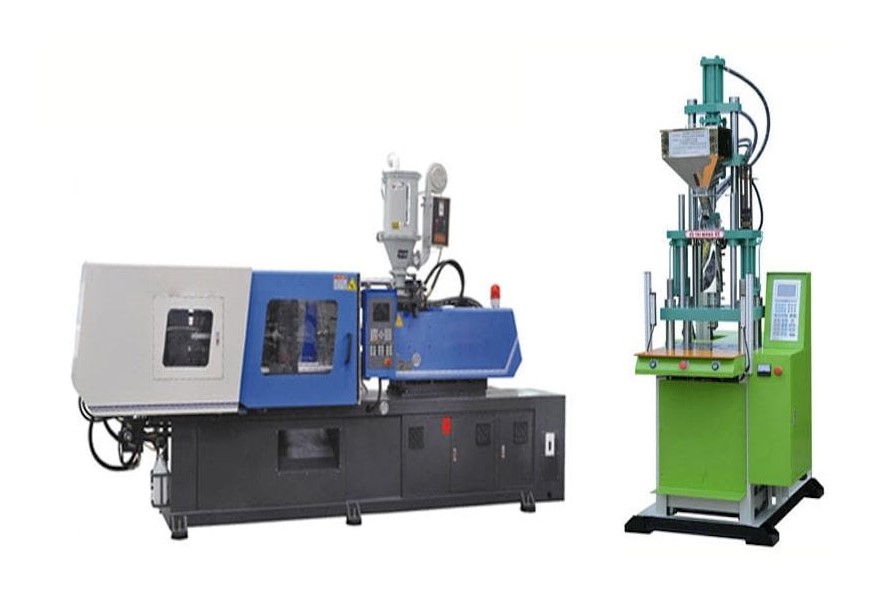

- Vertical injection molding machines
The machine molds the plastic vertically to create small molds and injects a greater range of objects while taking up less space. To improve production efficiency, it can include a conveyor belt or rotating table.
The machine's upward-facing surface and compact floor area make insert molding easier. A horizontal template supports the mold, enhancing accuracy and durability.
A basic robot can retrieve each plastic part cavity. The apparatus features an open universal clamping device that is adaptable to different automation devices and simple to configure. It also has an automated transmission mechanism for molding and production.
- Horizontal injection molding machines
This type of injection molding machine is quite popular due to its low body, quick molding, and ease of operation. Thanks to its low main structure, its installed height is not restricted.
The machine is easy to maintain because the system can create things autonomously without the need for a robot. It should be set up like a crane, and when several are placed side by side, a conveyor belt can be used to gather and package the molded goods with ease.
2.3. According to Applicable Raw Materials
- Thermoplastic injection molding machines
Thermoplastics change from solid to liquid after heating and then back to solid after cooling. Yet, thermoplastics such as ABS, TPU, PE, and PP are widely used in injection molding since they do not retain rigidity when heated.
The plastic pellets will be heated, and then the thermoplastic plastic injection machine will take advantage of thermoplastic properties to insert liquid plastic into the mold. After the plastic cools down and finally takes on its solid shape again, then the plastic components are extruded out of the machine.
- Thermosetting plastic injection molding machines
Thermosetting polymers change phases from liquid to solid when heated. This transition is not environmentally friendly because it can frequently only be made once and cannot be recycled in the same way that thermoplastics can.
Two examples of thermosetting polymers that are frequently utilized nowadays are melamine and FRP. The thermosetting plastic injection machine will inject liquid plastic into the mold after the processing step. The final step in creating the plastic components is to heat them until they solidify.
- Powder or metal injection molding machines
Powder injection molding is a technique used to manufacture precision-treated and bonding compounds in fine metal or ceramic powders. It is often referred to as metal injection molding (MIM), ceramic injection molding (CIM), or plastic injection molding.
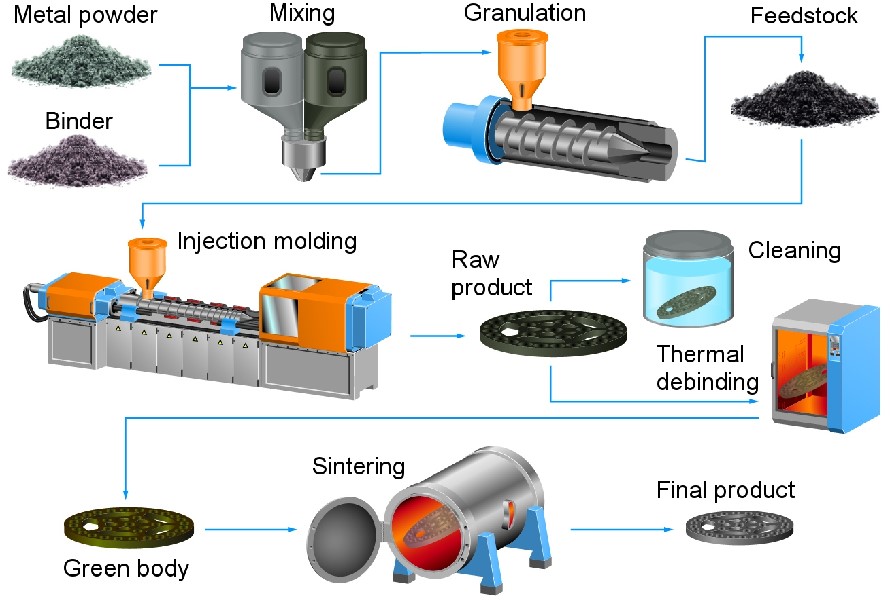
It is frequently utilized in the production of tiny, intricate parts with great strength and density for products like smart phones and portable electronics. To guarantee their quality and longevity, the parts go through post-processing procedures including heating and cleaning after manufacture.
2.4. According to Clamping Structures
- Single/double/four-cylinder direct-pressure injection molding machines
Direct-pressure injection machines are classified into single, double, and four-cylinder types based on hydraulic cylinders.
Because of the vast surface area, single-cylinder machines are challenging to make different components. With double-cylinder injection using two oil cylinders concurrently, single-cylinder direct-pressure injection machines are gradually being replaced by multiple-cylinder machines.
With its unique template design and automated balancing correction function, the four-cylinder direct-pressure clamping model ensures accuracy and a broad range of applications. The model has previously been plagued by uneven force, mold deterioration, and products that didn't fit size requirements.
Because of their extended lifespan, direct mold clamping, and low resistance while in motion, direct-pressure injection machines require less maintenance and upkeep. They are more expensive than toggle-type injection molding machines but also more durable.
- Compound direct pressure injection machines
This injection molding machine type is built with similar parts to direct pressure-type machines, with a stronger mold opening and a longer clamping stroke. Since its criteria for resistance to wear and tear are crucial, only a few manufacturers produce them.
- Toggling type of injection machines
Although the toggling injection machine's construction is difficult to understand, it offers simple operation, cheaper running costs, and lower machine expenses through acceleration and deceleration.
2.5. According to Injection Structures

- Monochrome plastic injection molding machines
The monochromatic injection is a technique used by this injection molding machine to inject plastic components with identical colors. This technique can likewise simultaneously inject two different colors into an item. The first color is injected into the first semi-finished product by operators of a color injection molding machine, and the second color is injected into the final product for manufacture.
- Multi-color plastic injection molding machines
Multi-color injection machines can concurrently insert plastic components of different colors. The two-color plastic injection molding machine is the most common type, combining LSR silicone rubber with other materials. This technology is becoming increasingly popular in the business because of its remarkable performance, efficiency, and environmental protection.
3. Composition and How An Injection Molding Machine Works
The specific parts of an injection molding machine include:
- Hopper: The hopper feeds stock material into the machine and is basically a big funnel.
- Barrel: The reciprocating screw is housed in the machine's outer barrel, which is also covered in heater bands and serves to both hold the material and heat the cycle.
- Reciprocating screw: Driven by electrical or hydraulic systems, the reciprocating screw is a corkscrew-like part that revolves back and forth in a cycle to carry material through heating sections, nozzles, and injection molds.
- Nozzle: Melted plastic is distributed from the barrel via the nozzle into the mold cavity, which is usually found inside the injection mold bushing. The plastic is heated to prevent temperature loss before it enters the mold.
- Heaters: Heaters provide precise temperature control and thermal energy by melting solid plastic pellets through a barrel. Usually, they are spaced apart to allow for slow heating.
- Mold: With the mold chamber and auxiliary features like ejector pins, runner channels, cooling channels, and vents, molds are crucial parts of machines. Generally, they are separated into moving and stationary portions, although depending on the machine under consideration, they may contain more than one segment.
- Mold cavity: Melted plastic fills, cools, and is expelled from the mold cavity, which is the negative shape of the desired item with all of its supports, gates, runners, and sprues included.
- Movable platen: The movable platen, driven either electrically or hydraulically, is a clamping device that firmly keeps the mold together and releases the core when the completed portion is exposed, preventing material escape during injection.
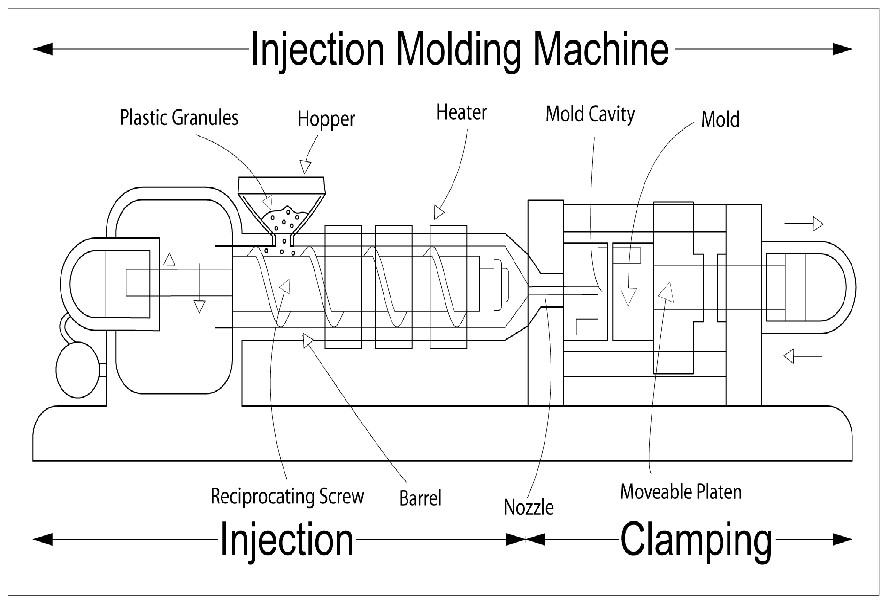
Here is how an injection molding machine works:
The machine is in charge of melting plastic pellets and injecting them into a mold cavity. Pellet loading, barrel melting, injection unit pouring molten plastic into the mold, and chilling and solidifying mold are the steps in the process. After being heated and melted in a barrel with a screw, the pellets are pumped under high pressure into the mold cavity, where they cool and solidify to form the required part shape.
4. Plastic Types Fitted For Injection Molding Machines
Below is a list of plastics types suitable for injection molding:
- Nylon
- ABS plastic
- Polycarbonate (PC)
- PC-ABS plastic
- Acetal Copolymer
- Acetal Homopolymer
- Engineered Thermoplastic Polyurethane (ETPU)
- High Density Polyethylene
- Liquid-crystal polymer
- Low-density polyethylene
- Linear low-density polyethylene
- Acrylic (PMMA)
- Polystyrene (PS)
- Polypropylene (PP)
- Polyether Ether Ketone (PEEK)
5. Conclusion
An injection molding machine is a single device that makes injection molding possible. It enables the mass manufacture of goods by combining material feeding, melting, injection, and ejection in a single, compact space.
A wide variety of molding machines are available depending on what you are producing and how the machine affects the final product. Take a look at the categories above and find the best suits your needs.
6. EuroPlas - Material Provider for Injection Molding
Engineering plastic compounds from EuroPlas are specialized materials used to make finished items with specific technical features. It is made up of primary resin, colorants, and reinforcements. It is utilized in many different applications, including electrical engineering, manufacturing, automotive, home appliances, and electronics.

We offer PBT GF-FR compound, mix PA6, PA66, PC fire retardant compound, ABS fiberglass compound, and ABS antistatic compound. These composites are flexible, of excellent quality, and serve multiple purposes in one material.
Contact EuroPlas right now for more information!