Thermoforming and injection molding are two common methods used in the plastic industry. Their applications appear in many different fields. But do you know which method is more optimal than the other? And which one will help improve production efficiency? EuP will answer these questions through the following article.
I. Thermoforming manufacturing process
Thermoforming is a manufacturing process performed by heating thin plastic sheets to a temperature just enough to make the plastic sheets pliable but not melted. These sheets of flexible plastic are stretched and shaped by using molds with specific shapes. The formed plastic is cooled and trimmed to obtain the finished product.
Thermoforming is divided into many different methods such as vacuum forming, pressure forming, mechanical forming, drape forming, matched mold forming, etc. But in general, they all go through the same steps.
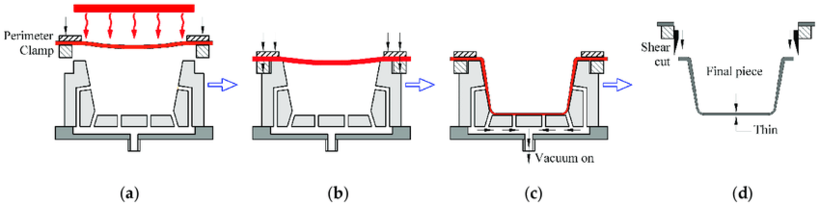
A basic thermoforming process diagram
1. Thermoforming process steps
1.1. Heating Plastic Sheets
The plastic sheets are clamped and transported into the heating machine to heat to forming temperature. They are heated by hot air or an infrared heater.
The type of heating machine selected depends on the plastic material used and the desired heat. Temperature is one of the most important parameters in the thermoforming process to meet quality standards because it creates the required ductility and flexibility of the plastic sheets.
1.2. Forming Plastic Sheets
This process is accomplished by stretching the heated thermoplastic sheet over the mold surface of the desired shape of the finished product. There are two types of mold tools depending on the finished product geometry.
The positive tool has a convex shape, and placing a flexible plastic sheet above that convex shape will create the final product. The outer surface of the positive mold gives the inner surface of the product.
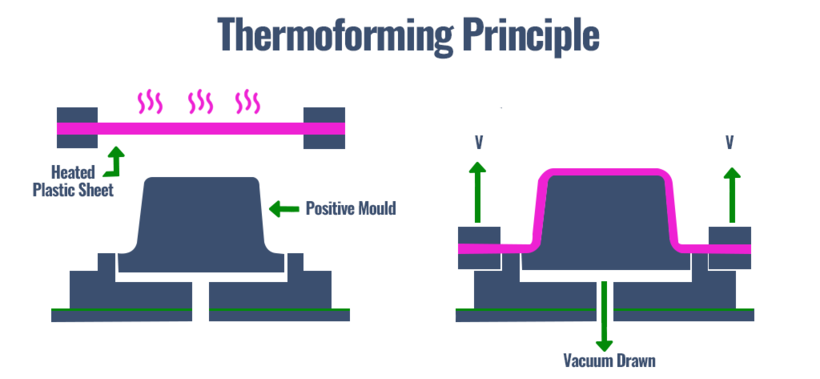
Thermoforming with positive mold
In contrast, the negative tool has a concave shape, and the inner surface of the negative mold generates the outer surface of the product.
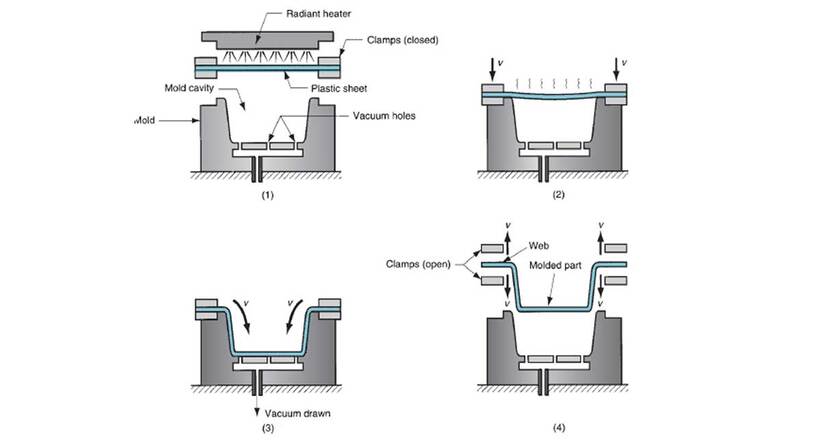
Thermoforming with negative mold
1.3. Trimming formed sheets
The plastic sheet, after being shaped, will move through a trimming machine to take out the final products. Scrap from the manufacturing process is treated and recycled for future production.
Related:
- Common applications of filler masterbatch in thermoforming
- After mixed with masterbatch, how was plastic processed with injection molding?
2. Plastic thermoforming advantages and disadvantages
2.1. Advantages
- Low cost: Thermoforming molds can easily be made from inexpensive materials such as silicone, fiberglass, etc., instead of expensive and laborious metal molds. This makes thermoforming capable of producing large parts at a cheaper cost than other plastic manufacturing methods.
- Durability: The thermoforming method has a simple machining process but produces high-quality products that are resistant to external influences and durable over time.
- Production time: Since thermoforming molds are made from materials that are easy to work with and do not require complicated machining, they can be put into production quickly.
- Design: Thermoforming can create objects with large designs. This aspect is one of the main reasons why thermoforming has become such a popular method of plastic production, especially in automotive design.
Some applications of thermoforming process
2.2. Disadvantages
- Scrap: The finished product of the thermoforming method after being trimmed will create scrap plastic. Fortunately, this scrap plastic is all recycled in production.
- Geometric limitations: The thermoforming is limited by complex geometry. Usually, small parts and intricate details are not feasible with this method.
- Surface thickness: The part thickness may not be uniform across all surfaces of the finished product. Therefore, the temperature parameters need to be optimized during operation to ensure the best quality.
- The cost: cost per finished product can be higher than other methods.
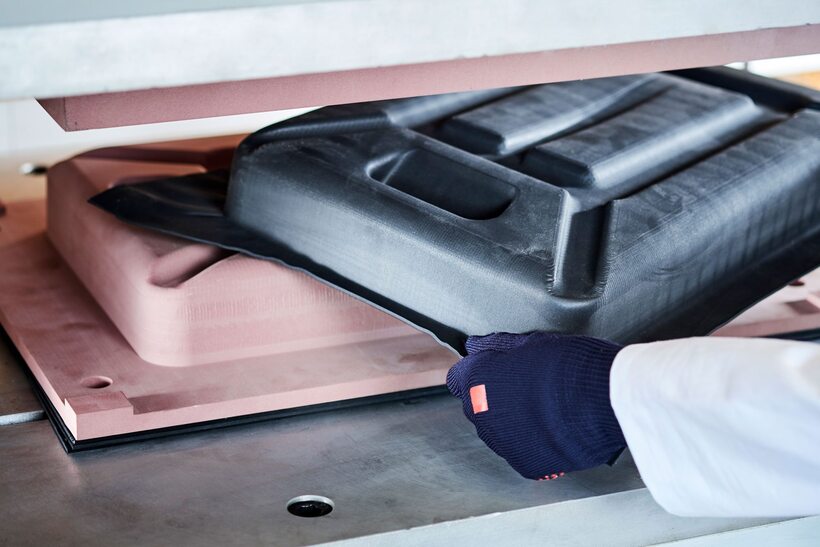

An application of thermoforming process
II. Injection molding manufacturing process
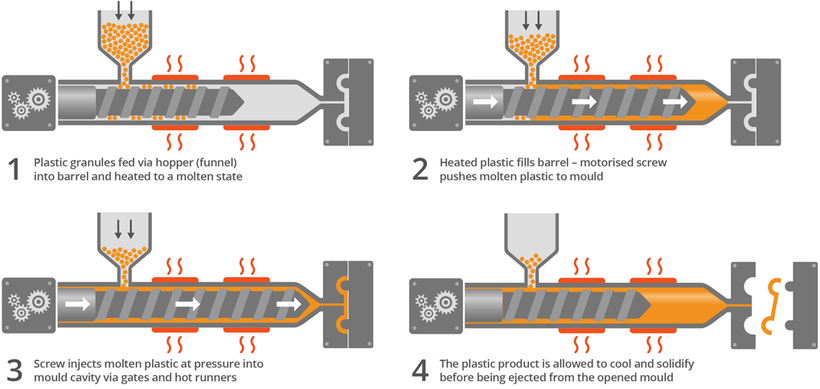
Injection molding is a method of manufacturing plastic by injecting molten plastic at high pressure into a mold where it is shaped. The entire injection molding process only lasts from 10 seconds to 2 minutes. There are four main stages in an injection molding cycle: clamping, injection, cooling, and de-molding.
1. Injection molding process steps
Related:
- Plastic injection molding cost
- Common plastics for injection molding that you need to know
- How to effectively apply colorants in your plastic injection molding?
1.1. Clamping
Before the material is injected into the mold, the two halves of the mold must be closed by a clamping device. Both mold halves must be held firmly while the material is injected.
1.2. Injection
The input material is put into the injection molding machine through a hopper. The plastic is then heated until completely melted. Next, the melted plastic is injected into the mold through a nozzle.
1.3. Cooling
The cooling process takes place using an air or water system. The plastic inside the mold begins to cool and harden to fix the desired shape.
1.4. De-molding
At this final stage, the mold is opened and the product is ejected from the mold. Then, the mold will clamp and prepare for the next cycle.
2. Plastic injection molding advantages and disadvantages
2.1. Advantages
- High efficiency: Thanks to the fast production cycle, this method can produce a large number of products per hour. The production speed depends on the complexity and size of the mold.
- Low labor costs: Plastic injection molding is an automated process, most of the process is done by machines and requires only one operator to manage.
- Low scrap rate: This is a plastic production method that produces very little scrap compared to the traditional manufacturing process. Scrap plastic, if any, is ground and recycled for future use.
- Good color control: The finished plastic product can be produced in any color by mixing the appropriate color masterbatches.
- Product consistency: Injection molding is a process with low tolerances and high precision in product dimensional specifications. This is a huge advantage in bulk production.
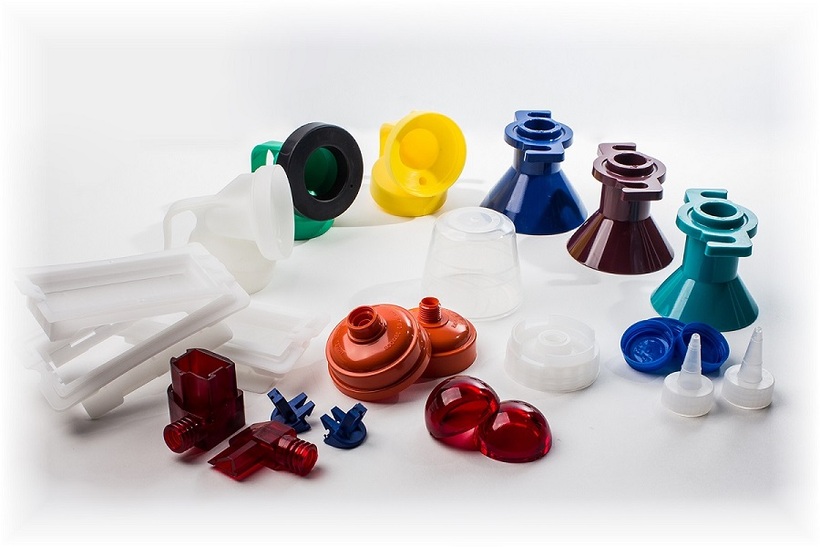

Injection molding application on small parts
2.2. Disadvantages
- Complex mold structure: Mold design plays a key role in determining the quality of the finished product. The mold must be strong and able to withstand the pressure during injection.
- High tooling costs: Since the mold must be made of metal and have high finishing, the initial cost of the manufacturing process is quite high.
- Long set-up time: Due to the meticulous requirements for the design and quality of the injection mold, it takes a long time to create the mold and successfully test it before being used in production.
- Design limitations: The injection molding technique is hard to meet the finished products with large weight and size. The larger the parts, the more difficult and expensive the manufacturing process.
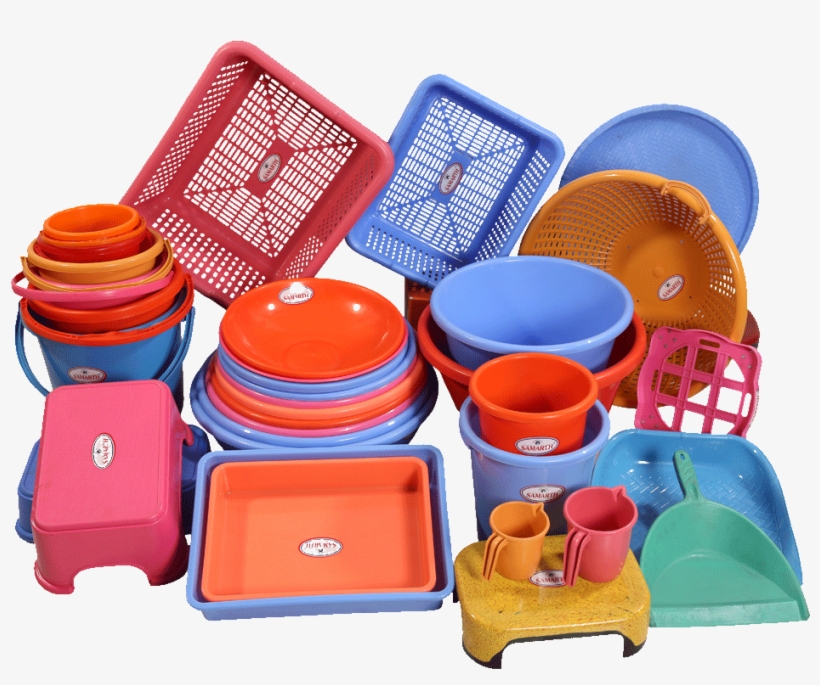

Injection molding application on large parts
III. Difference between thermoforming and injection molding
| |
Thermoforming |
Injection molding |
Mold
|
A single mold is created out of fiberglass, aluminum, wood, silicone,... |
A double-sided mold is created out of metal Flat thermoplastic sheets with a wide range of materials, colors, and thicknesses |
Input material
|
Flat thermoplastic sheets with a wide range of materials, colors, and thicknesses |
Thermoplastic pellets in a wide variety of materials and colors |
Production
|
A flat plastic sheet is heated to a pliable temperature, then molded to the shape of a mold |
Plastic granules are heated to a melted temperature, then injected into the mold |
Finishing
|
Products after molding need to go through the process of trimming out of the sheets to obtain the finished product |
Products after de-molding are often painted or silk-screened to obtain the finished product |
Cost
|
The initial tooling cost is low, but per piece cost is high |
The initial tooling cost is high, but per piece cost is low |
Size
|
Suitable for large parts without complex structure |
Suitable for small and complicated parts |
Production volume
|
Suitable for projects with a small production quantity |
Suitable for projects with bulk production volume |
Related: The Difference between Extrusion Blow Molding and Injection Molding
Both techniques provide their own features and benefits.
Generally, thermoforming is ideal for projects that require small production quantities, low tooling costs, and large parts with simple designs.
In contrast, injection molding is used for high-volume manufacturing that requires high precision and low-variance finished products. Injection molding is ideal for creating small parts with complex shapes.