Natural vs. Synthetic materials: What are the differences?
In our daily lives, we interact with an extensive array of materials, each with its unique characteristics and applications. Whether it's the clothes we wear, the buildings we live in, or the devices we use, the materials around us can be broadly categorized into two primary groups: natural vs synthetic.
Natural materials, derived from the environment, have been utilized by humans for centuries. Wood, stone, and cotton are examples of these materials, each offering a distinctive set of properties and a link to the natural world. On the other hand, synthetic materials, born from human ingenuity, have revolutionized industries and technology. Plastics, composites, and artificial polymers are just a few examples of these engineered marvels.
In this blog, we'll embark on a journey to explore the fascinating realm of natural vs synthetic materials. We'll uncover their characteristics, advantages, and applications, and delve into the critical factors to consider when choosing between them. So, let's unravel the differences between these two material worlds and understand their profound impact on our modern lives.
1. What is the difference between natural vs synthetic materials?

Natural vs synthetic materials
When it comes to materials used in our daily lives, we encounter two broad categories: synthetic vs natural materials. These categories represent the fundamental building blocks of our world, each with its unique characteristics and applications. Understanding the differences between them is essential for making informed choices in various industries, from fashion and construction to healthcare and environmental preservation.
1.1. Natural Materials:
Natural materials are derived from the environment, created by nature over time. They encompass a wide range of substances, including minerals, plants, and animals. Here are some key characteristics of natural materials:
- Origin: Natural materials originate from the natural world without human interference. They are found in nature and often require minimal processing to be used in various applications.
- Diversity: The diversity of natural materials is astounding. Examples include wood, stone, cotton, silk, leather, and various minerals. This diversity means they can serve an extensive array of purposes.
- Environmental Impact: Depending on how they are sourced and harvested, natural materials can be more sustainable and eco-friendly than synthetics. They are biodegradable and generally have a lower environmental footprint when handled responsibly.
- Variability: Natural materials can vary in quality, texture, and appearance due to the natural variations found in nature. This uniqueness often adds to their aesthetic value.
1.2. Synthetic Materials:
Synthetic materials, on the other hand, are artificially created through chemical processes, often using raw materials derived from natural sources. Here are some key characteristics of synthetic materials:
- Man-Made: Synthetic materials are entirely human-made, designed for specific purposes. They do not exist in nature and are produced in controlled environments like laboratories and factories.
- Uniformity: Unlike natural materials, synthetics can be manufactured with a high degree of consistency, ensuring uniform quality and performance.
- Customizability: Synthetic materials can be tailored to meet precise requirements, leading to innovations in various industries. Examples include plastics, nylon, polyester, and various high-performance polymers.
- Durability: Many synthetic materials are engineered to be highly durable and resistant to environmental factors, making them ideal for long-lasting products.
- Environmental Concerns: While some synthetic materials can be more durable, they are often not biodegradable, posing environmental challenges when not managed properly.
So in summary, what is the difference between natural vs synthetic materials? The main difference between synthetic vs natural materials lies in their origin, diversity, and impact on the environment. Natural materials are sourced from the natural world, offer diversity and can be environmentally friendly when managed sustainably. In contrast, synthetic materials are man-made, offer uniformity, customizability, and enhanced durability, but may raise concerns related to their environmental impact. Each type has its own advantages and drawbacks, and the choice between them depends on the specific application and the balance between functionality, sustainability, and environmental considerations.
2. What are natural materials?

What are natural materials?
Natural materials are substances that are sourced directly from the environment and exist in their unaltered or minimally processed state. These materials are a vital part of our everyday lives and have been used for millennia by humans in various applications due to their unique characteristics and benefits.
2.2. Advantages of Using Natural Materials:
Natural materials offer several advantages, making them appealing for a wide range of applications:
- Sustainability: Natural materials are often more environmentally friendly than their synthetic counterparts. They are typically renewable and biodegradable, reducing the environmental impact of their production and disposal. For example, wood, when sourced from sustainably managed forests, can be a highly sustainable building material.
- Biocompatibility: Many natural materials are compatible with the human body. This quality makes them suitable for use in various applications, such as natural fibers in clothing, organic materials in medical devices, and natural oils in cosmetics.
- Aesthetics: Natural materials often have a unique aesthetic appeal. Wood, stone, and leather, for instance, are valued not only for their functional properties but also for their natural beauty. This aesthetic quality contributes to their use in interior design and architecture.
- Comfort: In applications like textiles, natural materials like cotton and wool are known for their comfort and breathability, making them ideal for clothing, bedding, and upholstery.
2.3. Natural Materials Examples:
Natural materials are incredibly diverse, and they can be classified into several categories based on their source. Here are some of the most common natural materials examples:
Plant-Based Materials: These materials are derived from various plants and include:
- Wood: Used in construction, furniture, and various decorative items.
- Cotton: A popular natural fiber for clothing and textiles.
- Bamboo: Known for its sustainability and versatility in construction and textiles.
- Hemp: Used for textiles, paper, and even eco-friendly building materials.
Animal-Based Materials: Derived from animals, these materials include:
- Leather: Obtained from animal hides and used in fashion, furniture, and accessories.
- Wool: A natural fiber from sheep, known for warmth and softness in textiles.
- Silk: Known for its luxurious feel, often used in clothing and home textiles.
Mineral-Based Materials: These materials come from minerals and geological sources, and examples include:
- Stone: Used in construction, sculptures, and as a decorative material.
- Clay: Utilized for pottery, ceramics, and earthenware.
- Salt: Used in food preservation and various industrial processes.
Other Natural Materials: This category includes materials like cork, natural rubber, and seashells, each with its own unique set of properties and applications.
In summary, natural materials encompass a wide array of substances sourced directly from the natural world. They offer numerous advantages, such as sustainability, biocompatibility, and aesthetics, making them a valuable resource in various industries and for a variety of consumer products. The next section of this blog will explore the counterpart to natural materials: synthetic materials, highlighting their own set of characteristics and applications.
3. What are synthetic materials?

What are synthetic materials?
Synthetic materials are human-made substances that are engineered and produced through chemical or industrial processes. These materials are designed to meet specific requirements, offering a wide range of benefits and applications across various industries. In contrast to natural materials, which are sourced from the environment, synthetic materials are created with precise control over their properties.
3.2. Advantages of using synthetic materials:
Synthetic materials provide several advantages that make them valuable in modern society:
- Customization: One of the primary advantages of synthetic materials is the ability to customize their properties. Engineers and scientists can precisely control factors such as strength, flexibility, and electrical conductivity to suit a wide range of applications. This level of control allows for innovation in various industries, from aerospace to healthcare.
- Durability: Many synthetic materials are engineered to be exceptionally durable. They can resist factors like moisture, extreme temperatures, and chemicals, making them ideal for applications that require long-term performance, such as building materials, automotive parts, and electronic components.
- Reproducibility: Synthetic materials offer consistency in their properties, ensuring that the same material produced in a laboratory or factory will perform the same way each time. This predictability is crucial in industries where precision is paramount, including electronics, pharmaceuticals, and aerospace.
- Cost-Efficiency: The production of synthetic materials can often be more cost-effective than sourcing natural alternatives. This cost efficiency is especially beneficial in mass production, helping make products more accessible to consumers.
3.3. Synthetic Materials Examples
Synthetic materials are incredibly diverse, covering a wide spectrum of applications. Some common examples include:
- Plastics: These versatile materials, derived from petrochemicals, are used in countless products, from packaging and automotive components to medical devices and toys.
- Synthetic Polymers: Materials like nylon, polyester, and polyethylene are synthetic polymers used in textiles, ropes, and various industrial applications.
- Composite Materials: Composites combine different materials to create a product with enhanced properties. Examples include carbon fiber composites in aerospace and fiberglass-reinforced plastics in construction.
- Synthetic Rubber: Rubber compounds like neoprene and silicone are used in a wide range of applications, including tires, gaskets, and seals.
- Fiberglass: A composite material made of glass fibers and plastic, fiberglass is used in boat construction, automotive parts, and sporting equipment.
- Synthetic Foams: Materials like polyurethane foam are used for cushioning and insulation in furniture, mattresses, and insulation products.
In conclusion, synthetic materials are the result of human ingenuity and engineering, offering the benefits of customization, durability, and cost-efficiency. Their versatility has led to their widespread use in various industries, from everyday consumer products to cutting-edge technologies.
4. Should You Choose Natural or Synthetic Materials?
There is no one-size-fits-all answer. Choosing between natural materials and synthetic materials depends on practical needs, environmental conditions, and economic factors. Each material type has its own strengths and limitations.
If you're looking for environmentally friendly, aesthetically pleasing, and culturally rooted options, natural materials like wood, cotton, or natural stone may be ideal. These materials are especially favored in home décor, high-end fashion, and artisan crafts due to their unique textures and sustainability.
On the other hand, for applications requiring high durability, moisture resistance, thermal stability, and cost-effective mass production, synthetic materials are better suited. From automobiles and electronics to packaging and medical devices, materials like engineered plastics, synthetic fibers, and composites deliver exceptional performance and reliability.
In many cases, combining both material types yields optimal results. For instance, in modern green architecture, blending natural wood with recycled composite materials provides both aesthetic charm and structural integrity while minimizing environmental impact.
5. EuroPlas: Your Premier Source for High-Quality Plastic Solutions
When it comes to procuring top-tier plastic solutions that excel in both performance and sustainability, EuroPlas emerges as a global industry leader. With over 15 years of expertise, EuroPlas has established a sterling reputation for delivering innovative and eco-conscious products to customers spanning more than 85 countries.
As a masterbatch manufacturer headquartered in Vietnam, we take immense pride in our state-of-the-art facilities, unique natural resources, and cutting-edge technology. These assets empower us to tailor products for a wide array of industries and applications. At EuroPlas, we remain steadfast in our commitment to shaping a sustainable future by providing cost-effective and eco-friendly options that cater to the ever-evolving needs of our global clientele.
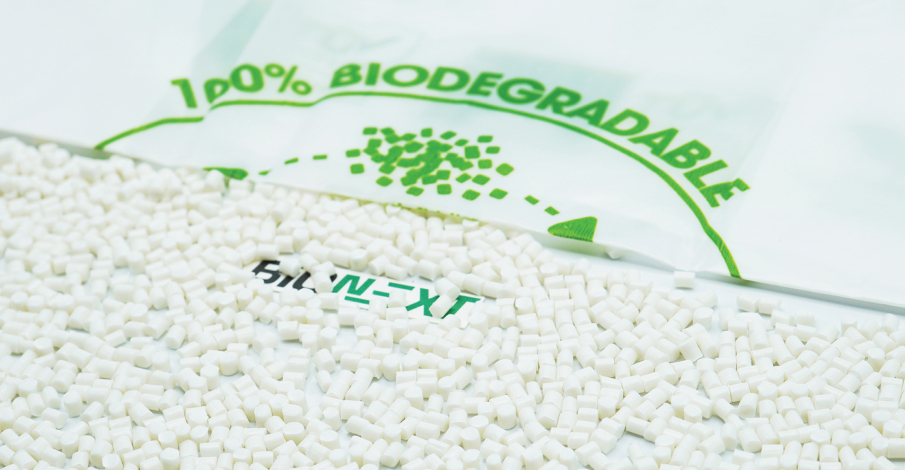

Bioplastic compound
One of our flagship products is the EuroPlas Bioplastic Compound, a testament to our dedication to environmental sustainability. Crafted from natural starch and biodegradable additives, this unique compound not only upholds exceptional performance but also facilitates the biodegradation of plastic items within a year. This makes it an excellent choice for applications in food packaging, agricultural films, and a myriad of industries, significantly contributing to a greener and more eco-friendly future.

Bio filler
In alignment with our sustainability commitment, EuroPlas proudly presents the Bio Filler, an eco-friendly alternative that renders plastic items biodegradable within a year. Comprising natural starch and biodegradable additives, our Bio Filler is ideal for applications in food packaging, disposable tableware, and agricultural films. It provides a sustainable choice that promotes environmental consciousness without compromising product performance.

Filler masterbatch
Our Filler Masterbatch is a game-changer for industries seeking to reduce production costs while enhancing the properties of plastic products. By replacing a portion of virgin resin with filler materials such as calcium carbonate or talc, this product improves stiffness, heat resistance, opacity, and printability. It finds applications in blowing films, injection molding, extrusion, and thermoforming, making it an indispensable component across various sectors.

Color masterbatch
At EuroPlas, we recognize the significance of aesthetics. Our Color Masterbatch offers precise and consistent colors for toys, household appliances, cosmetics, and more. Utilizing high-quality pigments and additives that can be blended with various resins, we ensure that your products showcase vibrant and captivating designs that perfectly align with market demands.

Plastic additives
Our range of Plastic Additives plays a pivotal role in improving production efficiency and functionality for films, pipes, and cables. Featuring a comprehensive suite of agents such as slip, anti-block, anti-static, anti-oxidants, and UV stabilizers, EuroPlas' additives enhance the performance and durability of plastic products while actively contributing to sustainability by minimizing waste.
Engineering plastic compound
For those in search of high-performance plastic solutions that meet stringent industry standards, EuroPlas offers Engineering Plastic Compounds. These all-in-one solutions combine engineering resins with a range of additives to enhance the mechanical, thermal, electrical, optical, and chemical properties of plastic products. Whether for automotive parts, electronic components, or medical devices, EuroPlas' Engineering Plastic Compounds consistently outperform competitors, ensuring quality and reliability.
EuroPlas stands as your unwavering partner in embracing the future of plastic materials – a future defined by excellence in performance and a profound commitment to environmental responsibility. With our diverse product range and unswerving dedication, we eagerly anticipate serving your plastic needs and being a part of your journey toward a more sustainable tomorrow. Contact us now for more information!