
The advent of 3D printing technology has revolutionized the manufacturing industry, allowing for the creation of complex and intricate objects with relative ease. One of the key factors that determine the success of a 3D printing project is the 3D printing plastics. There are a wide variety of plastic materials for 3d printing, each with its own unique set of properties and characteristics. In this article, we will explore the most common type of plastic used in 3d printers and their respective properties and applications.
I. What is 3D printing?

3D printing is a process of making three-dimensional solid objects from a digital file. A 3D printer will read a digital design file and build the object layer by layer. The materials used for 3D printing vary widely and can include plastics, metals, ceramics, and even food.
You can read more about 3D printing and how is masterbatch plastic applied in 3D printing.
II. Types of plastic for 3D printing
1. ABS

ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) is a thermoplastic renowned for producing lightweight components and having strong impact resistance at low temperatures. It is mostly employed in the home appliance industry, but it is also used in toys, boat hulls, décor items, and particularly the renowned LEGO bricks. Along with PLA, ABS plastic is highly well-liked in the FDM 3D printing market because of the following reasons:
- Strong mechanical properties: Particularly when compared to PLA, ABS has excellent mechanical qualities. It is a fantastic material for "wear and tear" applications because of its robustness, toughness, and ductility.
- Post-processing: ABS is a good candidate for a number of post-processing methods including sanding, painting (with acrylic paints), painting, gluing, milling, drilling, and cutting. ABS may also be polished using acetone to provide a glossy surface finish since it is a material that is soluble in acetone.
- New materials: Materials with better characteristics may be made using ABS. The characteristics of these materials includebiocompatibility, conductivity, and translucency. Similar to nylon, ABS may be combined with other substances to increase its mechanical qualities; an example of this is PC-ABS (polycarbonate-ABS), which has higher strength and heat resistance.
- Accuracy: ABS prints may make dimensionally precise parts which often have minimum features as tiny as 1.2 mm. However, printer settings and the complexity of a component mostly dictate the degree of accuracy.
2. PLA

Unlike other commercial materials derived predominantly from petroleum, PLA, also known as polylactic acid or polylactide, is a thermoplastic created from renewable resources such as maize starch, tapioca roots, or sugar cane. This material has gained popularity in the 3D printing because of the following reasons:
- Low printing temperature: Compared to other thermoplastics, PLA has a lower printing temperature (the optimal printing temperature for PLA is approximately 180°C, while the ideal printing temperature for ABS is around 250°C). This indicates that PLA has a lower propensity to distort and clog the nozzle during printing.
- Ease of use: PLA is one of the simplest materials to use as filament for 3D printing. Its versatility in adhesion and lack of need for a heated print bed further contribute to the material's use. PLA, unlike ABS, doesn't release unpleasant fumes when printing.
- Variety of color and blending options: PLA is readily colored and available in a wide variety of hues and mixtures. To create luminous or sparkly filaments, PLA may be combined with wood, carbon, pigment, metal, and many other materials.
- Easy post-processing: Since PLA prints are simple to sand, polish, and paint, a better surface quality may be achieved with minimal effort. Moreover, PLA pieces may be milled, drilled, and glued; just be cautious not to melt the part.
3. ASA

ASA (Acrylonitrile Styrene Acrylate) is the amorphous thermoplastic terpolymer material similar to ABS. The structural difference between these two materials is that the ASA utilizes an acrylic elastomer and the ABS uses a butadiene elastomer. Because of its development as an "advanced ABS," ASA is a material that 3D FDM/FFF printer users are using more often.
Why is ASA used in 3D printing?
- Ease of printing: ASA plastic is relatively easy to print, with a low shrinkage rate and good adhesion to the print bed. This means that it is less likely to warp or curl during the printing process, which can be a common problem with other types of plastics. ASA plastic also has a low printing temperature, which makes it easier to print with than other high-temperature materials.
- Compatibility with FDM printers: ASA plastic is compatible with Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) printers, which are the most common type of 3D printer. So it can be used with a wide range of 3D printers, making it a versatile material for 3D printing.
4. PET
PET is a rigid, durable plastic used to create goods for food packaging, bottling, and waterproofing. Due to its mechanical qualities, chemical resilience, and advantageous melting temperature, it is one of the most often used materials for FDM/FFF-style 3D printing.
Why is PET used in 3D printing?
- Ease of printing: PET does not require a heated build chamber like some other materials. Hence, users who do not have access to a high-end 3D printer can easily utilize this material. PET also has good layer adhesion, which means that printed parts have good strength and reliability.
- Low shrinkage rate: PET printed objects will not warp or curl as they cool down. This reduces the risk of print failure and ensures that the final product is accurate and precise.
- Transparency: PET is a popular choice for creating objects that need to be see-through, such as bottles or containers. It is also available in a range of opaque colors.
5. PETG

PETG, also known as glycolic polyester, is a thermoplastic that is often used in the market for additive manufacturing. It has the ease of use of PLA ,the durability of ABS and the recyclability of PET.
Why is PETG used in 3D printing?
- Combination of properties: PETG is seen as a mixture between ABS and PLA, but PETG is stronger than PLA (though weaker than ABS) and more flexible than ABS (though less flexible than PLA).
- Hygroscopic: PETG absorbs moisture from the surrounding environment. Its hygroscopic nature can help reduce the risk of warping or delamination during printing by pulling moisture out of the filament and preventing it from expanding and causing distortions.
- Ease of printability: PETG can be printed at lower temperatures. Additionally, it can be printed faster than other materials, reducing printing time and increasing productivity.
- Smooth surface finish: PETG's smooth surface finish makes it a great choice for creating objects that require a high-quality finish, such as consumer products or decorative objects. Additionally, the glossy finish can enhance the appearance of the printed object and help it look more polished and professional.
6. PC

PC is a high-performance synthetic filament that is used in the fused filament production method of 3D printing. It canbe recycled and modified via the use of engineering to fulfill specific application or processing criteria, such as minimal warping. Because of its tenacity and stiffness, it is an excellent choice as a material for challenging applications of 3D printing.
Why is PC used in 3D printing?
- Tough material: When it comes to online 3D printing, polycarbonate (PC) filament has certain benefits over other filaments like PLA and ABS since it is a durable substance.
- Flexibility and resilience: Compared to PLA and nylon, PC has a superior durability and flexibility rating. Although stronger than ABS, PLA, or PMMA, it is lighter and less thick than ABS. It can withstand higher torsional stress than other thermoplastics and is flexible enough to be twisted without breaking at room temperature.
- High heat resistance: As polycarbonate maintains structural integrity up to 150 °C (in contrast to PLA, which starts to distort at 60 °C).
7. PEEK

PEEK, or polyether ether ketone is a semi-crystalline thermoplastic with excellent mechanical qualities that are widely used in the 3D printing industry.
Why is PEEK used in 3D printing?
- Performance improvement: PEEK can withstand heavier loads, faster speeds, and severe resistance to oil and gas, and chemicals. It can also assist in halting corrosion and minimizing friction. The HDT glass transition temperature for PEEK is 0.45 MPa 180°C (356°F).
- Lightweight: PEEK's specific weight (1.3 g/cm3) is one-sixth that of steel and one-half that of aluminum. Therefore, the costs for installation, shipping, and maintenance are decreased by weight reduction.
- Less waste: 3D printing uses thermoplastic material because it is more energy-efficient than any other processing with metal. Thermoplastics can be melted, hardened, and again melted, hardened,...
8. PP
.jpg)
Polypropylene (PP) is often utilized in a range of applications, including packaging, consumer goods, and automotive products. With its technological advantages, PP, a material choice for selective laser sintering technology, provides solutions appropriate for a range of sectors.
Why is PP used in 3D printing?
- Greater bendability and improved deformation resistance: PP is more likely to bend than PLA, and it can withstand loads without deforming as well. This enables the use of polypropylene in circumstances when more bending is expected (e.g., plastic lid for Tic Tak).
- Lightweight: Polypropylene has the lowest density of all the materials often used to manufacture plastics. As a result, more components might be made from the same quantity of PP than, say, PLA.
- Better strength-to-weight ratio: While being lighter than steel, polypropylene is more prone to bending and can support heavier weights.
9. Nylon
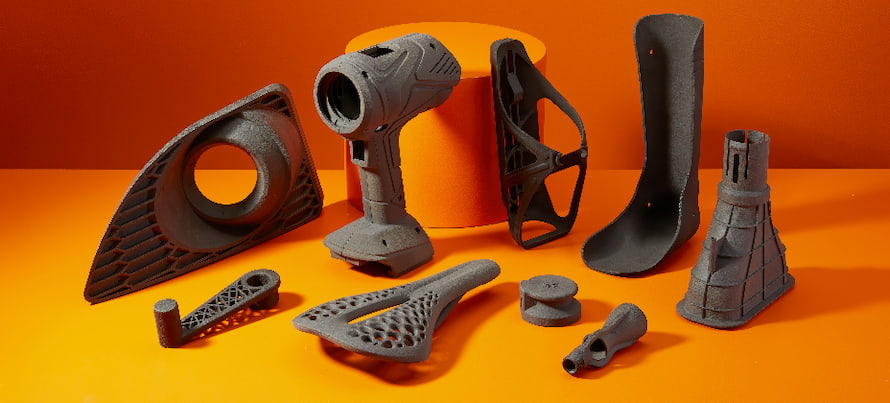

Nylon is a semi-crystalline thermoplastic. Despite having a bad reputation as a tough material to deal with, nylon is often utilized in 3D printing.
Why is Nylon used in 3D printing?
- Nylon may be reinforced with carbon or glass fibers to produce lightweight components with high mechanical qualities, making it ideal for prototypes and functional items like gears and tools.
- The rigidity-to-flexibility ratio of nylon is excellent. As a result, when you print your component with thin walls, it will be flexible, and when you print it with larger walls, it will be stiff. This makes it possible to create components with hard portions and flexible joints, such as living hinges.
- Less post-processing is needed since items printed in nylon often have an excellent surface polish.
- Moving and interconnecting pieces may be produced using 3D printing with nylon when powder-bed technologies like SLS and Multi Jet Fusion are used. This eliminates the need to assemble individually printed components and enables highly complex objects to be produced more quickly.
10. TPU
Thermoplastic Polyurethane, or TPU, is an engineering polymer with exceptional performance. This thermoplastic has a wide range of opportunities for designers, engineers, and producers because of its special qualities.
Why is TPU used in 3D printing?
- Creating adapted products: If you want flexible components that are produced to order, 3D printing TPU will be your best option. Your company will have a competitive edge if you offer customers both bespoke items and experiences.
- Design flexibility: With TPU, 3D printing enables the creation of components with differing degrees of elasticity, based on the various zones and thicknesses. It enables the production of lighter components that are simple to integrate into settings where this characteristic is important, like the automobile or aviation industries.
11. PVA
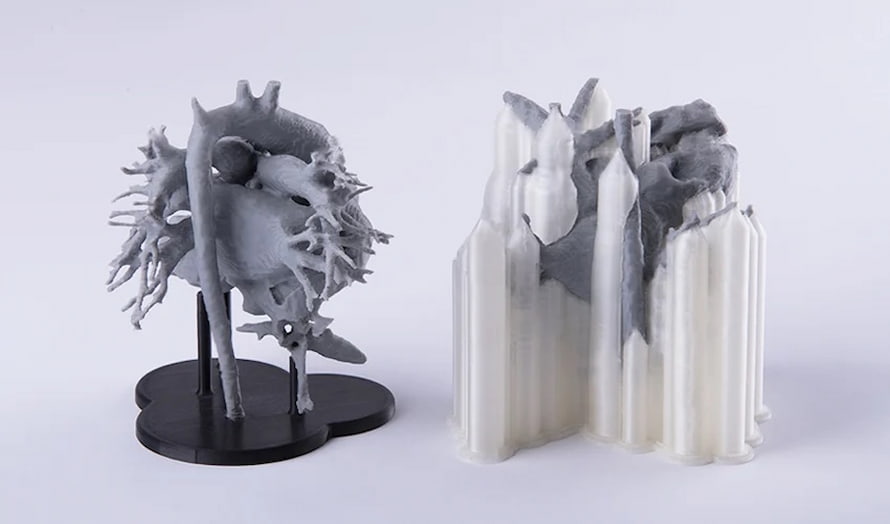

PVA, or Polyvinyl Alcohol, is a soft and biodegradable polymer that is highly sensitive to moisture. When exposed to water, PVA will actually dissolve, which makes it a very useful support structure material for 3D printing.
Why is PVA used in 3D printing?
- Water-solubility: PVA is highly soluble in water, which makes it easy to remove after the printing process is complete. This eliminates the need for manual removal, which can be time-consuming and can damage the printed object.
- Compatibility with other materials: PVA is compatible with a wide range of materials used in 3D printing, including PLA, ABS, and Nylon. PVA can be printed with a separate extruder or a dual-extruder printer, where one extruder is used to print the model and the other extruder is used to print the support structure.
12. HIPS

HIPS (High Impact Polystyrene) is a thermoplastic material that is commonly used as a support material in 3D printing. HIPS is similar to ABS in terms of its properties, but it is more brittle and has a lower melting point.
Why is HIPS used in 3D printing?
- Support material: HIPS is compatible with a wide range of materials used in 3D printing, including ABS. HIPS can be printed with a separate extruder or a dual-extruder printer, where one extruder is used to print the model and the other extruder is used to print the support structure.
- Ease of printing: HIPS is easy to use and can be printed with standard 3D printers. It does not require any special equipment or settings, but it does require careful control of temperature and cooling during the printing process to ensure optimal results.
- HIPS is also easy to post-process, as it can be sanded or painted to achieve the desired finish.
III. About EuroPlas

As the world's No. 1 filler masterbatch manufacturer, EuroPlas is proud to offer a unique plastic material solution that helps customers' factories optimize production costs and improve their competitiveness in the market. Our engineering plastics products are a full-featured solution for use in 3D printers.
Advantages of EuroPlas' plastic material:
- Bring the full features of the finished product in a single input material
- Specialized design according to finished product characteristics
- Improve mechanical properties for finished products: increase hardness, impact resistance
If you want to learn more information about our products, do not hesitate to contact us for the earliest advice and support!