PBS, short for polybutylene succinate, is an aliphatic polyester that is gaining significant attention due to its ability to be produced from bio-based sources, as well as its well-balanced properties, high processability, and excellent biodegradability. This article aims to provide information about the structure, synthesis process, and production of PBS as a foundation for understanding its biodegradability and key applications.
Read more: What are bioplastics made from? Materials to make bioplastics
1. Introduction to polybutylene succinate
Polybutylene succinate (PBS) has experienced significant demand growth in recent years due to its sustainability and biodegradability potential. In 2016, the production of this bioplastic reached 4.2 million tons and is expected to increase by 45% by 2021. PBS (poly(butylene succinate)) was first introduced in 1993 as a biodegradable polymer and continues to be widely favored in the industry.
Polybutylene succinate plastic is a type of thermoplastic polymer belonging to the polyester family and is produced from bio-based sources. PBS is a fatty polyester capable of biodegradation with properties equivalent to polypropylene. Specifically, PBS possesses various physical and chemical characteristics, such as:
- High tensile strength, compressive strength, and hardness, on par with some synthetic plastics.
- High melting temperature (180-190°C), good thermal stability, and resistance to high temperatures.
- Excellent chemical resistance, insoluble in water, alcohol, and certain organic solvents.
- Complete biodegradability by microorganisms in the natural environment, leaving no harmful residues.
- Effective gas barrier properties, improving the preservation of food and cosmetics.
- UV resistance protects products from the harmful effects of sunlight.
- Anti-static properties prevent static buildup on the product's surface.
.jpg)
Introduction to polybutylene succinate
2. Polybutylene succinate structure
Polybutylene succinate (PBS) is a versatile semi-crystalline polymer with a semi-crystalline structure. Due to these characteristics, PBS is in high demand in various fields. In terms of physical properties, PBS exhibits similarities to polyethylene terephthalate. PBS possesses strong elongation capabilities and can be applied in numerous different applications.
The chemical structure of PBS contains an ester group, which will degrade into low molecular weight polymers when exposed to water. As the temperature increases, the degradation rate of PBS also rises.
The chemical structure of the repeating unit in PBS is represented by the formula –[O–(CH2)m–O–CO–(CH2)n–CO]N, as depicted in Figure 2. Specifically, the values of m and n are determined to be 4 and 2, respectively. PBS can exist in two different crystalline forms, known as α and β. The β structure often appears when the material undergoes deformation.
However, PBS has soft characteristics and lacks gas barrier properties. Therefore, it often needs to be combined with other materials, such as fillers, to meet specific technical requirements of applications. PBS offers many processing capabilities, and its glass transition temperature must be lower than room temperature to enable use in various manufacturing methods, including extrusion, injection molding, and thermoforming.
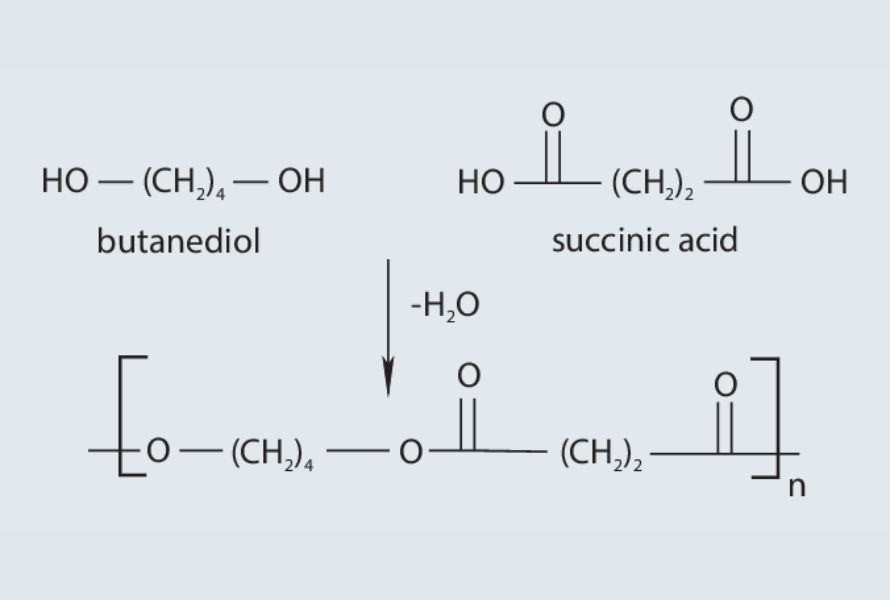
Polybutylene succinate structure
3. Synthesis and production of polybutylene succinate
Typically, PBS is produced through the condensation process of succinic acid (SA) and 1,4-butanediol (BDO). PBS can be manufactured from monomers derived from both petroleum sources and through bacterial fermentation pathways.
BioAmber Inc. commercialized bio-based succinic acid in 2010, while Novamont S.p.A. began producing 1,4-butanediol from renewable resources in 2016.
This synthesis process generally involves two main steps: the first step is the esterification of succinic acid and BDO to create oligomers. The second step is the condensation of these oligomers to produce high molecular weight PBS.
The synthesis process usually takes place in a reaction vessel equipped with mechanical stirring, inert gas injection (usually nitrogen to prevent oxidation during the esterification step), and a distillation column.
This reaction vessel is heated to 160–190 °C to initiate the esterification process during stirring, followed by continued reaction in a controlled environment. When no more water (or alcohol) is distilled at normal pressure, the condensation process continues at high temperatures (220–240 °C).
.jpg)
Synthesis and production of polybutylene succinate
4. Materials synthesized using PBS
Materials synthesized using PBS, also known as bio-based composite materials, are a type of synthetic material in which natural fibers, possessing biodegradability, are combined with a polymer matrix that can be either biodegradable or non-biodegradable.
The development of bio-based composite materials allows for a balance between economic and environmental considerations, as well as the customization of the final material's properties. Among the list of fatty polyesters, PBS stands out as a promising alternative choice for producing high-performance, environmentally friendly biodegradable plastic materials. PBS's excellent processability in fields like textiles and injection molding has made it a highly versatile polymer.
However, PBS also has some limitations, including excessively high softness, poor gas barrier properties, and insufficient viscosity for certain end applications, which need to be addressed. For this reason, the use of composite materials with a
PBS matrix becomes essential to overcome the limitations of the original matrix. Conductive polymers have attracted significant attention due to their potential applications in various fields, such as energy storage, sensors, electromagnetic shielding, corrosion resistance, electronics, electrochromics, and many other areas.
In particular, there is great potential in bio-based composite materials that combine renewable and biodegradable capabilities to create high dielectric constant and low dielectric loss materials used as base or insulating materials for electronic applications.
.jpg)
Materials synthesized using PBS
5. Biodegradability
The biodegradability of plastics refers to their ability to break down into CO2 and water through the action of enzymes and naturally occurring microorganisms after being discarded. PBS and its copolymers are no exception in this regard.
Increasing environmental concerns are driving the exploration of broader applications for these types of plastics.
The biodegradability of polyesters is influenced by various factors, including molecular weight, degree of crystallinity, and chemical structure. Specifically, regarding chemical structure, the presence of ester bonds is vulnerable to bacterial attack and is a primary cause of the biodegradation of these polymers.
The biodegradation of PBS can be studied through various methods, including hydrolytic degradation, enzymatic degradation, and biodegradation under different environmental conditions, such as in activated sludge, burial in soil (according to ISO 846 standards), and composting. In all these methods, the extent of biodegradation is assessed by monitoring the weight loss of the sample, considering changes in mechanical properties, and examining surface structures using scanning electron microscopy (SEM).
.jpg)
The biodegradation of PBS
6. Applications of polybutylene succinate
PBS is a biopolymer with numerous potential applications. With advantages such as biodegradability, biocompatibility, and good mechanical properties, polybutylene succinate products are increasingly being used in various industries.
6.1. Packaging
PBS is used in the production of food packaging, cosmetics packaging, and medical products. PBS can be processed into films, bags, or containers and can be used as a substitute for traditional plastics like polyethylene (PE) and polypropylene (PP). PBS possesses water resistance, gas barrier properties, and antibacterial properties, helping to preserve and protect food and other products.
- Food Packaging: PBS is used to produce food wrapping films, food storage bags, and food containers. PBS's water resistance, gas barrier properties, and antibacterial capabilities aid in prolonging the freshness of food.
- Cosmetics Packaging: PBS is employed for the production of bottles, jars, and cosmetic tubes. PBS's water resistance, gas barrier properties, and UV resistance protect cosmetics from deterioration.
- Medical Packaging: PBS is utilized for the production of medication pouches, syringes, and catheters. PBS's biocompatibility helps minimize the risk of infection.
.jpg)
Applications of polybutylene succinate
6.2. Agriculture
PBS is used in the production of agricultural films, fishing nets, and garden products. PBS's UV resistance helps protect crops from the harmful effects of sunlight, and its biodegradability helps minimize environmental pollution.
- Agricultural Films: PBS is used to produce agricultural films that shield crops from adverse weather conditions and pests.
- Fishing Nets: PBS is used to manufacture fishing nets, reducing environmental pollution.
- Garden Products: PBS is used to produce plant pots, trays, and other garden products.
6.3. Medical
PBS is employed in the production of medical products such as syringes, catheters, and wound dressings. PBS's biocompatibility helps reduce the risk of infection.
- Syringes: PBS is used to manufacture syringes, minimizing the risk of infection.
- Catheters: PBS is used to produce catheters for administering medications or fluids into the body.
- Wound Dressings: PBS is used to manufacture wound dressing pads, providing protection for wounds.
6.4. Other applications
PBS is also utilized in various other applications, including the production of toys, household items, and construction materials.
- Toys: PBS is used to make toys, reducing environmental pollution.
- Household Items: PBS is used to produce household items such as dishes, food containers, and water bottles.
- Construction Materials: PBS is used in the production of construction materials like wall panels and flooring.