Injection molding is a well-known method of producing polymers. It is commonly utilized in the mass production of identical parts with strict tolerances. It is a low-cost, highly reproducible technique that produces high-quality components for large-series manufacturing.
But how much does injection molding cost? The answer to this question depends on many factors. You've got mold costs, labor costs, part sizes, part design, project size, and several other elements that play into the final cost of this type of job.
In this article, we shall deconstruct the possible cost of injection molding by outlining all of the factors available. Understanding everything that goes into a plastic injection molding project allows you to quickly estimate the potential cost and break down quotations you receive to assess if you're getting a fair price. Let’s get started!
Đọc thêm:
- Injection molding color mixing problems and solutions
- Difference between thermoforming and injection molding
- The Difference between Extrusion Blow Molding and Injection Molding
- Common plastics for injection molding that you need to know
- How to effectively apply colorants in your plastic injection molding?
- After mixed with masterbatch, how was plastic processed with injection molding?
I. How much does injection molding cost
Injection molding
Source: Prototech Asia
1. How cost of injection molding is calculated?
Costs for injection molding range from $10,000 to $100,000, depending on the size of the order, the complexity of the item, and other elements. However, due to poor part quality and poor mold creation, cheap injection molding typically ends up costing the client more.
Large production quantities are where injection molding excels since it can be costly to start up but is less expensive in the long term. The cost of the resin itself, tooling, cycle time, mold cavitation, and other elements all have an impact on the total cost you would pay for injection molded items.
Plastic injection molding is a manufacturing technique that involves multiple phases as well as the skill to ensure that each step is completed correctly. Cutting shortcuts at any point in the process might have serious effects later on. When seeking economical injection molding solutions, it is critical to choose a provider with expertise and know-how. Everyone wants inexpensive injection molding, but not the cheap results that come with it.
The injection molding method offers low variable costs due to the affordable thermoplastics materials, quick cycle times, and gradually decreasing labor requirements as a result of automation and economies of scale, despite the significant fixed start-up costs. As a result, the manufacturing process becomes more effective and the cost per part lowers in bigger quantities as the expenses are divided over hundreds or thousands of components. This indicates that the variable costs of production are minimal.
2. Types of cost in plastic injection molding
2.1. Equipment cost
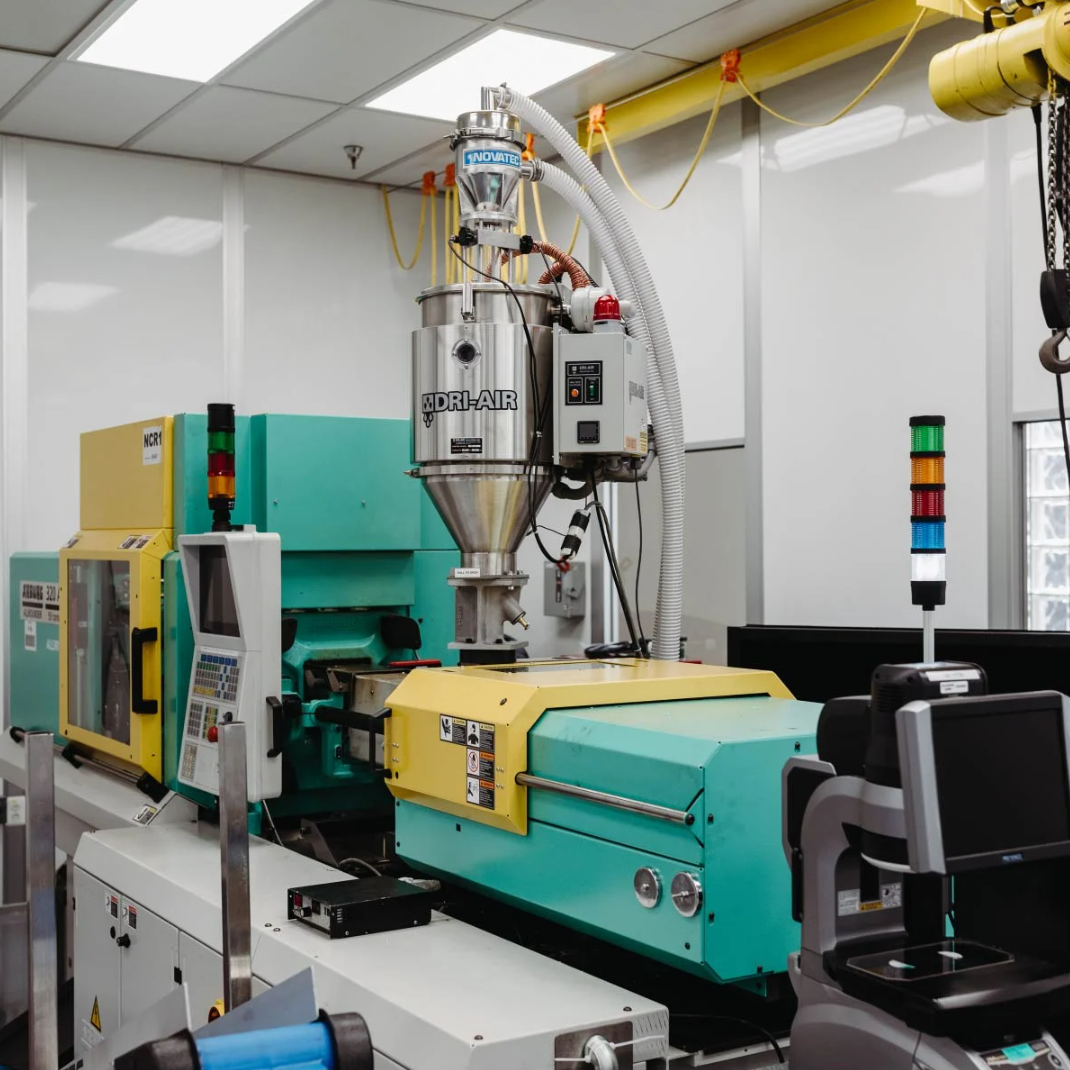

Injection molding machine
Source: Micron Solutions
Depending on the design and use, injection molding equipment can have a wide range of upfront costs.
Businesses maintain small-scale injection molding equipment internally. Then there are huge injection molding machines, which are frequently utilized by businesses that offer services as well as those engaged in extensive manufacturing.
Costs for professional industrial injection molding machinery range from $50,000 to $200,000. There can additionally be shipping fees. Due to the need for professional operators, these devices are not suitable for novices and enthusiasts.
Clearly, this is a significant expenditure for any firm. As a result, to reduce the equipment cost, the majority of businesses rent professionals with advanced injection molding equipment, like 3ERP, to handle the injection molding process. When injection molding is outsourced, the customer may find the lowest price for the item they need and cut down on production's variable expenses.
2.2. Tooling cost
Making the mold and mold foundation for the item requires money, even though the molding equipment is an initial expenditure. Every single element manufactured entails a cost. Therefore, one of the most significant driving forces for injection molding is tooling costs.
Depending on the technique utilized to make the molds, this price may change. Three procedures are typically used for this purpose:
- CNC Machining: The most popular equipment for producing highly precise aluminum and stainless steel molds is a CNC machine. By using a spinning tool and fixed components, CNC machining eliminates material. Although several tool changes may be necessary and slow down the process, machining may make molds with very complicated cavity designs, thus costs rise in direct proportion to complexity. Many businesses outsource the creation of molds to service providers since CNC machines are industrial instruments that need trained personnel and a dedicated area.
- Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM): The EDM technique is typically used to manufacture extremely intricate mold patterns that are difficult to duplicate using conventional machining techniques. To manufacture the appropriate mold form using EDM, a workpiece and a tool electrode are used. A dielectric fluid separates the tool electrode from the workpiece electrode, which is then exposed to voltages that result in repeated current discharges. The workpiece electrode is shaped into the final mold by the discharges. EDM is extremely precise and typically doesn't need any further post-processing. EDM is an industrial procedure that many businesses contract out to machine shops, much to CNC machining.
- 3D Printing: A potent method for quickly and cheaply fabricating injection molds is 3D printing. Very little equipment is needed, which frees up CNC time and expert operators for other high-value operations in the interim. Manufacturers can design molds that can be used on both desktop and industrial molding machines thanks to the quickness and adaptability of in-house 3D printing. Additionally, iterating on the design and testing the final product material before investing in hard tooling for mass production is advantageous for product development.
Simple low-volume 3D printed molds may be manufactured on a 3D printer for as little as $100. An aluminum mold for a mid-volume production run of 1,000 to 5,000 units costs between $2,000 and $5,000. Mold costs can range from $5,000 to $100,000 for molds with more complicated geometries and designed for bigger manufacturing runs of 10,000+ pieces.
A mid-level order of 1000–2000 tiny components can cost up to $10,000 in injection molding tooling. The plastic injection molding cost might increase to $100,000 for larger quantities and more complicated designs.
Depending on how complicated or huge your parts will be, tooling prices may vary. In other words, the manufacturer might need to employ a unique (and thus more expensive) machine to finish your order if your item is complicated (for instance, if it has sophisticated geometry or dense walls).
2.3. Material cost
Different types of thermoplastic resins can be utilized in the injection molding process. When calculating the cost of an injection mold, the type of plastic will also be a crucial component. Depending on what the component is intended to achieve, the best plastic resin will need to be chosen. Plastic resins will cost between $2 and $20 per pound. The size and intricacy of the mold will determine how much plastic is utilized in each injection. Several plastic properties that can influence price include:
- High impact
- High gloss
- Transparency
- High flow
- Fire retardant
- High heat
- Low temperature
- UV resistance
- Food grade
2.4. Labor cost
The majority of injection molding equipment is self-regulating and depends on automation to complete its function. However, there are some costs for labor that you should take into account:
- Setup/configuration cost: The setup labor focuses on the time required to configure the used equipment to make the mold and the end product.
- Repair cost: Repair and maintenance jobs entail the replacement of damaged parts as well as the usage of tools to carry out the maintenance procedure.
- Monitoring costs: Despite the dependence on automation, equipment operators are expected to monitor the injection molding process's development. Operator salaries are added to the entire cost of injection molding.
These charges are factored into the labor costs when producing in-house. When a company outsources injection molding, the labor and the service provider's markup are added to the service cost.
3. Other variables affecting the cost of injection molding
3.1. Size
The mold will be bigger to suit the larger object or part to be formed. To complete manufacturing cycles, larger items often require more injected materials. Larger mold designs are typically more expensive to produce than smaller designs of the same size.
3.2. Design
To complete the project, complicated molds are needed for part designs with elaborate geometries. Typically, mold designs feature two sides: sides A and B. The user typically sees Side A, often known as the cosmetic side. Smoothness and visual appeal are desired on Side A. The structures that facilitate the use of the component are hidden on Side B. The finish on Side B is often rougher than that on Side A, and it may feature ribs, bosses, etc.
Molds with intricate Side A and Side B designs often cost more to manufacture than simpler molds. Undercut-containing complex designs may additionally call for sliding side-actions and cores, raising the mold's price.
3.3. Volume
The manufacturing method and the quality of material to be used while making the mold depend on how many products will be produced using injection molding. Large production volumes may require high-grade steel molds or perhaps numerous molds to manage the process without wear and tear impacting the quality of generated objects. Low-volume projects may utilize 3D printed or lower-grade machined aluminum molds.
This has an impact on the price of the mold, but naturally, the higher cost of large-volume molds is spread out across a greater number of parts, which often results in a cheaper per-part cost.
3.4. Cavity
The price per component rate also includes the cost of mold cavitation, which rises as there are more cavities. It might cost thousands of dollars only to buy an injection mold.
The size and design of the component affect mold cavitation. Single cavity molds are typically cheaper if your item is very straightforward. To speed up manufacturing, it is desirable to use multiple-cavity molds if the part's shape permits it (making production less expensive over time). However, this might not be possible with larger pieces.
3.5. Secondary services
Secondary services might be expensive, but sometimes you can save money by buying both injection molding and secondary services from the same supplier (this also saves on shipping costs for another facility). These might take the form of:
- Other production techniques, such as drilling, inserting, and machining
- Services for assembly, such as gluing and sonic welding
Including logos or other graphics printed in pad print for decorating or marking
Other sections could require further servicing, while some may not. Some pieces will establish attachments to the gate while others will fall out of the machine and into a box. They need post-process machining to remove the gate, but are nevertheless utilized since gating improves process efficiency and reduces waste.
4. Optimizing plastic injection molding cost
Potential price-cutting tactics include the following:
- Before starting the job, inspect the CAD model to see how realistic it looks. Any complicated measurements and angles should be avoided.
- Remove any unnecessary traits. This reduces the size of the mold as well as the materials required during development.
- Side B's design should be simplified. The exterior cavities are collapsed into the base during this procedure, which lessens the requirement for acute angles. Furthermore, this will substantially enhance the surface finish.
Typically, injection molding is regarded as a method best suited for large-scale manufacturing operations with production volumes ranging from tens to hundreds of thousand of parts.
However, if your manufacturing demands aren't as large (for example less than 5000), you may use 3D printers to take advantage of this technique and optimize the cost.
II. Low-cost plastic for injection molding
1. Common injection molding materials

Depending on the needs of the finished products, injection molding can employ a broad range of polymers such as ABS, PS, PE, PC, PP, or TPU with each of them having its own properties.
The cost of obtaining mold materials varies depending on the material used. Here are the 7 most commonly used plastic for injection molding.
(Reminder: Prices for the mentioned plastics are not fixed prices. They depend on the market when you read the article. To check the price, you can go to some reputable websites about plastic prices, such as https://www.theplasticsexchange.com/)
1.1. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
Characteristics: ABS resin is an engineering-grade plastic and an opaque thermoplastic polymer. It's robust, has high dimensional stability, can withstand impacts and scratches, and is difficult to break. Furthermore, the low melting point makes it simple to mold.
Application: adaptors, keyboard keys, and plastic wall socket guards...
Why is this the case? Because ABS is an excellent insulator, it will not conduct electricity or emit gases if exposed to fire. These are critical issues for electrical device product developers.
Cost per pound: $1.30
1.2. Polyethylene (PE)
Characteristics: Polyethylene (PE) is a lightweight thermoplastic molding material with excellent chemical resistance, flexibility, and electrical insulation. It's not very powerful or hard, but it's cheap. PE is also the most often used injection molding plastic for the manufacture of toys since it is non-toxic and can withstand battering without complaint.
Applications: food packaging, milk jugs, toys
Cost per pound: $1.20
1.3. Polypropylene (PP)
Characteristics: Polypropylene (PP) is a thermoplastic injection molding material that is commonly utilized in the food storage and packaging business. Polypropylene (PP) is resistant to chemicals and moisture and may be washed in hot water without deteriorating. PP possesses exceptional impact strength, flexibility, and toughness.
Applications: tupperware, kiddie pools, toys, utensils, car batteries
Cost per pound: $0.90
1.4. Polystyrene (PS)
Characteristics: There are two kinds of polystyrene typically used in injection molding resins: High Impact Polystyrene (HIPS) and General Purpose Polystyrene (GPPS) (GPPS). HIPS is opaque, but GPPS is transparent. On the one hand, PS is robust and long-lasting. It can withstand a lot of punishment.
Applications: compact disc cases, packaging applications, household appliances
Cost per pound: $1.00
1.5. Nylon (PA)
Characteristics: Nylon is a synthetic polyamide (PA) having durability and high heat resistance. Moreover, it has excellent abrasion resistance, fatigue resistance, and noise-dampening qualities. However, it has a low tolerance to strong acids and bases. It is also prone to shrinkage and has insufficient mold filling.
Applications: high-ware parts, quick-release buckles, gears, hand cranks
Cost per pound: $2.20
1.6. Polyoxymethylene (POM)
Characteristics: Polyoxymethylene (POM) is a thermoplastic engineering material that is extremely strong, robust, and stiff. Despite its strong resistance to solvents such as alcohols, gasoline, detergents, and motor oils, POM should not be subjected to hydrochloric or nitric acid.
Applications: high-ware parts, quick-release buckles, gears, hand cranks
Cost per pound: $2.20
1.7. Polycarbonate (PC)
Characteristics: Polycarbonate is another transparent injection molding plastic with great optical characteristics and high durability. Because of its predictable and consistent mold shrinkage, this amorphous thermoplastic material allows for exact dimensional control while molding. When we need something much tougher than acrylic, we turn to polycarbonate.
Applications: automobile headlights, bulletproof glass, eyeglasses, greenhouses, DVDs, mobile phones
Cost per pound: $2.30
2. What is the least low-cost plastic injection molding?

Polypropylene and polyethylene are the least expensive materials for injection molding. They are often used in injection molding thanks to their extreme flexibility. They are used to produce anything from milk bottles to automobile batteries. These are the materials that most people use every day, and cheap material prices enable mass production.
When deciding on a material for your plastic injection project, keep in mind that the material should be determined by the purpose of the product. Understanding your alternatives and the costs connected with those materials will allow you to make an informed selection.
III. Plastic for injection molding supplier
EuroPlas is a top masterbatch manufacturer that supplies plastic for injection molding. We are headquartered in Vietnam and have been in the business for over 15 years. Our expertise and experience allow us to meet any requirement of our customers, and we always strive to provide you with the highest quality products.
We specialize in the production of various highly specialized plastic pellets with suitable properties at competitive prices. Our products are designed to meet the demands of the injection molding industry, which include automotive parts and appliances such as refrigerators, washing machines, dishwashers, and other household appliances.
We offer custom solutions as well as pre-designed products, so you won't need to worry about having your own facility or purchasing materials from another company. Our passionate staff will work closely with you throughout the entire process so that everything goes smoothly from start to finish! If you need the best plastic injection molding cost for your production line, contact us today.