Injection molding is an essential manufacturing process widely used in various industries. Understanding how injection molding works, its advantages, and alternatives is crucial for anyone involved in product development and manufacturing. In this comprehensive guide, we'll delve into the intricacies of injection molding and provide you with valuable insights into this innovative technique.
1. What is injection molding?
1.1. Definition of injection molding
Injection molding is a manufacturing process used to produce plastic parts and products in large quantities. It entails applying intense pressure while injecting molten plastic material into a mold cavity. The material solidifies within the mold, taking its desired shape, and is then ejected as a finished product. Injection molding enables the production of complex and intricate designs with high precision and repeatability.
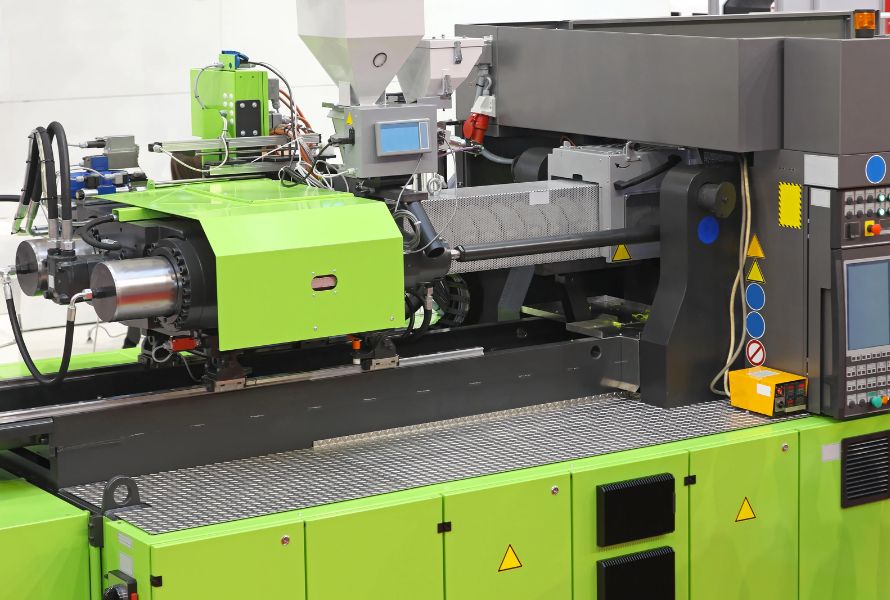

A manufacturing technique called injection molding is used to create plastic goods and parts in big quantities
1.2. Role of molds and plastic materials
Molds play a crucial role in injection molding. They are typically made of steel or aluminum and consist of two halves, the core, and the cavity. The mold determines the shape, features, and surface finish of the final product. Plastic materials used in injection molding are typically thermoplastic polymers that can be melted and solidified repeatedly. Common materials include polypropylene, polystyrene, polyethylene, and more.
1.3. Application areas of injection molding
Injection molding finds applications in various industries due to its versatility and efficiency. Some common application areas include:
- Automotive: Production of interior and exterior components, such as dashboards, bumpers, and door panels.
- Consumer Goods: Manufacturing of household items, toys, packaging, and appliances.
- Electronics: Creation of enclosures, connectors, and components for electronic devices.
- Medical: Production of medical devices, syringes, and equipment components.
- Packaging: Manufacturing of bottle caps, containers, and closures.
- Industrial: Production of various industrial components, tools, and equipment parts.
2. How does injection molding work?
2.1. Step-by-step process of injection molding
2.1.1. Mold preparation
The mold is prepared by ensuring it is clean and free from any debris or contaminants. The mold halves are securely clamped together, creating a closed mold cavity.
2.1.2. Plastic material selection and melting
The appropriate plastic material is selected based on the desired properties of the final product. The plastic material, usually in pellet form, is loaded into the hopper of the injection molding machine. It then travels through the barrel, where it is heated and melted by the rotation and pressure exerted by the screw.
2.1.3. Injection of molten Material into the mold
Once the plastic material reaches a molten state, it is injected into the mold cavity under high pressure. This pressure ensures that the material fills the entire cavity and takes on the shape of the mold.
2.1.4. Cooling and solidification
After the molten plastic is injected into the mold, it begins to cool and solidify. Cooling channels within the mold help dissipate the heat and accelerate the solidification process. This stage is crucial for achieving the desired dimensional stability and structural integrity of the final product.
2.1.5. Mold opening and ejection
Once the plastic has sufficiently cooled and solidified, the mold opens, and the finished product is ejected. Ejection mechanisms, such as ejector pins or plates, assist in the removal of the product from the mold without damaging its shape or features.
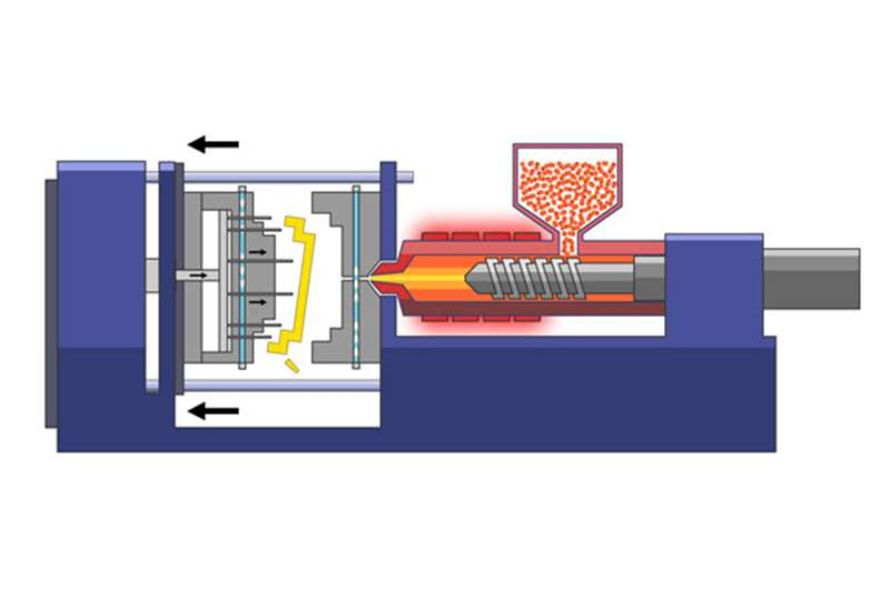
Injection Molding involves several steps to transform raw materials into finished products
2.2. Key factors influencing the success of injection molding
2.2.1. Material selection
Choosing the right plastic material with suitable properties for the intended injection molding application is crucial for achieving desired product characteristics.
2.2.2. Mold design
Proper injection molding design, including considerations for part geometry, cooling channels, and venting, plays a significant role in ensuring efficient and defect-free production.
2.2.3. Process optimization
Fine-tuning process parameters such as injection speed, temperature, and pressure help achieve optimal results in terms of part quality, cycle time, and production efficiency in the injection molding process.
2.3.4. Quality control
Implementing quality control measures in injection molding, such as inspection and testing of the molded parts, ensures that they meet the required specifications and standards.
Several key factors can significantly influence the success of the injection molding process
3. Injection molding machines
3.1. Definition and purpose of injection molding machines
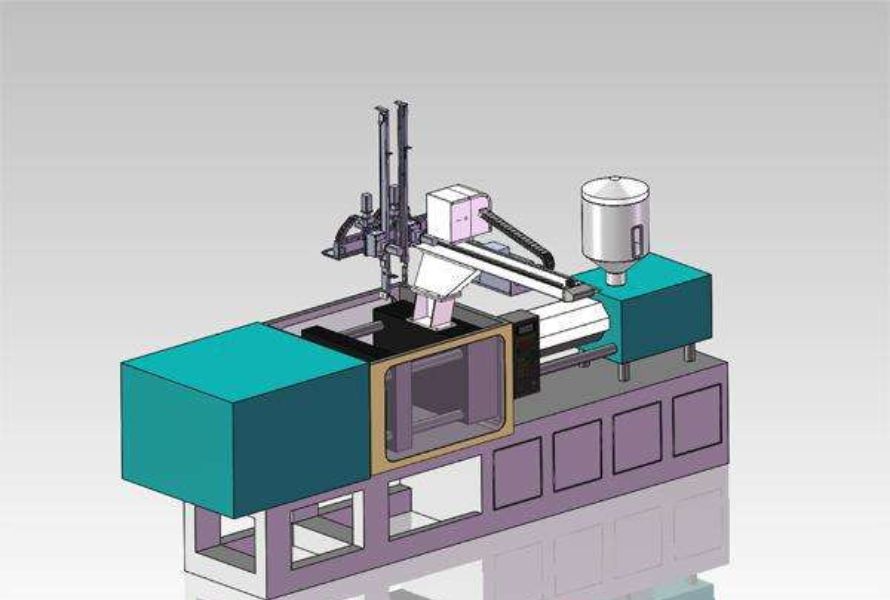
Injection molding machines are specialized machines used in the injection molding process to manufacture plastic products. They are designed to melt and inject plastic materials into molds under high pressure. These machines play a central role in the injection molding process by providing the necessary equipment and control to produce high-quality plastic parts and products efficiently.
3.2. Structure of injection molding machines
3.2.1. Overview of injection molding machine components
Injection molding machines consist of several essential components, including the injection unit, clamping unit, and control system. The injection unit melts and injects the plastic material, while the clamping unit holds the mold securely closed during the injection process.
3.2.2. Function of each component in the process of injection molding
The injection unit comprises the hopper, barrel, screw, and nozzle. The hopper stores the plastic material, which is then transported by the rotating screw, melted, and injected into the mold cavity through the nozzle. The clamping unit ensures precise and consistent clamping force to keep the mold closed during the injection and cooling stages. The control system oversees and regulates the entire process, including temperature, pressure, and timing.
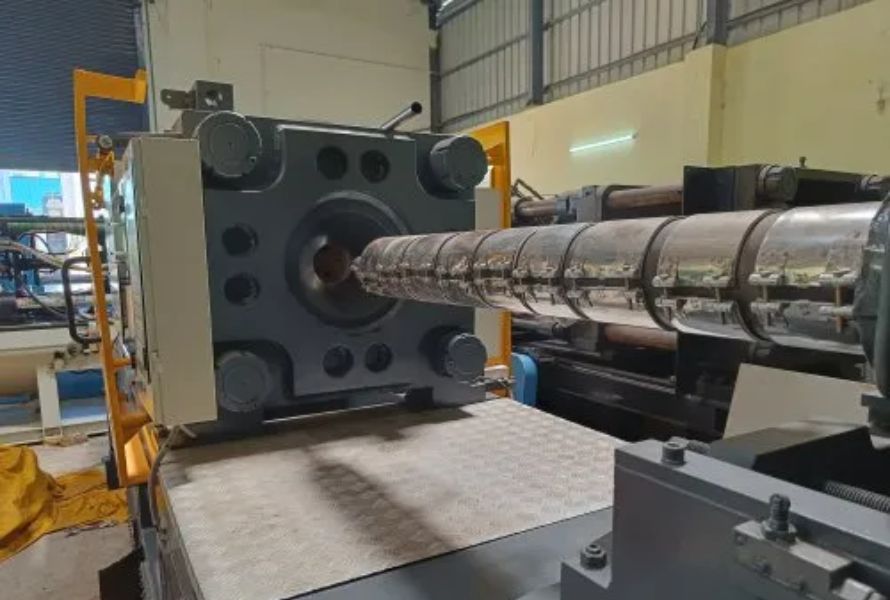

Each component in the injection molding process plays a critical role
3.3. Types of Injection molding machines
3.3.1. Hydraulic machines
Hydraulic injection molding machines use hydraulic systems to generate the necessary force for the injection process. They are known for their high clamping force capabilities and are suitable for a wide range of applications. Hydraulic machines offer excellent control and are often used for larger-sized molds and parts.
3.3.2. Electric machines
Electric injection molding machines rely on electric motors and servo drives to power the various machine functions. They offer precise control over the injection process, resulting in high accuracy and repeatability. Electric machines are energy-efficient and provide fast cycle times, making them ideal for producing small to medium-sized parts.
3.3.3. Hybrid machines
Hybrid injection molding machines combine hydraulic and electric technologies to leverage the advantages of both. These machines utilize electric drive systems for the injection unit and hydraulic systems for the clamping unit. Hybrid machines offer improved energy efficiency, reduced noise levels, and enhanced precision and speed, making them versatile for a wide range of applications.
3.3. Features and capabilities of modern injection molding machines
3.3.1. Control systems
Modern injection molding machines are equipped with advanced control systems that allow for precise monitoring and adjustment of various process parameters. These systems enable operators to optimize the injection process, ensuring consistent part quality and minimizing waste.
3.3.2. Automation and robotics
Injection molding machines can be integrated with automation and robotics systems to streamline production and improve efficiency. Automated systems can handle tasks such as mold loading and unloading, part inspection, and packaging, reducing manual labor and increasing productivity.
3.3.3. Multi-Cavity molding
Injection molding machines can be configured for multi-cavity molding, where multiple identical parts are produced in each cycle. This capability significantly increases production output and efficiency, making it suitable for high-volume manufacturing.
3.3.4. Quick Mold Change (QMC) systems
QMC systems allow for rapid mold changes, reducing downtime between production runs. This feature enables manufacturers to switch between different molds quickly, facilitating production flexibility and facilitating the manufacturing of different products on the same injection molding machine.
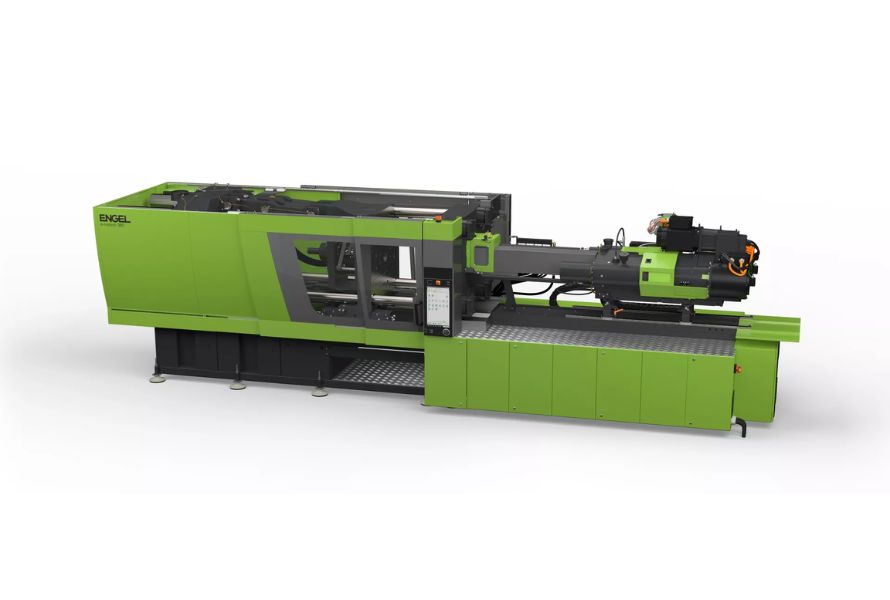

The features and capabilities of modern injection molding machines contribute to improved production efficiency
4. Advantages of injection molding
4.1. Cost-effectiveness and efficiency
Injection molding offers cost-effectiveness and efficiency in plastic part production. Once the molds are created, the injection molding process allows for high-volume production at a rapid pace. The automated nature of injection molding machines reduces labor costs and increases production efficiency, resulting in lower per-unit costs for large production runs.
4.2. Ability to create complex designs
Injection molding enables the production of plastic parts with complex and intricate designs. The high-pressure injection process allows for the precise replication of intricate details, such as fine textures, intricate geometries, and small features, that would be challenging or impossible to achieve with other manufacturing methods. This makes injection molding suitable for producing products with intricate shapes, precise dimensions, and unique design elements.
4.3. Consistency and precision in product manufacturing
Injection molding ensures consistency and precision in the manufacturing of plastic parts. The use of highly controlled and automated processes, along with the ability to monitor and adjust various parameters, results in consistent part quality and dimensional accuracy. This level of precision is particularly important in industries where tight tolerances and uniformity are critical, such as automotive, aerospace, and medical sectors.
4.4. Fast Production cycle times
Injection molding offers fast production cycle times, making it an efficient manufacturing method. The high-speed injection process, coupled with rapid cooling and solidification of the molten plastic, allows for quick production cycles. This rapid turnaround time is advantageous for meeting tight project deadlines and keeping up with market demand.
4.5. Wide range of compatible materials
Injection molding supports a wide range of plastic materials, providing flexibility in material selection for specific applications. Various thermoplastic polymers, such as polypropylene, polystyrene, polyethylene, and ABS (acrylonitrile butadiene styrene), can be used in injection molding. Additionally, specialty materials with specific properties, such as high strength, flame resistance, or chemical resistance, can be utilized to meet specific product requirements.
4.6. Sustainability and recyclability of injection molded products
Injection-molded products can contribute to sustainability efforts. The ability to use recyclable and recycled materials in the injection molding process helps reduce waste and environmental impact. Additionally, the durability and longevity of injection molded products contribute to their sustainability, as they can be used for an extended period, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
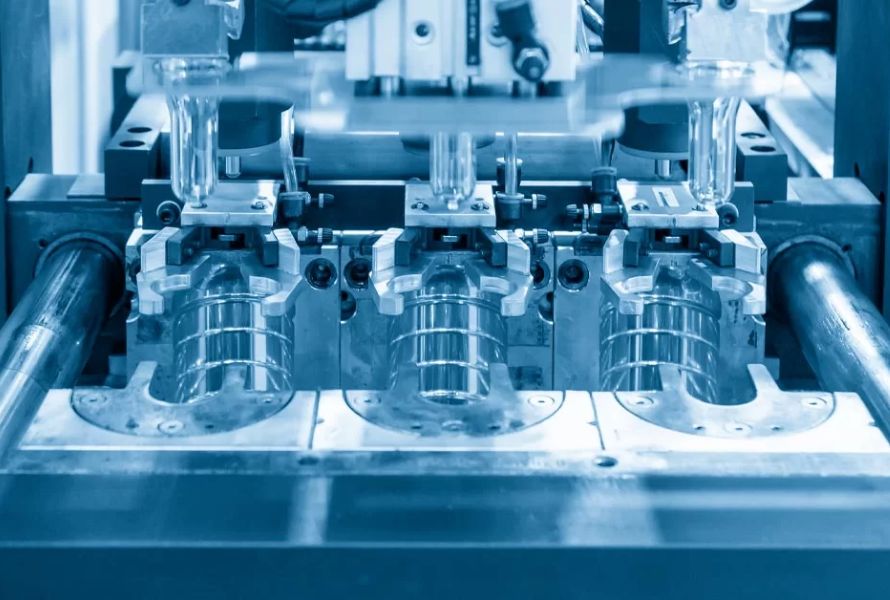

There are a number of benefits that injection molding has over other manufacturing techniques
5. Alternatives to injection molding
Injection molding is a widely used manufacturing process for producing plastic parts, but there are alternative methods available for certain applications or specific requirements. Here are a few alternatives to injection molding:
5.1. 3D Printing/Additive manufacturing
3D printing technology allows for the creation of complex geometries and customization with relatively low setup costs. It is suitable for prototyping, low-volume production, and manufacturing parts with intricate designs.
5.2. Blow molding
This process is commonly used for producing hollow plastic parts such as bottles and containers. It involves inflating a molten plastic tube inside a mold to create the desired shape.
5.3. Compression molding
Compression molding is suitable for producing larger parts or parts with reinforced materials. It involves placing a pre-measured amount of material into a heated mold cavity and compressing it under high pressure until it takes the desired shape.
5.4. Thermoforming
Thermoforming is commonly used for producing thin-gauge plastic parts such as packaging trays, disposable cups, and automotive interior components. It involves heating a thermoplastic sheet and then draping it over a mold, where it is shaped using vacuum or pressure.
5.5. CNC machining
Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining involves the use of computer-controlled machines to precisely cut and shape plastic materials. It is suitable for producing high-precision parts, prototypes, and low- to medium-volume production runs.
5.6. Reaction Injection molding (RIM)
RIM is a process used for producing large, lightweight, and structurally strong plastic parts. It involves mixing two liquid components, typically polyurethane, in a mold where they react and solidify to form the desired part.
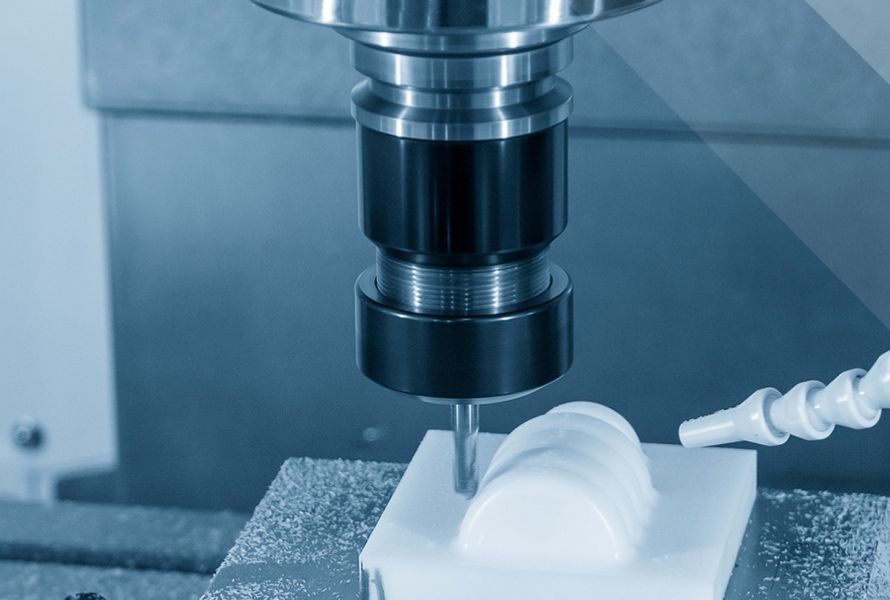

While injection molding is widely used for manufacturing the process, there are alternative methods for producing plastic parts
6. Conclusion
In summary, injection molding is a highly efficient and versatile manufacturing process that enables the production of high-quality plastic parts and products. However, it is important to consider the limitations and considerations associated with injection molding. By understanding these factors and making informed decisions, manufacturers can leverage the benefits of injection molding while mitigating potential challenges.
One of the best masterbatch suppliers for injection molding is EuroPlas. We have been in the business for more than 15 years, with our headquarters located in Vietnam. We can satisfy any need of our clients thanks to our knowledge and experience, and we constantly work to deliver the best products possible. Contact us right now for more detailed information!