Polysulfones (PSU plastic) were invented in the 1960s by the Union Carbide Corporation. It was originally developed for use in the aerospace industry, but its unique properties have since led to its adoption in a wide range of other applications. In this article, we'll take a closer look at polysulfone. We'll discuss its properties, production methods, and applications.
1. What is polysulfone?
1.1. How is polysulfone material made?
Polysulfone is made in a process called polycondensation, involving bisphenol A and 4,4'-dichlorodiphenyl sulfone. The mixture is then heated, helping to accelerate and produce a high-quality polymer.
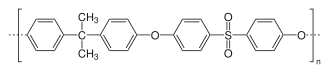
Picture 1. Chemical structure of polysulfones
Polysulfone is precipitated out of the solution by adding a non-solvent, such as water, to the completed reaction. The polysulfone is then filtered and dried to produce a white powder that can be processed into a variety of forms, such as pellets, granules, or films.
1.2. What are the properties of PSU plastic?

Picture 2. 3D-printed polysulfone parts are strong and durable
High-temperature resistance: Polysulfones are ideal for high-temperature applications, such as in aerospace, automotive, and medical devices, as they can withstand continuous use temperatures of up to 180°C (356°F) and brief exposure to temperatures of up to 250°C (482°F).
Chemical resistance: Polysulfones are also resistant to a wide range of chemicals, including acids, bases, solvents, and oils, making them ideal for use in chemical processing and food and beverage industries.
Durability: Polysulfone material is durable, with excellent impact strength and wear resistance. This makes it ideal for use in demanding applications where other materials may fail.
Transparency: Polysulfone material is transparent, making it ideal for applications where visibility is important, such as in medical devices and optical components.
Lightweight: Polysulfones are lightweight, making them ideal for applications where weight is a concern, such as aerospace and automotive components.
Biocompatible: Polysulfone material is safe to use in the human body, making it ideal for use in medical devices and implants.
Flame retardant: Polysulfone is naturally flame retardant, making it ideal for use in applications where fire safety is a concern.
Electrically insulating: Polysulfones are excellent electrical insulators, making them ideal for use in electrical and electronic components.
1.3. What are the different types of polysulfone?
There are three main types of polysulfone material:
- Polysulfone (PSU): Transparent, amber-colored thermoplastic with excellent high-temperature resistance, chemical resistance, and durability.
- Polyethersulfone (PES): Less transparent than PSU, but has even better high-temperature resistance and chemical resistance.
- Polyphenylene sulfone (PPSU): The most expensive type of polysulfone material, but also has the best high-temperature resistance, chemical resistance, and durability.
In addition to these three main types of polysulfones, there are also several other specialized types of polysulfones available.
Learn more about how they differentiate from each other: The Ultimate Guide to High-Performance Plastics
1.4. What are the advantages and disadvantages of polysulfone for businesses and consumers?
Advantages for businesses & customers:
- High performance: PSU plastic offers various high-performance properties. This makes it ideal for a variety of demanding applications, such as medical devices, aerospace components, and food and beverage processing equipment.
- Long lifespan: The material can last for decades, even in demanding applications. This reduces the need for frequent replacement of parts and equipment, which can save businesses money in the long run.
- Versatility: Polysulfones can be processed into a variety of forms and applications, such as sheets, rods, and tubes or electronics, appliances, and housewares.
- Biocompatibility: Polysulfone material is safe to use in the human body. This makes it ideal for use in medical devices and implants.
Disadvantages of polysulfones:
- Cost: The material is relatively expensive, making it a less attractive option for some businesses and consumers.
- Processing: Polysulfones can be difficult to process, requiring specialized equipment and expertise
2. Applications of polysulfones

Picture 3. Polysulfone rods and sheets
2.1. Medical devices
Medical device manufacturers choose PSU plastic for its biocompatibility, durability, transparency, and resistance to sterilization.
Some specific examples of medical devices that use polysulfones include:
- Implants, surgical instruments, and diagnostic equipment: The material is used for implants (artificial joints, dental implants, pacemakers), surgical instruments (scalpels, hemostats, clamps), and diagnostic equipment (MRI machines, CT scanners, X-ray machines).
- Blood dialysis equipment: Polysulfone membranes are used in blood dialysis equipment to filter blood and remove toxins because of their high hydrophilicity, chemical resistance, and durability.
- Laboratory equipment: Polysulfone material is used in laboratory equipment, such as test tubes, centrifuge tubes, and Petri dishes, because of its durability, transparency, and resistance to chemicals.
2.2. Aerospace and automotive components
Polysulfone material is high-performance and is used in a variety of aerospace and automotive components. It's so tough and durable, that it can withstand the extreme temperatures and harsh chemicals of outer space and the open road.
Some specific examples of aerospace and automotive components that use polysulfones include:
- Aircraft components: Polysulfone is used in aircraft components such as windows, interior panels, and wiring insulation. It is also used in engine components such as fuel lines and manifolds.
- Automotive components: Polysulfone is used in automotive components such as bumpers, headlights, and fuel systems. It is also used in engine components such as intake manifolds and turbocharger parts.
2.3. Electronic components
Polysulfone material is like the bouncer of the electrical world. It keeps the flow of electricity going smoothly, while also protecting the sensitive components inside from the outside world.
Some specific examples of electronic components that use polysulfones include:
- Electrical connectors: Polysulfone's excellent electrical insulating properties ensure safe and reliable electricity flow even in demanding conditions.
- Semiconductor packaging: Polysulfone's high-temperature resistance, chemical resistance, and flame-retardant properties protect semiconductor chips from heat, chemicals, and fire.
- Printed circuit boards: Polysulfone's excellent electrical insulating properties, dimensional stability, and resistance to heat and chemicals provide a reliable foundation for all other components and ensure smooth operation.
2.4. Food and beverage processing equipment

Picture 4. Storing food with polysulfone food pans
PSU plastic is a vital part of the food and beverage processing industry, and it helps to keep our food safe and fresh. Some specific examples of food and beverage processing equipment that use polysulfone material include:
- Food processing equipment: Polysulfone is used in food processing equipment such as mixers, conveyors, and packaging machines. It is chosen for its high-temperature resistance, chemical resistance, and durability.
- Beverage processing equipment: Polysulfone is used in beverage processing equipment such as bottling machines, canning machines, and kegs. It is chosen for its high-temperature resistance, chemical resistance, and transparency.
2.5. Water filtration membranes
Polysulfone material is highly hydrophilic, making it ideal for water filtration membranes. Polysulfone membranes are used to remove a wide range of contaminants from water, including bacteria, viruses, and heavy metals.
Polysulfone membranes are used in a variety of water filtration applications, including municipal, industrial, and residential water treatment.
3. Conclusion
Polysulfone is a versatile and amazing thermoplastic material with a wide range of applications. It is a vital material for many modern products and technologies.
If you are interested in learning more about polysulfone or other high-performance plastics, please visit EuroPlas website. We have a wide range of articles and resources to help you learn more about these materials and their applications.