1. Antiblocking Additives
Polyolefin and other plastic films tend to follow together, regularly making it hard to isolate layers. This bond between film layers, called blocking, is an innate property of a few polymers. Antiblock additives can be added to the plastic to limit this attachment thus bringing down the blocking power between layers. Once exacerbated into a plastic these added substances make a micro-rough surface which lessens the bond between film layers and brings down the blocking tendency. Two variables decide the anti-block impact: - The number of particles of anti-block at the film surface. - Size of the anti-block particles. The more prominent the centralization of anti-block present then the rougher the film surface created. Anyway, it is critical that the particles are very much scattered as agglomerates diminish anti-block execution. Alternately the coarser the particles the further the two film layers are kept separated.
Read more: What are plastic additives? 8 most common plastic additives in plastic industry
2. Kinds of Antiblocks Additives
The decision of anti-block additives relies on the polymer being utilized and the quality prerequisites of the finished result. The sorts accessible include:
2.1. Engineered Silica
This is a shapeless type of hydrous silicon dioxide with high microporosity, a hydroxylated surface, and a high surface territory. Engineered silica is utilized in superb movies and as it has a refractive list near that of PE and PP it is conceivable to create films with high straightforwardness and lucidity.
2.2. Limestone
This is a normally happening mineral essentially comprising of calcium carbonate together some of time with magnesium carbonate contingent upon the storage. It has a tendency to be utilized as an enemy of the square in bringing down quality film applications.
2.3. Common Silica
Common silica is a sedimentary shake made out of the skeletons of single-celled diatoms. The skeletons are made of undefined silica and have an extensive variety of permeable structures and shapes. Polluting influences, for example, water and organics can without much of a stretch be evacuated, anyway, the expulsion of quartz is more mind-boggling so common silicas have a tendency to contain varying levels of quartz relying upon the store.
2.4. Powder
The powder is a magnesium hydrosilicate. It has low hardness and a refractive record near that of Polyethylene PE and Polypropylene PP. Stores are found far and wide and despite the fact that it contains certain levels of pollution these can be limited through refining.
2.5. Zeolites
These are crystalline, hydrated alumosilicates. They have to a great degree uniform, three-dimensional permeable structures and again a refractive file near PE and PP. Zeolites happen as characteristic minerals or can be blended, anyway their utilization as antiblock-added substances is little.
2.6. Natural Additives
Certain natural materials, for example, hard waxes and unsaturated fat amides indicate anti-block impacts. Contrasted with inorganic added substances they have low anti-block productivity yet brilliant slip impact. Regularly slip, anti-static and anti-block added substances are utilized together to give the ideal harmony among slip and anti-block execution.
3. Slip Additives
Polyolefin films have a tendency to cling to themselves and metal surfaces because of their high coefficient of rubbing (COF). For handling ease, films require a COF close to 0.2. Slip-added substances can adjust the surface properties of a film and in this way bring down the rubbing between film layers and different surfaces. To be viable the slip needs to move out of the polymer to the surface and along these lines, it must have a level of inconsistency with the polymer.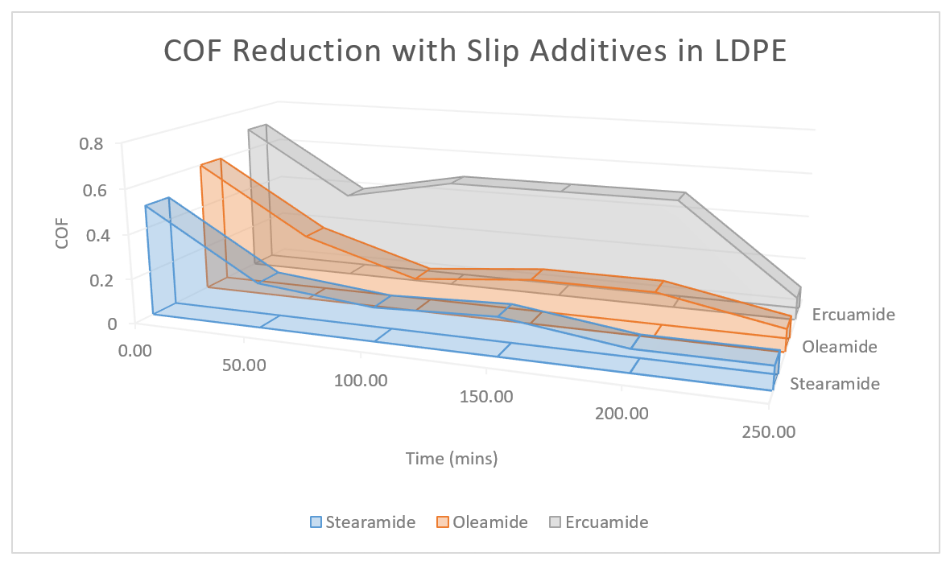
The effectiveness of different slip additives at 0.1% in LDPE[/caption] Unsaturated fat amides are frequently utilized as slip-added substances. Amid handling they are solubilized in the undefined soften, yet as the polymer cools and solidifies the unsaturated fat amide is "crushed" out framing a greasing up the layer at the polymer surface. The expansion of a slip-added substance can forestall film adhering and pulling expanding throughput.
4. Sorts of Slip Additives
The most regularly utilized slip-added substances are erucamide (C-22) and oleamide (C-18). Oleamide relocates faster than erucamide and is regularly called "quick blossoming". Anyway, after a specific time, the slower erucamide will furnish films with a lower COF than oleamide. Erucamide, with its lower vapor weight and unpredictability, is utilized in higher temperature handling applications and it likewise remains at the surface longer, not venting off as smoke. Oleamide is utilized where a low COF is required in a brief timeframe, while the slower movement of erucamide can be profitable in move-stock applications and on-line crown treatment. Another unsaturated fat amide is Stearamide. This is regularly utilized together with erucamide or oleamide to give an enemy of blocking impact when film straightforwardness is vital. The centralization of slip present influences execution. At first, the COF is delicate to little varieties in focus until the point that a basic level of slip is come to, after which additionally slip has little impact on the COF. The measure of slip required relies upon movie form thickness, the slip added substance being utilized, and the nearness of different added substances, for example, enemies of squares.