Polycarbonate chemical resistance has propelled its popularity in numerous industries. From automotive to electronics, this versatile material offers unparalleled protection against a wide range of chemicals, solvents, and corrosive substances. Its inherent ability to withstand harsh environments while maintaining its structural integrity makes it a top choice for applications requiring robust chemical resistance.
In this article, we delve into the key factors that make polycarbonate stand out in terms of chemical resistance. Explore the unique properties and advantages that have made polycarbonate the preferred material for manufacturing durable, long-lasting, and chemically resistant products. Let’s get started!
Table of Contents
- What is polycarbonate?
- The common characteristics of polycarbonate
- Polycarbonate chemical resistance
- Application of polycarbonate
- European Plastic Company: A reliable polycarbonate supplier
1. What is polycarbonate?

Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate is a versatile and widely used thermoplastic polymer that has gained immense popularity due to its exceptional properties and applications in various industries. It belongs to the family of engineering plastics, known for their strength, durability, and high-performance characteristics.
The synthesis of polycarbonate begins with the combination of BPA, a key building block, and phosgene, a reagent. This reaction takes place in a controlled environment, typically in the presence of a catalyst. The resulting chemical reaction forms the polycarbonate polymer, with the molecular structure characterized by repeating carbonate groups.
The polymerization process can be carried out using various methods, such as interfacial polymerization or melt polymerization. Interfacial polymerization involves the reaction of BPA and phosgene in two immiscible liquid phases, typically an aqueous phase and an organic phase. This method allows for the efficient synthesis of high molecular weight polycarbonate.
Melt polymerization, on the other hand, involves the direct reaction of BPA and phosgene in the molten state. This process is more commonly used for industrial-scale production, as it offers higher productivity and easier handling of the materials.
Once the polymerization is complete, the resulting polycarbonate is typically in the form of pellets or granules. These can then be further processed into various shapes and sizes using techniques such as injection molding, extrusion, or thermoforming.
2. The common characteristics of polycarbonate
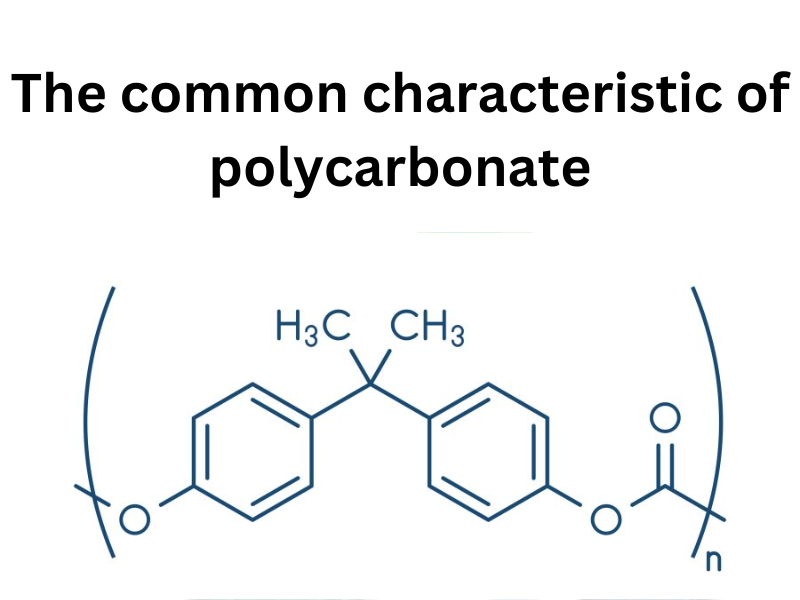
Common characteristics of polycarbonate
Polycarbonate exhibits several common characteristics that contribute to its popularity and widespread use across various industries. These shared properties make it a sought-after material for numerous applications. Let's explore some of the key characteristics of polycarbonate:
- Transparency and Optical Clarity: Polycarbonate is highly transparent, allowing for the efficient transmission of light. It offers exceptional optical clarity, making it an excellent choice for applications that require visibility, such as windows, eyewear, and display screens. Its transparency is comparable to that of glass, but with added benefits of being lightweight and impact-resistant.
- High Impact Resistance: Polycarbonate is renowned for its outstanding impact resistance. It can withstand significant physical force without shattering or breaking, making it an ideal material for safety equipment, protective shields, and impact-resistant windows. This property ensures a high level of safety and durability in demanding environments.
- Wide Temperature Range: Polycarbonate exhibits excellent thermal stability over a wide temperature range. It can withstand both high and low temperatures without significant deformation or degradation of its properties. This characteristic makes polycarbonate suitable for applications that involve extreme temperature conditions, such as automotive components and electronic enclosures.
- Chemical Resistance: Polycarbonate possesses remarkable resistance to a broad range of chemicals, including acids, bases, alcohols, and many solvents. It remains unaffected by exposure to these substances, making it an ideal choice for chemical storage containers, laboratory equipment, and medical devices.
- Electrical Insulation Properties: Polycarbonate is an excellent electrical insulator. It has low electrical conductivity, which makes it well-suited for applications that require insulation against electric currents. It is commonly used in electrical connectors, switches, and insulating components.
- Lightweight: Despite its exceptional strength and durability, polycarbonate is relatively lightweight compared to other materials like glass or metals. This characteristic is particularly advantageous in industries such as aerospace and automotive, where weight reduction is crucial for improving fuel efficiency and overall performance.
- Easy Processing and Versatility: Polycarbonate is highly moldable and can be processed using various techniques, including injection molding, extrusion, and thermoforming. Its versatility allows for the production of complex shapes and designs, making it suitable for a wide range of applications.
3. Polycarbonate chemical resistance

Polycarbonate chemical resistance
Polycarbonate chemical resistance is renowned as it is one of its most notable characteristics. This property makes polycarbonate a preferred choice for applications where exposure to various chemicals is expected. Let's delve into the chemical resistance of polycarbonate and understand why it is highly valued in such environments.
Polycarbonate's molecular structure, consisting of repeating carbonate groups, contributes to its robust chemical resistance. It exhibits resistance to a wide range of chemicals, including acids, bases, alcohols, and many solvents. This resistance stems from the stability of the carbon-oxygen bonds within the polycarbonate structure.
- Acids: Polycarbonate demonstrates resistance to both organic and inorganic acids, including sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acid, nitric acid, and acetic acid. This resistance allows it to withstand exposure to corrosive environments, making it suitable for acid storage containers, chemical processing equipment, and laboratory apparatus.
- Bases: Polycarbonate also displays resistance to bases, such as sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide, and ammonia solutions. It remains unaffected by alkaline environments, enabling its use in applications where contact with strong bases is prevalent, such as wastewater treatment systems and alkaline cleaning processes.
- Alcohols: Polycarbonate exhibits excellent resistance to a wide range of alcohols, including methanol, ethanol, isopropyl alcohol, and many more. This characteristic makes it suitable for applications involving alcohol-based solutions, such as medical devices, laboratory equipment, and beverage containers.
- Solvents: Polycarbonate showcases resistance to various solvents, including common ones like acetone, toluene, and chloroform. This resistance makes it an ideal choice for applications where exposure to solvents is expected, such as chemical storage containers, automotive parts, and electronic components.
It is important to note that while the level of polycarbonate chemical resistance is pretty high, certain aggressive chemicals and conditions may still have an impact on its properties over time. It is advisable to consult chemical compatibility charts and conduct thorough testing in specific chemical environments to ensure the suitability of polycarbonate for a particular application.
In summary, polycarbonate chemical resistance is a key factor in its popularity for applications requiring resistance to acids, bases, alcohols, and solvents. Its ability to withstand exposure to a wide range of chemicals makes it a reliable choice in environments where chemical resistance is crucial. By selecting polycarbonate, industries can benefit from its durability, longevity, and performance in challenging chemical environments.
4. Application of polycarbonate

Applications of polycarbonate
Polycarbonate finds widespread application across numerous industries, thanks to its unique combination of properties and versatility. Its exceptional characteristics make it a preferred material for various products and components. Let's explore some of the key applications of polycarbonate:
- Automotive Industry: Polycarbonate is extensively used in the automotive sector for a range of applications. It is employed in headlight lenses, taillight covers, interior trim components, instrument panels, and automotive glazing. Its high impact resistance, lightweight nature, and excellent optical properties make it an ideal choice for enhancing vehicle safety, design flexibility, and fuel efficiency.
- Electrical and Electronics: Polycarbonate plays a crucial role in the electrical and electronics industry. It is used in the manufacturing of electrical connectors, switches, insulators, and enclosures. Its electrical insulation properties, thermal stability, and resistance to flame and chemicals make it a reliable choice for applications where electrical safety and performance are paramount.
- Construction and Architecture: Polycarbonate is widely utilized in the construction and architecture sectors. It is employed in the production of skylights, roofing sheets, canopies, façades, and safety glazing. Polycarbonate's transparency, impact resistance, weatherability, and lightweight nature make it an excellent material for maximizing natural light, ensuring durability, and enhancing energy efficiency in building designs.
- Medical Equipment and Devices: Polycarbonate is extensively used in the medical industry for a range of applications. It is employed in the manufacturing of medical devices, such as surgical instruments, diagnostic equipment, IV connectors, and housings for electronic medical devices. Its biocompatibility, sterilizability, chemical resistance, and transparency make it suitable for critical medical applications.
- Safety Equipment: Polycarbonate's exceptional impact resistance and transparency make it an ideal choice for safety equipment. It is utilized in the production of safety goggles, face shields, riot shields, and helmets. Its ability to provide effective protection while maintaining clear visibility is crucial in industries such as manufacturing, construction, and law enforcement.
- Consumer Goods: Polycarbonate is used in various consumer goods, including eyewear, smartphone and tablet casings, luggage, bttles, and food containers. Its lightweight nature, impact resistance, and aesthetic appeal make it a preferred material for these applications.
- Aerospace Industry: Polycarbonate is finding increasing use in the aerospace industry. It is utilized in aircraft windows, cabin interiors, and cockpit components. Polycarbonate's high strength-to-weight ratio, impact resistance, and flame-retardant properties contribute to enhancing aircraft safety and fuel efficiency.
- Greenhouses and Agricultural Applications: Polycarbonate is favored for greenhouse construction due to its high light transmission, durability, and resistance to extreme weather conditions. It provides an optimal environment for plant growth while withstanding harsh outdoor elements.

EuroPlas polycarbonate plastic compound
EuroPlas takes pride in being a trusted supplier of premium polycarbonate plastic compounds. With our commitment to quality and innovation, we offer a wide range of polycarbonate products that cater to the diverse needs of industries worldwide.
Our polycarbonate compounds are meticulously developed using advanced manufacturing processes and high-quality raw materials. This ensures that our products exhibit exceptional properties, including excellent mechanical strength, outstanding heat resistance, superior impact resistance, and excellent dimensional stability. Whether you require materials for automotive applications, electrical components, or consumer goods, our polycarbonate compounds are engineered to meet the highest standards.
We understand the importance of consistent quality and performance in your projects. That's why our team of experts conducts rigorous testing and quality control measures at every stage of production. This ensures that our polycarbonate compounds consistently meet or exceed industry standards, providing you with reliable and high-performance materials.
At EuroPlas, we are not only committed to delivering exceptional products but also providing excellent customer service. Our dedicated team is ready to assist you throughout your journey, from product selection to technical support and after-sales service. We value your success and strive to build long-term partnerships based on trust and mutual growth.
When you choose EuroPlas as your polycarbonate supplier, you gain access to a comprehensive range of products, technical expertise, and a reliable partner that is focused on meeting your specific requirements. Contact us today to discover how EuroPlas can provide you with superior polycarbonate solutions for your industry.