The differences between aramid fiber vs carbon fiber
When talking about the strongest synthetic fibers, people always call aramid fiber vs carbon fiber. The reason why they occupy a leading position in the materials industry must include properties such as super durability, light weight, heat resistance, weather resistance, chemical resistance and very good strength. Aramid fibers are widely used in the aerospace and marine industries due to their strong heat and chemical resistance. It seems that the commercial viability of carbon fiber is higher with its widespread use from fields such as aerospace, automobiles and sports equipment that tend to favor carbon fiber due to its optimal performance and high durability. Although there are quite similarities in general properties, in terms of each type, there will be different levels in each category. Understanding aramid fiber vs carbon fiber and their differences is very important in the process of calculating and choosing the right material for each production need. Let's dig deeper in the article below to get more interesting information about these two high-quality fibers!
1. What is carbon fiber?
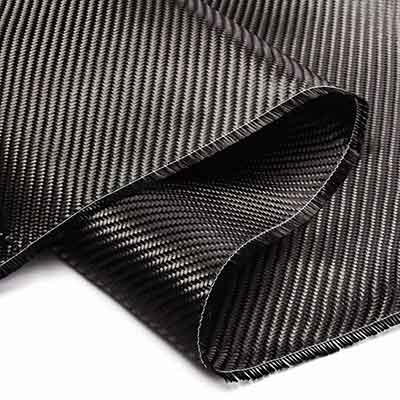

Carbon fiber sheet
Many manufacturers are familiar with carbon fibers, also known as graphite fibers, because of their excellent properties. Carbon fiber belongs to the polymer group, with a diameter of only about 5 micrometers. The precursor for fiber production is Polyacrylonitrile (PAN). Crystalline carbon fibers are twisted together along the longitudinal axis into long, super strong fibers. They are 5 times stronger than steel but much lighter than steel. The basic benefits that carbon fiber brings include good elasticity, hardness, high durability, high temperature resistance, weather resistance and excellent chemical resistance. In addition, carbon fiber also has the ability to combine with other materials to complement each other's properties without losing the original properties. To produce carbon fiber requires a skilled team because the fiber production process is complex and requires careful observation.
Read more: What is carbon fiber?
2. What is aramid fiber?
Aramid fiber sheet
Not only carbon fiber, aramid fiber is also one of the top rated materials. This is a type of synthetic fiber also known as "aromatic polyamide". The structure of aramid fibers is long chains in which at least 85% of the amide bonds, (−CO−NH−) are directly attached to two aromatic rings that act as fiber-forming agents in production. Aramid fibers are also bonded along the longitudinal axis. In terms of properties, this type of fiber is 5-6 times stronger than steel and is only half as strong as steel. This can be considered a material with excellent heat resistance with a melting level of up to about 500 degrees Celsius. Fields such as military materials, aerospace and transportation are very fond of aramid fiber because of its unique characteristics. Outstanding properties such as high temperature resistance, strong chemical resistance, flexibility and high tensile strength.
Read more: What is aramid fiber?
3. What are the differences?
3.1 Material performance: Aramid Fiber vs Carbon Fiber
Aramid fiber and carbon fiber are both synthetic fibers with excellent properties such as high elastic modulus, high tensile strength, good durability, good corrosion resistance and anti-aging. However, the durability of the two fibers is different according to the basic comparisons below:
3.1.1 Aramid fiber:

Aramid fiber ropes
- Common specifications: AK-40 and AK-60 respectively 0.193 mm and 0.286 mm
- Safety reserve coefficient: 0.75 to 0.95
- Fluctuation intensity: 0.85×2 060=1 751 MPa
- More flexible than carbon fiber
3.1.2 Carbon fiber:

Carbon fiber cable
- Common specifications: 0.11mm, 0.167 mm and 0.333mm
- Safety reserve coefficient: 0.5 to 0.7
- Fluctuation intensity: 0.7×3 600=2520 MPa
- Brittleness shows few signs before deterioration
In general, the strength of carbon fiber is much greater than that of aramid fiber, but its properties are more brittle, so it is suitable for applications with structures subjected to long-term static loads. In contrast, aramid fibers are more flexible and have strong local impact resistance, so they are suitable for applications with parts subjected to dynamic loads.
3.2 Application capabilities: Aramid Fiber vs Carbon Fiber
These fibers are widely used in technical works such as bridges and roads, industrial and civil works, underground works, etc. The general reason is that because of the tensile strength of aramid and carbon fibers, they are used to reinforce parts that require tension, compression, and bending.
3.2.1 Aramid fiber application:

Aramid fiber applications
- In the aerospace industry: aramid fibers are used to produce rocket engine casings and aircraft tires thanks to their heat-resistant properties and high durability.
- Sports equipment: used in the design of helmets, bulletproof vests, and other protective gear to prevent impacts for athletes.
- Industrial applications: used to make gaskets, conveyor belts, flexible pipes, due to its high abrasion and heat resistance
It has excellent shear resistance, so they are used as shear-resistant components of piers and seismic reinforcements.
3.2.2 Carbon fiber applications:

Carbon fiber applications
- In the aerospace industry: used to produce parts such as wings, fuselages and landing gear.
- Sports equipment: used to design bicycles, tennis rackets, and golf clubs to help reduce weight and improve performance for athletes
- In the automotive technology industry: often used in the production of vehicle covers such as body, chassis, and suspension parts. Thanks to the application of carbon fiber, the car's weight is significantly reduced, which greatly helps save fuel.
It has high strength but is brittle leading to low compressive strength, so it is used for tensile concrete connections and beam reinforcement.
3.3 Pros and cons of Aramid Fiber and Carbon Fiber
Aramid fiber is used in reinforcing cables
Advantages: high impact resistance, resistance to abrasion due to friction, high heat resistance, chemical resistance
Disadvantage: higher price compared to other materials

Carbon fiber is used in cover of a car
Advantages: high strength-to-weight ratio, high modulus of elasticity, very stiff and resistant to bending, withstands repeated stress cycles, resists corrosion from chemicals, including acid and alkaline.
Disadvantages: Higher cost with other materials
4. Conclusion

Aramid fiber and carbon fiber in use
In general, although aramid fiber and carbon fiber both have different properties, they are both classified as high-performance materials. If you need to choose a high-strength, hard and fatigue-resistant material for the aerospace, automotive or sports industries, you can choose carbon fiber. But if you need to choose a material that is resistant to impact, abrasion, and heat to protect the user, you should choose aramid fiber. EuroPlas is proud to bring our customers reliable analysis and extremely useful information about a variety of leading plastic materials on the market. Learn more here!