ABS injection molding is a versatile manufacturing process that involves injecting molten ABS plastic into a mold to create a variety of products. This technique is widely used in industries such as automotive, electronics, and consumer goods due to ABS's excellent mechanical properties. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of ABS injection molding, exploring its benefits, applications, and the key factors to consider for successful production.
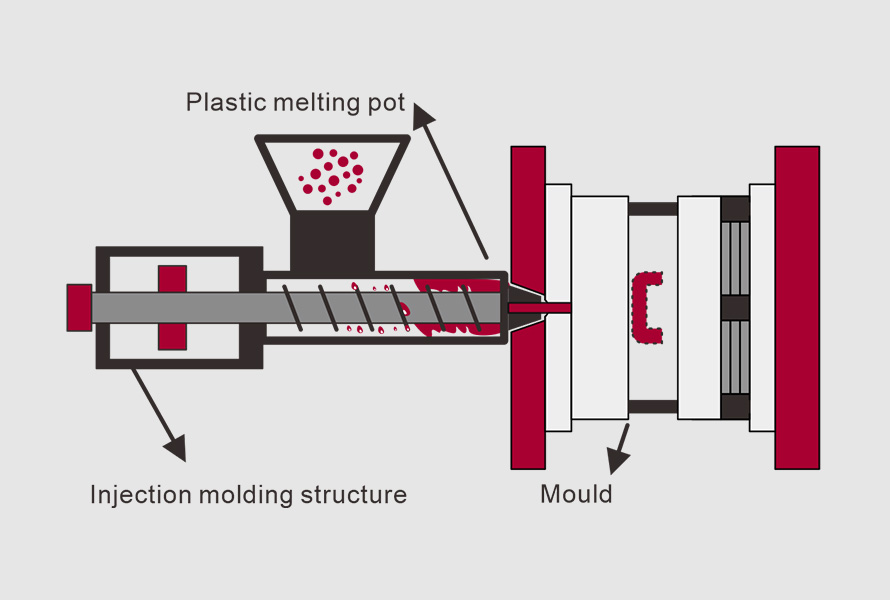
ABS injection molding is a versatile process that injects molten ABS plastic into molds to create various products
1. Overview of ABS Plastic
1.1. What is ABS Plastic?
ABS plastic, short for Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene, is a versatile and widely used thermoplastic polymer made from three monomers—acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene. Each component contributes unique qualities:
- Acrylonitrile offers chemical resistance and rigidity of ABS.
- Butadiene provides excellent impact resistance, making ABS a tough material that can withstand bumps and shocks. This makes it ideal for products requiring durability.
- Styrene contributes to rigidity, processability, a naturally glossy and surface finish.
By adjusting the ratios of the three primary components, different ABS grades can be produced, each with distinct properties optimized for specific applications. In general, ABS combines chemical stability, toughness, and ease of processing, making it ideal for various industries.
Read more: ABS plastic - Everything you need to know
1.2. ABS Plastic Properties
Positioning between standard resins (PVC, polyethylene, polystyrene, etc.) and engineering resins (acrylic, nylon acetal, etc.), ABS plastic often meets property requirements with cost-effectiveness. It offers a compelling combination of benefits:
- Strength and Impact Resistance: Can take a beating and maintain its shape, even in low temperature environments.
- Electrical Insulation: Provides high weldability, and insulating properties
- Chemical Properties:
+ Strong resistance to diluted acids and alkalis
+ Moderate resistance to aliphatic hydrocarbons
+ Poor resistance to aromatic hydrocarbons, halogenated hydrocarbons, and alcohols.
+ Stands up to mild chemicals for many applications.
- Glossy Finish: High surface brightness and excellent surface quality. Creates visually appealing products.
- Superior Dimensional Stability: Mechanically strong and stable over time
- Versatility: Can be molded, machined, glued, and 3D printed.
However, it's important to consider its limitations:
- Limited Temperature Resistance: Can deform at high temperatures.
- Susceptible to Strong Solvents: Can be attacked by harsh chemicals.
1.3. Processing and Applications
Injection Molding
This technique, known as ABS injection molding, involves injecting molten ABS plastic into a mold cavity to create precise and complex shapes. It's a popular choice for high-volume production of parts like automotive components, electronics enclosures, and toys.
Extrusion
In extrusion, molten ABS is forced through a die to create continuous shapes like pipes, sheets, and profiles. These can be used for building materials, furniture components, and various industrial applications.
3D Printing
The ease of processing ABS also makes it a popular material for 3D printing. This allows for rapid prototyping and creation of customized parts.
1.4. How do additives enhance ABS properties?
While ABS offers a good baseline of properties, manufacturers can further enhance its performance by incorporating various additives:
- Flame Retardants: Improve fire resistance for safety applications.
- Impact Modifiers: Increase toughness for even greater shock absorption.
- UV Stabilizers: Protect against sun damage for outdoor applications.
- Color Pigments: Allow for a vast array of color options.
By strategically using these additives, manufacturers can tailor ABS to meet the specific requirements of their products.

Manufacturers can enhance ABS's baseline properties by incorporating additives
2. Key Steps in the ABS Injection Molding Process
Understanding the key steps in ABS injection molding is essential for achieving consistent, reliable results. Each phase, from material preparation to final cooling, directly impacts the quality and strength of the molded ABS parts.
2.1. Designing the ABS Injection Mold
A well-designed mold is crucial for successful ABS injection molding. A thorough understanding of ABS properties is essential for effective mold design. Considerations like ABS’s response to heat, pressure, and cooling influence mold structure.
Key design factors include wall thickness, rate of shrinkage, melt temperature, stress concentration, injection pressure, molding speed, and cooling rate.
Achieving optimal injection molding parameters requires extensive experience, often best guided by professionals skilled in mold design and injection processes.
2.2. ABS Material Preparation
As previously mentioned, ABS plastic is available in a variety of grades. Proper ABS material preparation is essential for achieving high-quality molded parts.
Otherwise, since ABS is hygroscopic, it absorbs moisture, which can cause defects during molding. To address this, ABS is dried in industrial dryers at precise temperatures and times to reduce moisture without compromising its qualities.
2.3. Melting and Injecting ABS into the Mold
ABS is melted and injected under specific temperature and pressure conditions, generally between 170 and 320 °C and 700 to 21800 psi, respectively. The injection process consists of three stages:
- Fill stage: 95-98% of the ABS material is injected.
- Pack stage: Additional ABS is injected to counter shrinkage and ensure part integrity.
- Hold stage: Pressure is maintained as cooling begins.
2.4. Cooling, Solidifying and Ejecting the ABS Part
Cooling channels within the mold enable consistent cooling to solidify ABS without defects. Temperature monitoring ensures uniformity. After cooling, the solidified part is ejected from the mold using ejector pins.
2.5. Part Finishing and Inspection
After the molding process, the parts may require additional finishing operations, such as:
- Trimming: Removing excess material from the parts.
- Deburring: Smoothing sharp edges and removing burrs.
- Cleaning: Removing any contaminants or residue.
- Inspection: Verifying the dimensions, appearance, and functionality of the parts.
Mastering the key steps in ABS injection molding is crucial for achieving consistent, high-quality, and durable ABS parts.
3. Things To Remember for ABS Injection Molding
ABS injection molding requires careful attention to specific process factors to ensure optimal results and part quality. From material preparation to precise temperature and pressure control, each step in ABS injection molding impacts the final product’s performance and durability.
3.1. Design Considerations for Parts
Uniform wall thickness is crucial in ABS part design, with a tolerance variation of no more than 25% to minimize stress. Adding ribs or radii strengthens parts, but the radius-to-wall thickness ratio should be at least 0.3 to reduce stress without excessive shrinkage. Larger radii can decrease stress but may increase shrinkage, so balance is key.
3.2. Pre-Processing Drying of ABS Material
ABS plastic absorbs moisture, which can cause defects if not properly dried. To prevent clouding and maintain quality, dry ABS to a moisture content of 0.05% or lower at 80-95°C for 3-4 hours. This step reduces operational issues and ensures consistent molding results.
3.3. Control of Molding Temperature
Precise temperature control prevents ABS degradation, which can result in discoloration or structural flaws. High-gloss parts require higher temperatures, typically between 180-230°C. Use higher temperatures for shorter times to avoid thermal decomposition, especially with older equipment prone to temperature inconsistencies.
3.4. Regulation of Injection Pressure
Due to its viscosity, ABS generally requires high injection pressure. While this is essential for uniform filling, excess pressure can cause parts to stick together, raising production costs. Conversely, low pressure can increase shrinkage, impacting part tolerance and quality.
3.5. Optimization of Injection Molding Speed
A balanced injection speed is essential for high-quality ABS parts. Too high a speed may cause thermal decomposition, burning, and poor finish, while too low a speed risks incomplete mold filling. Optimal speed control ensures dimensional stability without compromising material integrity.

ABS injection molding requires careful attention to specific process factors to ensure optimal results and part quality.
4. Applications of ABS Injection Molding
ABS injection molding is widely applied across industries due to its adaptability to complex designs. From automotive and electronics to consumer goods, ABS injection molding provides a reliable solution for producing high-quality, long-lasting parts.
4.1. Household and Office Equipment
ABS is widely used in home appliance manufacturing, providing durability and aesthetic appeal to items like juicers, rice cookers, kettles, and hair dryers. In office equipment, ABS is favored for cases and housings for items such as typewriters, keyboards, and routers, offering strength and an attractive finish.
4.2. Automotive Applications
In the automotive sector, ABS is valued for its impact resistance and ability to be molded into complex shapes. It is commonly used for interior parts, contributing to the structural integrity and visual appeal of dashboards, panels, and engine component housings.
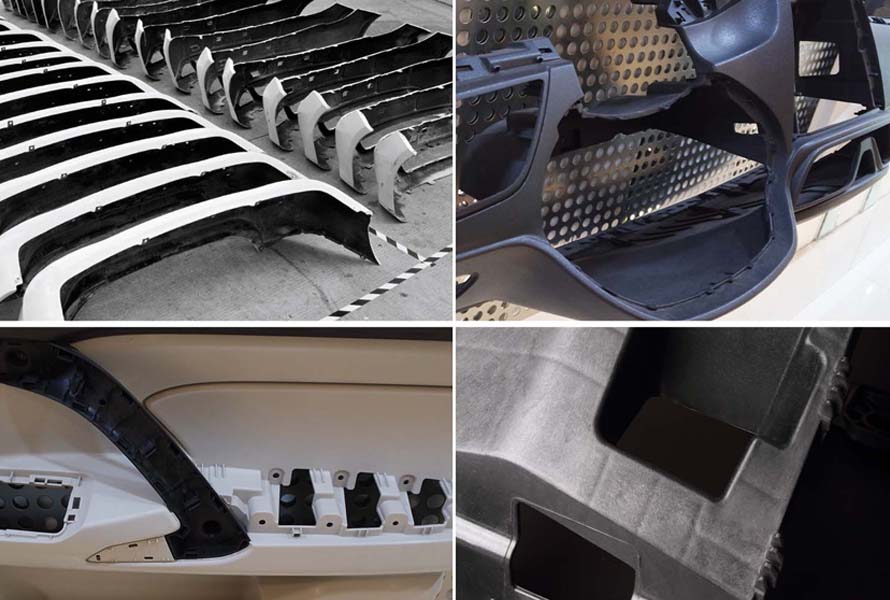

ABS is valued in automotive for impact resistance and shaping complex, durable interiors.
4.3. Toy Production
The toy industry relies heavily on ABS for its durability and safety, with iconic products like Lego blocks benefiting from ABS plastic's strength and ability to retain intricate designs even under impact.
4.4. Medical Equipment
ABS is also found in medical device manufacturing, where its chemical resistance, ease of sterilization, and strength make it ideal for durable and safe components in various medical applications.
4.5. Electronics for Consumers
ABS is a material of choice for casings and internal components in consumer electronics, including televisions, computers, and smartphones, where its durability and aesthetic qualities enhance product design and longevity.

ABS is preferred for electronics casings, offering durability and aesthetics in product design.
4.6. Components for Industrial Machinery
In industrial machinery, ABS is used for panels, covers, and guards, offering robust performance and ease of maintenance for various equipment.
4.7. Pipes and Fittings for Industrial Use
ABS's chemical resistance and durability make it ideal for pipes and drain-waste-vent (DWV) systems, as well as connectors, elbows, and joints, providing reliable corrosion resistance and long-term performance.
4.8. Domestic Appliances
For common household devices such as vacuum cleaners and coffee makers, ABS provides a cost-effective and durable solution for parts exposed to regular use.
4.9. Defense and Communication Equipment
In the defense sector, ABS is utilized in the construction of radio casings, communication equipment, and training simulator parts, offering reliability and resilience under demanding conditions.
ABS injection molding is widely applied across industries due to its adaptability to complex designs.
5. Conclusion
To conclude, ABS injection molding is essential for creating durable, complex parts with consistent quality, making it a preferred choice in various industries. Mastering the injection process involves understanding ABS plastic’s unique properties and controlling key factors like temperature, pressure, and material drying. Proper mold design also plays a significant role in achieving reliable, high-quality results. Whether for automotive, consumer electronics, or medical applications, ABS injection molding offers flexibility and resilience, ensuring that manufacturers can meet diverse demands with precision and efficiency.
6. About EuroPlas
As a leading innovator in filler masterbatches, plastic additives and compounds, EuroPlas empowers manufacturers worldwide to achieve superior performance and cost savings in their ABS injection molding processes. We offer a diverse range of high-quality solutions specifically designed to address the unique challenges of ABS injection molding.
Tailored solutions for enhanced performance including:
- EuroPlas ABS Glass Fiber Compound: This compound significantly enhances the mechanical properties of ABS, offering increased impact strength, rigidity, and dimensional stability, ideal for demanding applications like automotive components and structural parts.
- EuroPlas ABS Antistatic Compound: This masterbatch effectively mitigates electrostatic discharge (ESD) issues commonly encountered in ABS products. It's perfect for applications in the electronics industry and environments requiring static control.
- EuroPlas ABS Flame Retardant Compound: This compound incorporates flame retardant additives to improve the fire resistance of ABS, meeting specific safety requirements for various industries, including electronics and consumer goods.

EuroPlas, a leader in plastic additives and compounds, delivers top-grade products for ABS injection molding.
By leveraging EuroPlas' filler masterbatches and compounds, ABS injection molders can achieve numerous benefits as:
- Enhanced material properties
- Reduced production costs
- Consistent quality
With our extensive product portfolio and dedication to innovation, EuroPlas positions itself as a reliable partner for your ABS injection molding needs. We offer customized solutions tailored to your specific applications, ensuring optimal performance and cost savings.
Contact us today to explore how EuroPlas can elevate your ABS injection molding processes.