Nylon, a ubiquitous material known for its strength and printability, is experiencing a renaissance. Traditionally crafted from polyamide (PA), a family of synthetic polymers, nylon excels in creating functional parts that endure wear and tear. But the story doesn't end there. Cutting-edge filament advancements are pushing the boundaries of what this versatile material can achieve.
Are you curious to discover how the future of this essential material is shaping up? Find out the compelling trends and innovations that promise to propel nylon filament to new peaks.
1. Unveiling sustainable nylon filaments: recycled and bio-based solutions
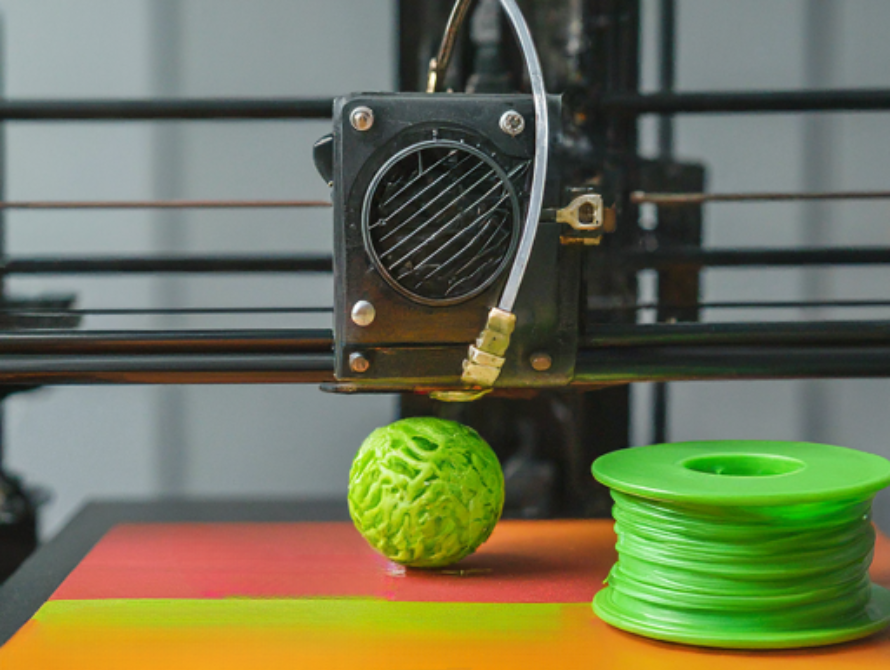

Bio-based nylon filaments offer a sustainable alternative for 3D printing, reducing environmental impact.
The nylon filament industry is experiencing a surge in demand for sustainable alternatives. This trend is fueled by the development of filaments made from recycled nylon waste or bio-based materials derived from renewable resources.
Consumers and businesses alike are increasingly prioritizing environmental responsibility and seeking eco-friendly options, driving the demand for sustainable nylon filaments.
Recycled Nylon-6 granulate filaments exemplify the sustainable revolution in nylon filaments. They offer both eco-friendliness by reusing waste and impressive strength, making them potential game-changers for 3D printing.
Traditional nylon production relies heavily on fossil fuels, raising significant environmental concerns. Recycled nylon and bio-based filaments offer a solution to this challenge:
- Recycled nylon: This type of filament is created by reprocessing pre-consumer or post-consumer nylon waste, such as discarded fishing nets or carpet scraps. This not only minimizes reliance on virgin nylon production but also reduces the environmental impact by diverting waste from landfills and conserving resources.
- Bio-based nylon filaments: Derived from renewable plant-based sources like castor beans or plant-based monomers, bio-based filaments offer a completely renewable alternative with a potentially lower carbon footprint compared to traditional methods.
Both recycled and bio-based filaments exhibit impressive versatility. They can be seamlessly integrated into a wide range of applications currently dominated by traditional nylon. Additionally, advancements in incorporating fillers like glass into recycled or bio-based nylon filaments are being explored to potentially improve their mechanical performance while maintaining sustainable practices.
The adoption of sustainable nylon filaments has the potential to significantly reduce the environmental impact of the nylon industry. By promoting resource efficiency and aligning with the growing principles of the circular economy, this trend signifies a shift towards a more sustainable future.
2. High-performance nylon filaments: conquering demanding applications
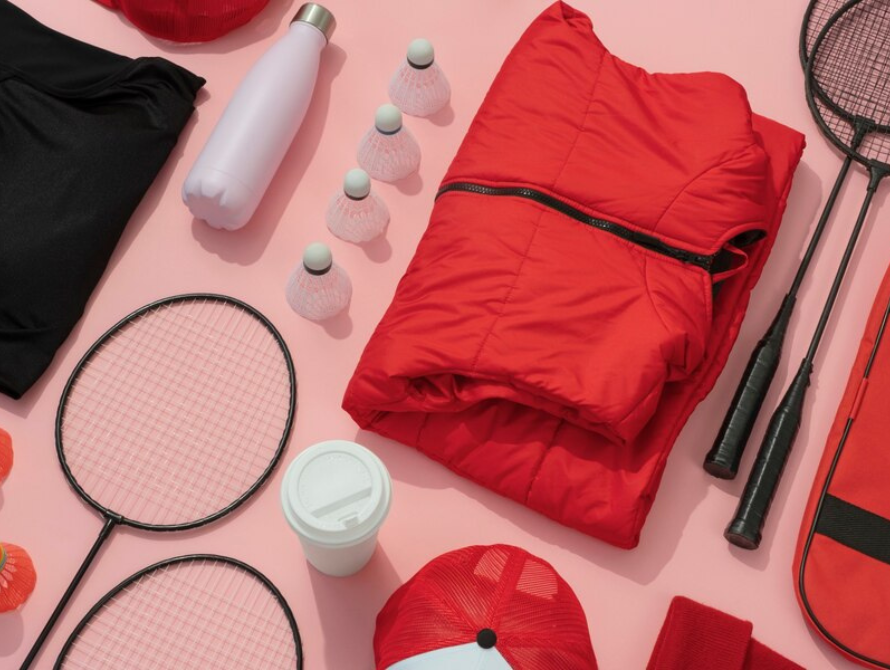

Carbon fiber reinforced nylon filament is ideal for demanding applications like high-performance sporting goods.
The global high-performance plastics market, valued at USD 24.80 billion in 2023, is forecast to experience significant growth, reaching an estimated USD 54.92 billion by 2032.
The increasing demand for lightweight yet robust materials in various industries, such as aerospace, automotive, and extreme sports equipment, is driving the development of high-performance nylon filaments.
High-performance nylon filaments are often reinforced with special additives, significantly enhancing their characteristics, including:
- Enhanced strength and durability: Ideal for components in extreme environments, like automotive parts and machinery.
Improved heat resistance: Withstands high temperatures, making them suitable for applications like engine parts and heat deflection components.
- Chemical resistance: Unaffected by harsh chemicals, perfect for use in laboratories and industrial settings.
- Lightweight yet robust: Many high-performance nylons achieve exceptional strength while maintaining a lightweight profile. This translates to weight reduction in applications where it matters, such as aerospace and automotive components.
Best nylon filament manufacturers are introducing innovative high-performance filaments, such as carbon fiber reinforced nylon or glass filled nylon grades.
Carbon fiber reinforced nylon combines incredible strength with easy processing, making it ideal for demanding applications like aerospace, automotive under-the-hood components, and sporting goods (think strong, lightweight bicycle frames).
For a step up in everyday uses, there's also glass-filled nylon filament. These filaments have tiny glass particles mixed in, boosting strength, stiffness, and stability. They're perfect for automotive parts needing moderate heat resistance, durable housings for tools and appliances, or even industrial components like gears and bearings.
3. Innovative nylon filament blends: unveiling unique properties
Conductive nylon filament blends in robotic arms with integrated electrical conductivity.
There's another exciting development in nylon filaments: increased versatility. By combining nylon with other materials, manufacturers are creating unique blends with special functionalities. Imagine filaments for super specific applications or even products you wouldn't have thought possible with nylon! Here are some examples:
3.1. Conductive nylon filaments:
During production, the chosen conductive material is mixed with molten nylon using techniques like melt blending or co-extrusion. This ensures the conductive particles are evenly distributed throughout the filament.
The choice of conductive filler has a significant impact on the filament. Carbon nanotubes provide excellent conductivity but come at an expense. Metal flakes are less expensive, but have somewhat lesser conductivity and may wear down your printer nozzle faster. Graphene, a rising star, has high conductivity and printability, but its application in filament production is still being developed.
Conductive nylon filaments open doors for a wide range of applications due to their ability to transmit electricity:
- Printed electronics: Create functional circuits for sensors, LED lights, and even simple embedded systems directly within your 3D printed object.
- Wearable tech: Integrate conductive elements into clothing or accessories for health monitoring, touch sensors, or even light-up designs.
- EMI shielding: Print enclosures for electronic components to block electromagnetic interference.
3.2. Heat-resistant nylon filaments:
Similar to conductive filaments, heat-resistant nylons are created by incorporating heat-resistant additives during the melt blending or co-extrusion process.
Common additives include heat-resistant ingredients like aromatic rings for enhanced heat tolerance, short glass fibers for added strength and deflection, and heat stabilizers to prevent the nylon from breaking down under high temperatures.
Heat-resistant filaments open doors for projects that encounter high temperatures:
- Functional prototypes: Print prototypes for engines, hot water components, or even parts used in high-temperature environments.
- End-use parts: Create durable tools, jigs, or fixtures that can withstand significant heat without warping or melting.
- Automotive and aerospace applications: Print lightweight, heat-resistant components for use in vehicles or aircraft.
4. Nylon filaments in medical and healthcare: a growing trend
Nylon filament is offering personalized solutions for improved patient care.
This trend capitalizes on nylon's inherent advantages – biocompatibility, strength, and printability – making it a prime candidate for the development of next-generation medical devices and equipment.
The increasing demand for personalized medical solutions, coupled with advancements in 3D printing technology, is fueling the use of nylon filaments in healthcare. These filaments offer several advantages:
- Biocompatibility: Certain nylon formulations exhibit biocompatibility, meaning they can be safely implanted in the body with minimal risk of rejection.
- Strength and durability: Nylon filaments offer good mechanical properties, making them suitable for applications requiring strength and wear resistance.
- Printability: Nylon filaments possess excellent printability, allowing for the creation of complex and customized medical devices using 3D printing techniques.
The trifecta of biocompatibility, strength, and printability makes them suitable for medical applications, such as:
- Prosthetics and orthotics: Nylon filaments can be used to create customized prosthetics and orthotics, tailored to individual patient needs for improved comfort and functionality.
- Surgical guides and instruments: 3D-printed surgical guides made from nylon can enhance surgical precision and efficiency. Additionally, nylon filaments can be used in certain surgical instruments requiring strength and biocompatibility.
- Drug delivery systems: Novel drug delivery systems can be designed using nylon filaments, allowing for controlled release of medication over time.
- Surgical sutures: High-strength nylon filaments can be used as sutures, promoting faster healing and minimal tissue disruption.
5. 3D printing with nylon filaments: revolutionizing construction and architecture
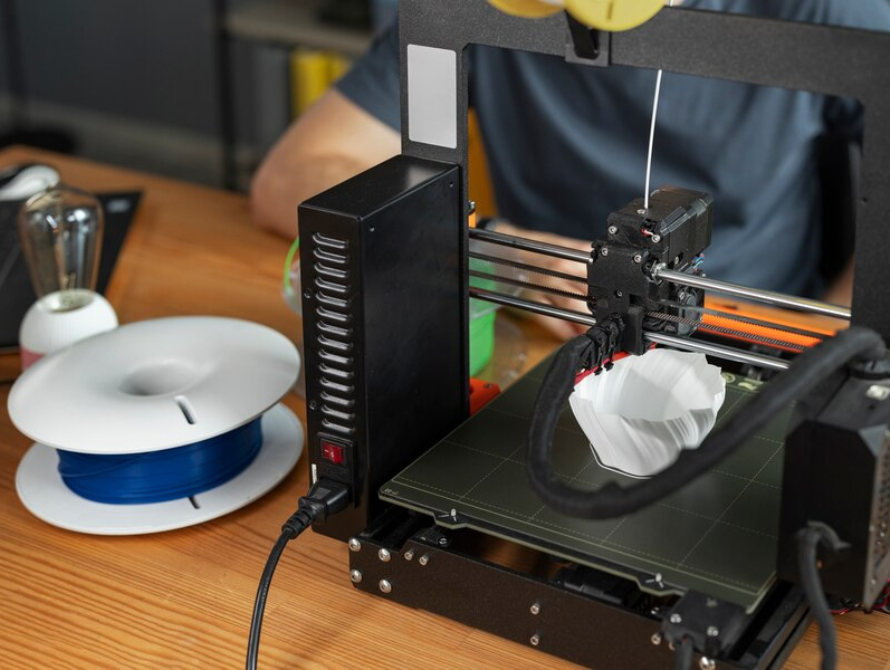

3D printing with nylon filament opens doors for innovation and efficiency.
The capabilities of 3D printers have steadily improved over the past few decades. Larger build volumes, faster printing speeds, and better material handling have made 3D printing more feasible for larger-scale construction projects.
Nylon filament, known for its strength, versatility, and printability, is playing a pivotal role in this revolution. 3D printing with nylon filament offers exciting possibilities in construction and architecture, including:
- Prototyping architectural models: Complex architectural models can be rapidly fabricated using nylon filament. This allows architects and designers to iterate on designs quickly and efficiently, leading to more optimized and innovative structures.
- Functional building components: Nylon's strength and lightweight properties make it suitable for 3D printing functional building components. These can include non-load-bearing walls, cladding panels, and even customized furniture elements.
The integration of 3D printing with nylon filament in construction and architecture brings several benefits:
- Revolutionizes construction workflows: 3D printing offers on-demand manufacturing of building components, potentially streamlining construction workflows and reducing reliance on traditional prefabrication methods.
- Reduces waste: With precise material deposition, 3D printing helps minimize construction waste compared to conventional methods.
- Fosters innovation in building design: The ability to create complex geometries and customized elements unlocks new possibilities for architects and engineers, pushing the boundaries of design innovation.
- Caters to the growing 3D printing industry: The construction sector's adoption of 3D printing further expands the market for this rapidly developing technology.
6. Conclusion
The unique properties of nylon, including its strength, versatility, and printability, combined with ongoing advancements, position it as a key player in the future of 3D printing.
The future of this market is bright, promising continued growth and a wave of innovative applications that will transform the way we design, create, and interact with the world around us. Whether it's creating customized medical devices, functional prototypes for electronics, or even educational tools, the potential of nylon filaments is truly limitless.
7. About EuroPlas
At
EuroPlas, we're more than just a filler masterbatch manufacturer. We're a team of passionate innovators dedicated to providing our customers and partners with the tools they need to succeed in a globalized market.
Our core values – a global mindset, unwavering innovation, and a commitment to sustainability – are woven into everything we do. We translate these values into tangible benefits for our partners. By partnering with EuroPlas, you gain more than just a supplier – you gain a trusted advisor with a global perspective and a commitment to your success.
Need help navigating the ever-evolving world of plastic materials? Visit our
blog for a library of articles on various plastic types and their applications.