Thanks to its ductile properties, plastic can be molded, extruded or injection molded into solids of various shapes. In addition, plastics carry a wide range of outstanding properties such as being lightweight, durable, flexible, and inexpensive which has led to them being used in every aspect of people's lives today from packaging to cars and even in medical implants.
To enhance the properties of plastics to meet the technical requirements of different areas, the plastic products industry uses several chemicals that can be harmful to human health. This article will outline common chemicals used in the production of plastics and what dangerous chemicals are in plastics.
You may be interested in:
- Is plastic chemical resistant? The chemical resistance of plastics
- Why Does Plastic Turn Yellow Over Time? Preventing Plastic Discoloration
- List of plastic toxins and how to avoid toxic chemicals in plastics

1. BPA
Bisphenol A, abbreviated as BPA, is one of the chemicals used in the manufacture of plastics in general and PC plastic products in particular. Also, it isan additive in the production of other hard plastic and transparent plastics. We can find BPA in consumer goods such as food and beverage containers, sports equipment, dental sealants, and more.
BPA is classified as a hormone disruptor in women and is one of the dangerous chemicals that can cause cancer in humans. Another danger of BPA is that it can affect the brain development of infants. Therefore, BPA belongs to the group of bisphenol chemicals that are restricted by regulators.
2. Phthalates
Phthalates are plastic softening chemicals used to make finished plastic products less brittle, increasing flexibility, transparency, durability, and longevity.
However, because this chemical does not bind tightly to other molecules in the plastic, they often migrate from the plastic product into the human body. Phthalates classified as endocrine disruptors have been linked to reproductive malformation in boys.
Recently, the use of phthalates has been declining due to increasing awareness of its dangers. Factories have been reducing the use of phthalates as plasticizers and are looking for safer alternatives.

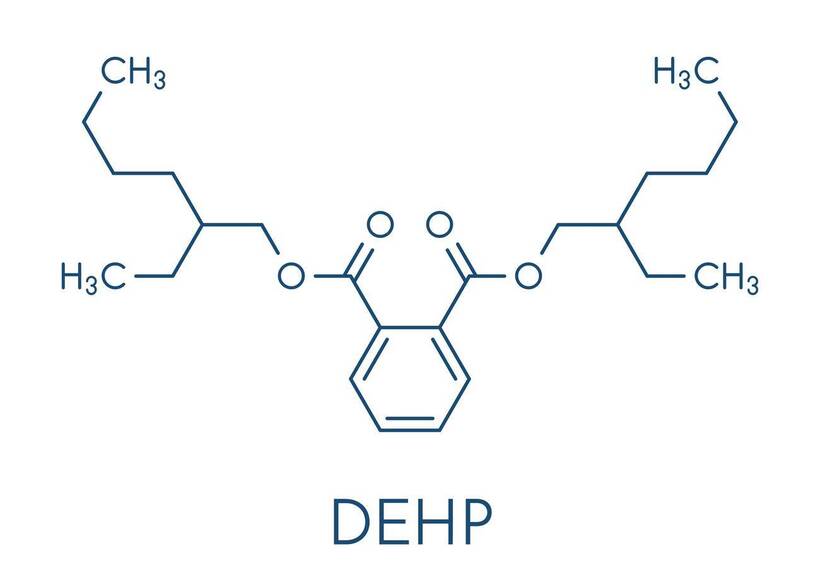
3. DEHP
Another chemical used to makde plastic is DEHP. DEHP or Bis(2-Ethylhexyl) phthalate,is one of the most common phthalates. Low cost but high properties are the main reasons why DEHP is the plasticizer that manufacturers choose for the production of plastics.
Today, DEHP has been banned for use in the plastics industry because it is carcinogenic, teratogenic, and also an irritant to the human body because DEHP acts as an endocrine disruptor. This will cause long-term damage to the reproductive function of both adults and children exposed to it.
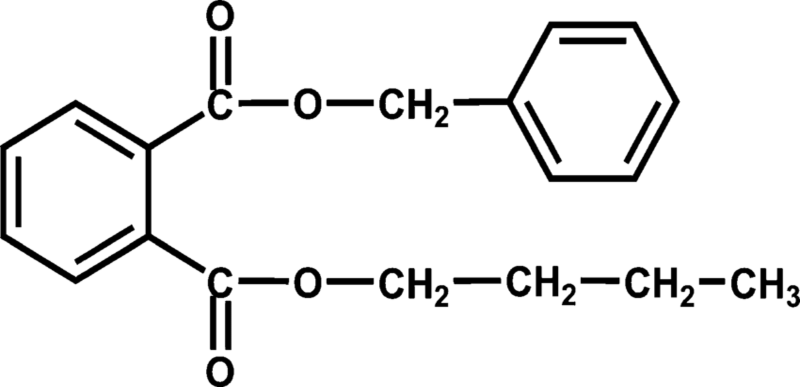
4. BBP
BBP stands for Benzyl butyl phthalate, a substance in the group of phthalates, commonly used to make soft and pliable plastic products. It is present in many consumer products such as plastic bags, bottles, wrappers, food containers, synthetic leather, etc.
Consuming foods that are exposed to BBP can increase fat flow in the body, cause cancer, cause gene mutations, and harm reproduction.
In the European Union (EU), BBP is banned in all toys and baby care products. The EU has also banned the use of BBP in nail polish because it can still be toxic due to prolonged contact with nails. The United States and several other developed countries have established limits on the allowable percentage of BBP in certain consumer products.
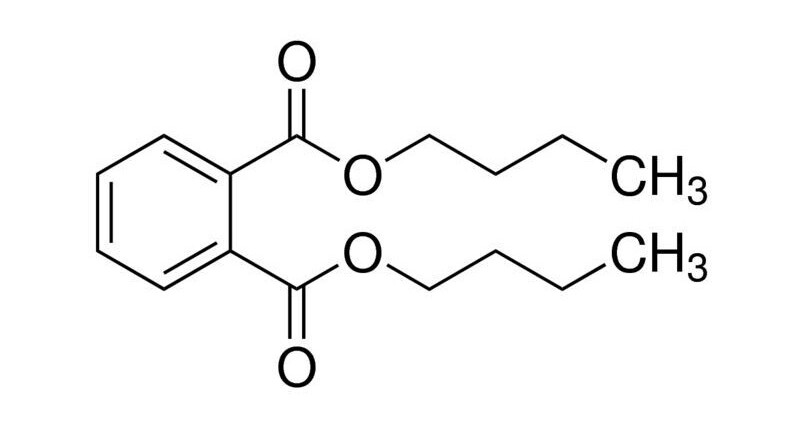
5. DBP
Dibutyl Phthalate (DBP) is also a chemical of the phthalate group used to plasticize PVC. It is also used as a binder additive in printing inks and paints.
Similar to other chemicals of the phthalate group, DBP also causes artificial endocrine disruption. The use of this substance in cosmetics and nail polish is prohibited in the European Union and the United States. In addition, it is also limited to certain concentrations in the production of children's toys.
6. Carbon
Carbon is one of the most common chemicals in plastic production. It can be said that plastic cannot be created without carbon. Carbon bonds when combined with other elements make different types of plastic. An example is polyethylene (PE) plastic which is composed of many ethylene groups CH2-CH2 (one carbon and two hydrogens) joined together.
7. Hydrogen
Hydrogen is a transparent, odorless gas. But when hydrogen is bonded to the carbon atom in different proportions will create different monomers. Thence, the monomers bond with other elements to create diverse forms of polymers. In short, like carbon, hydrogen is an integral part of the plastic manufacturing process because all plastics start with a hydrocarbon chain.
8. Oxygen
Oxygen is one of the chemicals used in the manufacture of plastics. With a certain amount of carbon and hydrogen elements, the introduction of two oxygen molecules form ethyl methacrylate which is used to polymerize into PMMA plastic, or form ethyl acrylate polymerized with other monomers to produce thermoplastics.

Plastic products that use chemicals
9. Nitrogen
Nitrogen is used instead of oxygen in the injection molding process. Because oxygen can lead to the discoloration of clear plastics, such as polycarbonate. Polycarbonate is known for its high transparency, and oxidation can change this.
Gas-assisted injection molding (GAIM) is a process used to manufacture large plastic parts. The problem with large molds is that the plastic can shrink at the cooling stage. However, when nitrogen is injected into the mold, the polymer expands to fill the void in the mold during cooling.
With plastic extrusion to create tubular plastic products, nitrogen is used to replace oxygen. This prevents oxygen damage to the production equipment and final product properties.
10. Parabens
Parabens are a type of antimicrobial preservative widely used in various consumer products, including plastic packaging. So far, studies have shown that this substance is relatively safe, with only negligible risks to the endocrine system.
However, there are still some studies that classify parabens as endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs). More time and data are needed to evaluate the possible health effects of parabens on the human body.
11. ALKYLPHENOLS
Alkylphenols have long been used in industries, as a surfactant found in detergents, cleaning products, antistatic agents, hair care products, and additives in plastic production.
Alkylphenol compounds are used in thermoplastic manufacturing as antioxidants and flame retardants. Another alkylphenol derivative is alkylphenol phosphite which is used as a UV stabilizer in plastics.
12. DIOXIN
Dioxin appears during the manufacturing of plastic products containing BFRs (brominated flame retardants) and when BFR-containing plastics are burned or heated during recycling to be re-molded into new products.
Dioxin is considered the most toxic substance in the world, it affects brain development, disrupts the function of the immune system, and increases the risk of cancer.
In fact, dioxin is not used in the manufacture of anything, including plastics. However, dioxin exposure can occur through the use of recycled plastic products derived from plastics containing brominated flame retardants.
13. PERFLUORINATED COMPOUNDS
Perfluorinated compounds are widely used in water, stain-resistant clothing, food wrappers, paints, and other industrial and consumer applications. In addition, perfluorinated chemicals are used to make fluoropolymer plastic. Fluoropolymers are used in industrial coatings because they possess excellent non-stick properties.
Industrial use of perfluorinated chemicals pollutes drinking water and groundwater. In the consumer sector, they seep from food wrappers and nonstick cookware onto our food. They disrupt metabolic processes that affect the immune system, liver, and thyroid function, increasing the risk of cancers.

Applications of fluoropolymers
14. UV STABILIZERS
UV stabilizers are additives used to protect plastic building materials, plastic auto parts, and other plastic products from damage caused by UV rays.
UV stabilizers can seep from food containers into our food. They disrupt endocrine function, hindering normal development in humans. Therefore, UV stabilizers are listed as persistent organic pollutants.
15. BROMINATED FLAME RETARDANTS, BFRs
A brominated flame retardant (BFR) is a chemical used to reduce flammability in plastic products and prevent the spread of fire. They are found in PS and epoxy plastics used to manufacture electronic enclosures and wire coatings, household appliances, and plastic children's toys.
This chemical leaches out from plastic products that contain BFRs, for example, young children get BFR from toys made from recycled plastic containing BFRs. BFRs disrupt reproductive development in both men and women, altering thyroid and nerve development.

BFRs in some plastic products