Plastic, a material that is very helpful and adaptable, permeates our contemporary society. Plastic has made many of our innovations and comforts possible, from food packaging to space rockets. Because of this ubiquity, we often forget that plastics come in a wide variety. Knowing which plastic is appropriate for your project is crucial.
The main component of all plastic items is plastic resin. But what is plastic resin? How is plastic resin made? Find the answer in this article.
You may be interested in: Masterbatch - definition, applications, market trends and more
.jpg)
1. What is plastic resin?
Plastic resins are the main base of all plastics, but these resins are modified via various procedures to meet diverse demands.
Where does plastic resin come from? The plastic made from oil is called primary plastic resin. When utilized, fundamental plastic resins are often natural white; however, color granules are frequently added to provide a variety of hues, including blue, red, purple, and yellow...

To create the specific kind of product required, the right kind of plastic resin is chosen. When packed, certain plastics are loaded with hot items, such as those found in some food processing facilities. Others would need to have distinct qualities since they are utilized for chemical goods.
Products like soft drink bottles, bottles, and trash cans are made from a kind of plastic resin called polyethylene terephthalate. High-density Bottles for vitamins, milk jugs, and film containers are all made of polyethylene. Vinyl/polyvinyl chloride is the material used in the plastic wrap you use at home to preserve the freshness of your food. Low-density polyethylene is used to make netting, plastic bags, and garment bags.
Many people are unaware that plastic resin can be recycled, despite the fact that it may be used to manufacture a variety of everyday items. Only over half of items made from plastic resin are utilized to create additional products. The remainder is disposed of in the trash, which is bad for the environment.
2. How plastic resin is made?
-(1).jpg)
What is plastic resin made of? The plastic resins-making process is performed by heating hydrocarbon in what is known as the "cracking process." The bigger molecules are to be broken down into ethylene, propylene, and other kinds of hydrocarbons. The cracking temperature affects how much ethylene is generated.
The chemicals are then synthesized into polymeric chains when the cracking process is complete. Plastic resins are created by combining several polymers to give them the properties required for various uses. After being manufactured, plastic resins are utilized to create a wide range of items.
The detailed process of making plastic resins is as below:
Step 1: Petroleum extracting
Drilling is used to extract petroleum, which is then sent to an oil refinery for processing.
Step 2: Creating petrochemicals
Petrochemicals like ethane and propane are created by refining the crude oil extracted from the ground.
Step 3: Cracking
The hydrocarbons ethylene and propylene are then produced from ethane and propane via a heating process called cracking or catalytic cracking. Through this process, bigger molecules are broken down into hydrocarbons like ethylene, propylene, and others.
Step 4: Adding a catalyst
A catalyst is introduced to a reactor after the material has been cracked to produce a polymer, which is a powder. This substance, which the refineries refer to as "fluff", is blended continuously with various additives (depending on the kind of plastic needed).2.5
Step 5: Melting
After that, an extruder is used to melt and create the polymer.
Step 6: Shaping
The material is chopped and shaped into the plastic pellets you see in every plastic plant when it has cooled after being extruded. The petroleum-derived pellets are utilized in extrusion, injection, and blow molding, as well as other plastic production processes.
3. What are plastic resin pellets used for?

Plastic resin pellets have a short diameter of a few millimeters and are formed like little disks or cylinders. These plastic resin pellets are remelted and formed in manufacturing facilities to create new goods.
The homogeneous composition required for the production of bottles and other plastic goods is provided by plastic resin pellets. Other frequent uses for resin pellets include a range of plastic goods, such as plastic bags and industrial wraps.
Related:
- 5 types of plastic masterbatch are mainly used for packaging production
- Compare HDPE, MDPE, LDPE, and LLDPE masterbatch
Manufacturers may choose from a number of plastic materials for plastic resin pellet manufacturing. To utilize them as raw materials for creating new plastic components, the various plastic kinds must be kept apart. The distinctive qualities of various plastic materials make them more or less suitable for certain uses. When selecting the best resin pellets, color and pellet density are crucial elements to take into account. Transparent or mixed colors are required for many applications, and manufacturing methods might be impacted by density.
The 3 most often used kinds of plastic resin pellets are as follows:
3.1. ABS plastic resin pellets
ABS plastic resins are available in natural white or opalescent. Although ABS plastic is stiff and unyielding, it is also insulating and neither crisp nor moist. Helmets, containers, and various motorbike parts are all made with ABS due to their impact resistance and hardness.
You may be interested in:
ABS plastic - Everything you need to know
ABS vs HDPE - What are the differences?
Is ABS plastic safe for food?
3.2. PP plastic resin pellets
The most widely used plastic resin in daily life is PP. PP is translucent white, but manufacturers often combine it with colored beads to produce full-color items. It is used to make yarn because of its high mechanical strength (tear strength and tear strength), hardness, lack of elongation, and lack of flexibility compared to PE. PP is non-toxic, tasteless, odorless, and colorless. The bright blue flame of PP resin burns with a flexible flow and a rubber-like burned odor. PP is often used in the production of toys, baskets, and plastic trays.
3.3. PA66 plastic resin pellets
Since PA plastic resins have high viscosity, excellent toughness, surface lubrication, and notably wear resistance, they are utilized in a variety of home appliances, clothing, electrical components, motorcycles, automobiles, and other vehicles.
Additionally, there are several kinds of plastic resin pellets with various uses available in the globe, including HDPE, LDPE, POM, PS, HI, PET, PBT, PC, and PVC.
4. Plastic resin price
As mentioned above, plastic resin is made from petroleum, so the price of plastic resin is also affected by the oil price. To update the price of virgin plastic, please refer to prestigious newspapers and forums, such as theplasticsexchange.com.
Besides, don’t hesitate to follow EuP's blog regularly to update information about plastic information.
5. Which plastic resin codes can be recycled?
Related:
- PE, PP, LDPE, HDPE, PEG plastic masterbatch
- How will the Vietnamese masterbatch industry change after the EVFTA is signed?
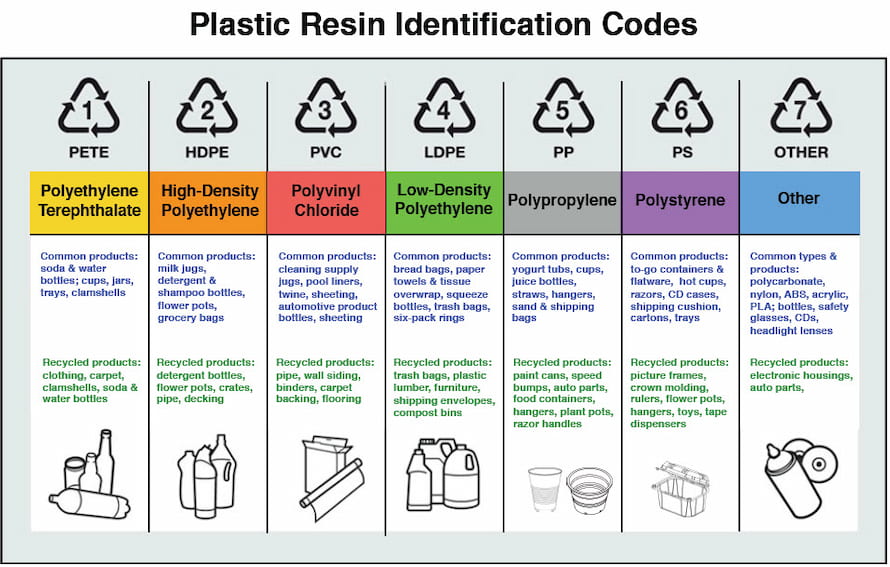
Some rigid plastic packaging has a number on the bottom known as a resin identification code. They were first established in the 1980s to classify plastic into categories, to assure uniformity in the production of plastics, and to reprocess used plastics.
To protect the value of the recycled material and allow for its subsequent usage in other goods, different types of plastics, such as PET plastic bottles, must be recycled separately from related materials.
The Resin Identification Codes 1 to 6 indicate which of six distinct types of plastic resins were used to make the plastic packaging: 1 indicates polyethylene terephthalate (PET), 2 indicates high-density polyethylene (HDPE), 3 indicates polyvinyl chloride (PVC), 4 indicates low-density polyethylene (LDPE), 5 indicates polypropylene (PP), and 6 indicates polystyrene (PS). The number 7 denotes a plastic-type different from the first six or a combination of polymers in the package. This group includes materials such as polycarbonate, bioplastics, and composite plastics.
Although the use of resin identification codes on the packaging does not ensure that it is recyclable, substantial strides are being made in lowering the use of non-recyclable materials, particularly in the food industry.
Here are the recyclable plastic resin codes:
5.1. PET resin plastic (1)
PET, which carries the designation 1, is the plastic that is most often recycled. Our PET plastic bottles, which are often used for transparent plastic bottles, are made of this substance. It gives high chemical resistance and a gloss finish. PET may be used to fill fleeces, carpets, and cushions as well as be recycled into polyester fabric. Additionally, it may be recycled into rPET plastic, going through the whole life once more to create rPET plastic bottles.
5.2. HDPE resin plastic (2)
High-Density Polyethylene is another kind of plastic that is often recycled. It is compatible with the majority of acidic and alkaline solutions and has a matte finish. Solvent compatibility for HDPE is not very good. Milk bottles, plastic bottle tops, and closures, shampoo bottles, cleaning product bottles, tubs, and jerry cans are just a few items that often use HDPE.
5.3. PVC resin plastic (3)
In typical Local Authority collections, polyvinyl chloride cannot be recycled. Cling film, hoses, and plastic pipes are common examples of this sort of plastic.
5.4. LDPE resin plastic (4)
If you want to recycle low-density polyethylene, check with your local authority. Bin liners, carrying bags, packing films, and hand lotion tubs are just a few items that often use LDPE.
5.5. PP resin plastic (5)
Recycling polypropylene is possible. It is very chemically compatible and has a satin finish. Packing tape, plastic straws, ketchup bottles, microwaveable meal platters, and butter tubs are common places to find them. Plastic trays, brooms, brushes, and yard rakes may all be made from recycled polypropylene.
5.6. PS resin plastic (6)
In most Local Authority collection programs, polystyrene cannot be recycled. Expanded polystyrene and brittle plastic are the two varieties of polystyrene (light, insulating, waterproof plastic). The softer variant is used in frothy takeout packing, Styrofoam, and certain forms of insulation, whilst the harder variety is utilized in items like plastic forks and yogurt pots.
5.7. Other resin plastics (7)
Plastics having the resin identification number 7, which stands for "other plastics," cannot be recycled in regular collection programs. However, they can still be recycled under several circumstances.
6. EuroPlas - Where provides different plastic solutions
As the world's No. 1 filler masterbatch manufacturer, EuroPlas is proud to offer unique plastic material solutions, helping customers' factories optimize production costs and improve business competitiveness. EuroPlas provides various plastic solutions such as bioplastics and bio fillers, color and filler masterbatch, engineering plastic compounds, and other plastic additives. Please contact EuroPlas to raise your questions, or if you have specific needs for your next project.