The shift towards sustainability has propelled PBAT polymer to the forefront of the global bioplastics industry. Known for its biodegradability and flexibility, this innovative material is poised to reshape industries ranging from packaging to agriculture in 2025. Let’s dive into the trends, opportunities, and challenges defining the PBAT polymer market this year, and discover why it holds immense potential for businesses worldwide.
1. Key market trends of PBAT polymer in 2025
The market for PBAT polymer is projected to grow significantly in 2025, thanks to increasing environmental awareness, stricter regulations, and advancements in materials science. Below are the primary trends shaping the industry:
1.1. Accelerating demand for eco-friendly packaging
In 2025, the global packaging industry continues to face mounting pressure to reduce its environmental footprint. Governments and corporations alike are championing biodegradable materials to combat the mounting waste crisis. PBAT polymer, which can be blended with materials like PLA to create fully compostable packaging solutions, is becoming a preferred choice for manufacturers.
- Key applications: Shopping bags, food wrappers, and industrial packaging films made with PBAT polymer offer an effective alternative to traditional plastics. These products degrade more rapidly in composting environments, aligning with global sustainability goals.
- Market insight: Analysts predict that PBAT-based flexible packaging solutions will capture a sizable share of the $10 billion global bioplastics market by 2025.
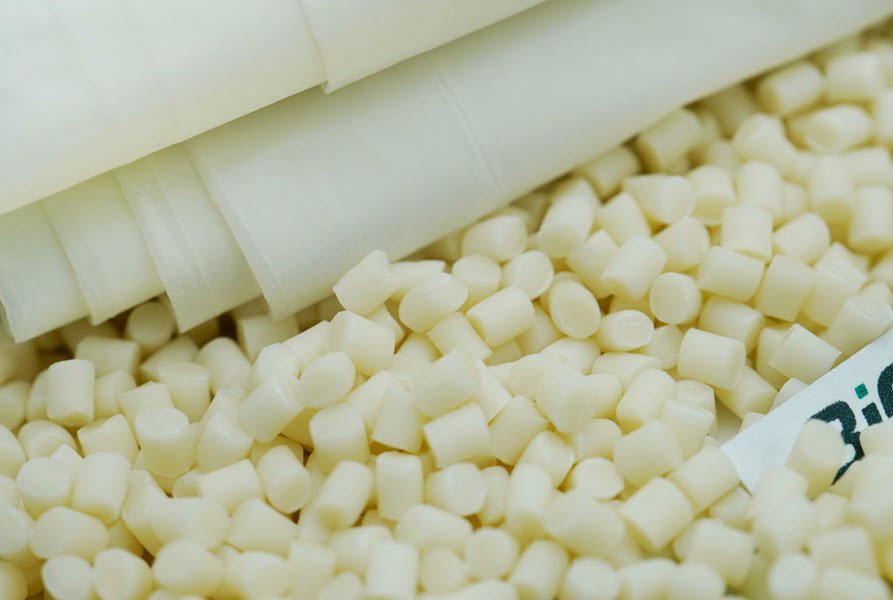

PBAT polymer offers an effective alternative to traditional plastics
1.2. Global regulations driving adoption
Stricter environmental regulations are reshaping the polymer industry. The European Union, for example, has mandated the use of compostable materials for certain types of packaging, pushing companies to integrate PBAT polymer into their operations. Similarly, Asian countries, including China and India, are implementing policies to curb plastic waste, opening up significant opportunities for PBAT polymer.
1.3. Technological innovations in PBAT manufacturing
Manufacturers are addressing one of the biggest hurdles in PBAT polymer adoption—cost. By refining production processes, including more efficient polymerization methods and introducing advanced additives, companies are improving the cost-effectiveness of PBAT products.
Breakthroughs: Enhanced blending techniques allow PBAT polymer to exhibit superior mechanical properties, such as improved flexibility, heat resistance, and tensile strength, making them suitable for broader applications.
1.4. Integration in sustainable agriculture
PBAT polymer is gaining ground in agriculture as farmers adopt biodegradable mulch films and seed coatings. Unlike traditional plastic films, PBAT-based alternatives decompose naturally, reducing soil pollution and labor costs associated with waste disposal.
Future growth: By 2025, the agricultural applications of PBAT are projected to grow at a CAGR of over 9%, driven by increasing awareness about the need for sustainable farming practices.
1.5. Collaborative R&D efforts
Research collaborations between academic institutions and private manufacturers are accelerating the development of next-generation PBAT polymer products. For instance, companies are working on enhancing the polymer’s thermal stability and resistance to moisture, allowing it to replace conventional plastics in even more challenging environments.
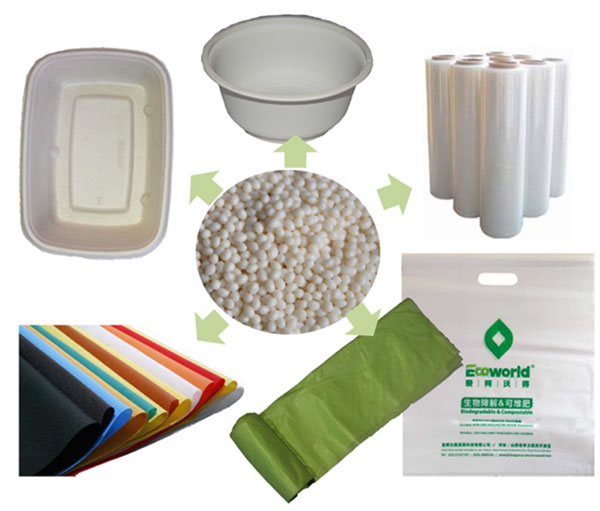

PBAT polymer products are increasingly diverse and have the ability to replace conventional plastics
Read more: What is PBAT plastic? Pros and cons of PBAT
What are the effects of PBAT plastic?
2. Opportunities for businesses
The PBAT polymer market in 2025 offers numerous opportunities for businesses, particularly those looking to establish themselves as pioneers in sustainable solutions. As global industries shift toward environmentally conscious practices, PBAT polymer provides a versatile and promising avenue for companies to diversify their portfolios, enhance their brand value, and meet emerging consumer demands. Let’s explore these opportunities in detail:
2.1. Expanding product portfolios with sustainable solutions
PBAT polymer's unique characteristics, including biodegradability, flexibility, and compatibility with other bio-based materials, allow businesses to develop innovative and eco-friendly products. This diversification helps companies meet the dual demands of sustainability and functionality, gaining an edge over competitors still reliant on traditional plastics.
Examples of applications:
- Retail sector: Developing compostable shopping bags that can break down naturally in household composting environments. This aligns with global regulatory trends banning single-use plastics.
- Food packaging: Companies can use PBAT polymer to create biodegradable wrappers, trays, and films for food products, reducing plastic waste while ensuring food safety.
- Industrial packaging: For shipping and logistics, PBAT-based stretch films offer high tensile strength, ensuring product protection while being environmentally friendly.
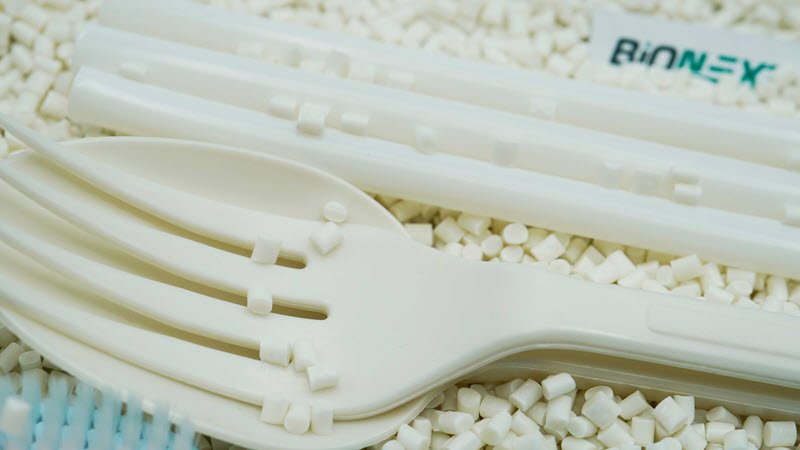
- Disposable consumer products: Items like compostable cutlery, straws, and single-use plates made with PBAT polymer are increasingly in demand as consumers seek sustainable alternatives.
This versatility allows businesses across sectors—from retail to hospitality and healthcare—to replace traditional plastics in their product lines, ensuring compliance with global regulations and meeting consumer expectations.

Biodegradable food packaging easily ensures food safety
2.2. Tapping into lucrative export markets
The increasing demand for PBAT polymer in developed markets, particularly in regions such as Europe, North America, and Japan, presents significant export opportunities for businesses in Asia and other developing regions. These markets are leading the global transition toward sustainability, driven by strict regulatory frameworks and strong consumer awareness about environmental issues.
Case study:
- A South Korean bioplastics company increased its market share in Europe by exporting PBAT polymer-based agricultural films. These films, favored for their quick biodegradation and cost-effectiveness, became a staple in sustainable farming practices.
- Similarly, Indian manufacturers of PBAT polymer bags have successfully entered North American markets, capitalizing on bans on single-use plastic bags in various U.S. states and Canadian provinces.
Exporting PBAT polymer products can not only generate significant revenue but also position businesses as leaders in the international green materials market.
2.3. Forming strategic partnerships for R&D and scaling
Collaboration is a powerful strategy for businesses to overcome the technical and financial challenges of adopting PBAT polymer. Strategic partnerships with research institutions, chemical manufacturers, or environmental organizations can accelerate innovation and improve cost efficiency.
Benefits of partnerships:
- Access to advanced manufacturing techniques, such as blending PBAT polymer with PLA or starch, to create superior materials.
- Joint ventures with global distributors to streamline supply chains and reduce logistics costs.
- Collaboration with universities or research centers to develop PBAT polymer with enhanced properties, such as greater tensile strength or improved thermal resistance.
For instance, a partnership between a bioplastics startup and a major packaging company in Germany led to the development of compostable PBAT polymer-based pouches for high-demand sectors like pet food and fresh produce.
Blend PBAT polymer with PLA
2.4. Building a strong green branding strategy
Incorporating PBAT polymer into products gives businesses an opportunity to strengthen their brand identity as sustainability leaders. Eco-friendly branding has become a critical factor in consumer decision-making, especially among younger generations who prioritize environmental responsibility.
Effective branding tactics:
- Highlighting the biodegradability and compostability of PBAT polymer products through packaging and marketing campaigns.
- Obtaining certifications such as “Compostable” or “Biodegradable” from recognized environmental organizations to enhance credibility.
- Engaging in corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives tied to sustainability, such as planting trees or supporting waste reduction programs, to further build goodwill.
For example, a Southeast Asian food chain transitioned to PBAT polymer-based food containers, launching a campaign under the slogan “Serving Food, Saving the Planet.” This initiative not only attracted environmentally conscious customers but also helped the company differentiate itself in a competitive market.
2.5. Capturing long-term cost advantages
While the initial costs of switching to PBAT polymer can be significant, businesses stand to gain long-term cost advantages in various ways:
- Reduced disposal costs: Many countries now impose taxes or penalties for improper disposal of non-biodegradable materials. PBAT polymer products, being compostable, eliminate this burden for businesses.
- Compliance with future regulations: By proactively adopting PBAT polymer, businesses can ensure they remain ahead of stricter environmental regulations, avoiding fines or disruptions to their operations.
- Increased consumer loyalty: Studies show that consumers are willing to pay a premium for sustainable products. By offering PBAT polymer-based solutions, businesses can attract a loyal customer base, ensuring steady revenue growth.
.png)
PBAT polymer products, thanks to their compostability, eliminate this burden for businesses
2.6. Exploring emerging sectors for PBAT polymer applications
PBAT polymer’s versatility allows businesses to explore new and emerging industries beyond traditional markets like packaging and agriculture. These sectors are increasingly recognizing the value of PBAT polymer in their operations:
- Healthcare and pharmaceuticals: PBAT polymer is being explored for use in biodegradable medical films, drug delivery systems, and temporary implants, providing an eco-friendly alternative to conventional materials.
- Construction: Biodegradable films made from PBAT polymer are being tested as protective layers for construction materials, reducing waste on job sites while maintaining functionality.
- Textiles: Companies are investigating PBAT polymer as a component for biodegradable fibers, enabling the creation of compostable fabrics for fashion and home goods.
3. Challenges in the PBAT market
The PBAT polymer market, while promising, faces significant challenges that limit its growth and adoption. These include high production costs, competition from alternative bioplastics, insufficient infrastructure, consumer misunderstandings, and unstable raw material supply chains.
3.1. High production costs
The complex manufacturing process of PBAT polymer, which relies heavily on petroleum-based raw materials, results in higher production costs compared to traditional plastics like polyethylene (PE) and polypropylene (PP). SMEs, especially in cost-sensitive markets, struggle to absorb these costs or pass them onto consumers. In emerging regions, affordability becomes a major barrier. Efforts to lower costs include investing in bio-based feedstocks and advancing production technologies. Government incentives, subsidies, or partnerships could also play a key role in making PBAT a more economically viable option.
3.2. Competition from alternative bioplastics
PBAT faces strong competition from other biodegradable materials like PLA (polylactic acid), PHA (polyhydroxyalkanoates), and starch-based plastics. These alternatives often outperform PBAT in specific applications or cost efficiency. For example, PLA is derived from renewable resources and offers high strength and clarity, while PHA is fully biodegradable in marine and soil environments. PBAT producers are exploring blends with other bioplastics to combine advantages and meet diverse market demands. Collaborations between manufacturers could drive innovation and expand PBAT’s applications.

PBAT polymer must compete with other biodegradable materials such as PLA
3.3. Infrastructure gaps
PBAT polymer requires industrial composting facilities to fully degrade, but such infrastructure is limited in many regions, especially in developing countries. Without proper composting systems, PBAT-based products often end up in landfills, where they fail to decompose effectively, reducing their environmental benefits. Governments must prioritize investments in composting and waste management infrastructure, while companies could establish closed-loop systems to ensure proper disposal and recycling of PBAT products.
3.4. Consumer misunderstanding
Consumers often misinterpret PBAT’s biodegradability, assuming it will decompose in any environment, such as home compost bins or landfills. In reality, PBAT requires specific industrial conditions—such as high temperatures and controlled humidity—to break down. Improper disposal undermines PBAT’s eco-friendly image and contributes to environmental pollution. Businesses can address this through clear product labeling, disposal instructions, and public awareness campaigns. Education initiatives in schools and communities can also help correct misconceptions about biodegradable plastics.

PBAT requires high temperature and controlled humidity to decompose
3.5. Supply chain challenges
PBAT production is heavily reliant on petrochemical-derived raw materials, making it vulnerable to supply chain disruptions, geopolitical tensions, and fluctuating oil prices. The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted these vulnerabilities, causing delays and cost increases in raw material shipments. To mitigate risks, manufacturers are exploring renewable feedstocks, such as sugarcane, corn, or vegetable oils, which could not only stabilize supply chains but also improve PBAT’s sustainability appeal. Transitioning to bio-based raw materials will be crucial for the long-term stability and growth of the PBAT market.
By addressing these challenges, the PBAT polymer industry can unlock its full potential and establish itself as a viable, sustainable alternative to conventional plastics.
4. Conclusion
PBAT polymer represents a key innovation in sustainable materials, addressing critical environmental challenges with applications spanning packaging, agriculture, and consumer goods. While hurdles like high production costs, competition from other bioplastics, and infrastructure limitations persist, advancements in production efficiency and waste management are enhancing its viability. Increased investments, strategic collaborations, and government support are driving the adoption of PBAT, positioning it as a transformative solution in the shift toward sustainability. With its potential to support a circular economy and provide businesses with a competitive edge, PBAT polymer is set to play a pivotal role in shaping a greener, more sustainable future across industries.

The development of PBAT polymer points towards a green future
5. About EuroPlas' Bioplastics
BioMates, a groundbreaking product line by EuroPlas, utilizes PBAT polymers to deliver high-performance, eco-friendly solutions for various industries. Designed with sustainability at its core, BioMates is a cutting-edge bioplastics product that perfectly aligns with global sustainability goals while offering the benefits of PBAT polymer's biodegradability and compostability.
At EuroPlas, we combine advanced production technologies with a commitment to environmental stewardship to produce BioMates. This product leverages the outstanding properties of PBAT polymer, ensuring it meets the rigorous performance standards of conventional plastics while offering a more sustainable alternative. The PBAT polymer used in BioMates is renowned for its ability to degrade naturally in the environment, making it an ideal choice for eco-conscious manufacturers.
Whether in packaging, agriculture, or consumer goods, BioMates provides reliable, sustainable alternatives to traditional plastic solutions. From biodegradable agricultural films to eco-friendly packaging, BioMates is leading the way in delivering green solutions that do not compromise on performance.
Key benefits of BioMates with PBAT Polymer:
- Biodegradable and compostable: PBAT polymer ensures BioMates breaks down naturally, significantly reducing environmental impact.
- High performance: BioMates maintains the strength, flexibility, and durability necessary for various applications, all while using PBAT polymer.
- Eco-friendly manufacturing: With PBAT polymer at its core, BioMates is produced using renewable resources and advanced manufacturing techniques, making it a more sustainable choice.
- Versatile applications: Perfect for packaging, agriculture, consumer goods, and more, BioMates offers sustainable alternatives across industries.
By choosing BioMates, you are investing in a future-focused, environmentally responsible solution that leverages the benefits of PBAT polymer. Join us in leading the green revolution and building a sustainable future for all. Contact us today to learn more about BioMates and explore how it can help your business and the planet.