PA12 vs PA11 are two common types of polyamide plastics, sharing a similar chemical structure, but they differ in certain physical and chemical properties.
Today, nylons have gained extensive utilization in industries such as automotive and aerospace for both functional prototyping and final product applications. Among the prevalent nylons used in 3D printing, Nylon 11 (PA11) and Nylon 12 (PA12) stand out.
1. What Are PA11 vs PA12?
Nylon 11 and Nylon 12 belong to the polyamide family. Despite their common nylon classification, they have distinct origins. PA12 is primarily derived from petroleum sources, whereas PA11 is exclusively sourced from vegetable oil, rendering it one of the rare bio-based thermoplastics.
Nylon 12 is designed to substitute many functions of Nylon 11, thus sharing numerous properties. Both PA11 and PA12 find widespread use in powder bed fusion processes like selective laser sintering (SLS) and multi-jet fusion (MJF), known for their rapid 3D printing capabilities. They exhibit robust resistance to various chemicals, including fuels, bases, and salts, offer exceptional resolution, and have the capacity to recycle approximately 70% of unfused powder following a printing process.
From a chemical perspective, PA11 vs PA12 are highly similar polymers, differing only by a single carbon atom in their polymer backbone. However, this singular carbon atom has a significant impact on how the polymer arranges itself to create three-dimensional objects.
.jpg)
What Are PA11 vs PA12?
1.1. Nylon PA11 vs PA12 characteristics
Nylon PA11 characteristics
- Resistant to various chemicals including hydrocarbons, ketones, aldehydes, fuels, alcohols, oils, fats, mineral bases, salts, and detergents.
- Exhibits minimal water absorption.
- Boasts impressive heat resistance.
- Has a minimal environmental footprint.
- Requires fewer renewable resources.
- Finds application in mechanically demanding functional prototypes, automotive interior components, long-lasting moving parts (e.g., hinges), and production runs.
Nylon PA12 characteristics
- Displays chemical resistance to substances like oil, fuels, hydraulic fluids, grease, salt, solvents, and water.
- Effectively attenuates noise and vibrations.
- Demonstrates outstanding heat resistance.
- Highly suitable for processing.
- Boasts exceptional abrasion resistance.
- Available from multiple manufacturers.
- Primarily employed for fully functional plastic components, such as gears, often serving as a viable alternative to conventional injection molding plastics.
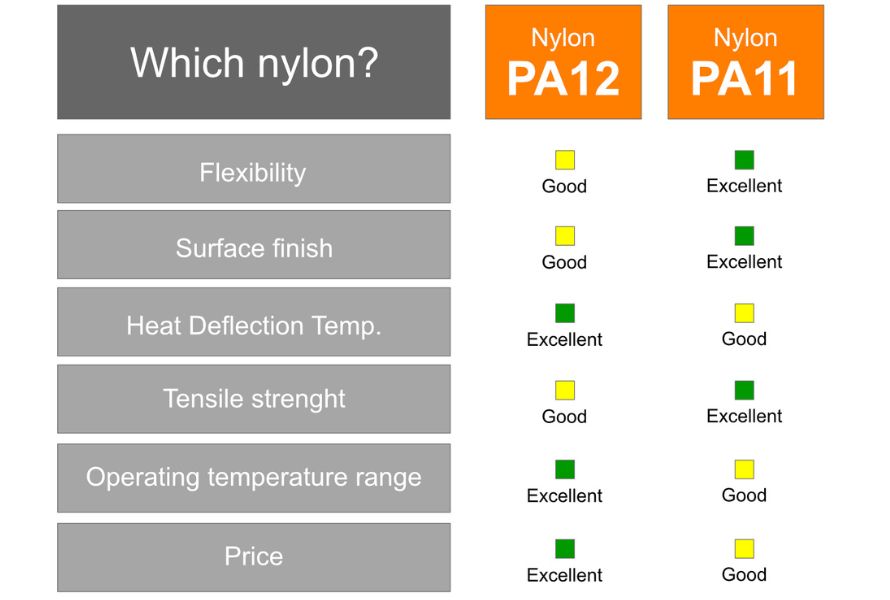
Nylon PA11 vs PA12 characteristics
1.2. Mechanical Properties of PA11 vs PA12
The mechanical properties should be determined for each specific application. In principle, you can't go wrong with either PA11 or PA12 materials. PA11 components tend to be up to 50% more expensive than PA12 components. This is not necessarily due to the material cost and the ratio of blending the old material with the new one but rather because the demand for PA11 is currently much lower, leading to limited utilization. Below is a comparison of the mechanical properties of both materials:
|
Properties
|
Testing Standards
|
Units
|
PA12 (PA2200)
|
PA11 (PA1101)
|
|
Melting Temperature (20°C/min)
|
ISO 11357-1/-3
|
°C
|
176
|
201
|
|
Flexural Modulus (+23°C)
|
ISO 178
|
MPa
|
1500
|
-
|
|
Charpy Impact Strength (+23°C)
|
ISO 179/1eA
|
KJ/m²
|
4.8
|
7,8
|
|
Charpy Impact Strength (+23°C)
|
ISO 179/1eU
|
KJ/m²
|
53
|
N
|
|
Tensile Modulus
|
ISO 527
|
MPa
|
1650
|
1600
|
|
Tensile Strength
|
ISO 527
|
MPa
|
48
|
48
|
|
Elongation
|
ISO 527
|
%
|
18
|
45
|
|
Shore Hardness
|
ISO 7619-1
|
-
|
75
|
75
|
3. Nylon 11: More Flexibility, Competitive Edge
While both nylon PA11 vs PA12 find applications in prototyping and end-use scenarios, Nylon PA11 outperforms PA12 in terms of flexibility, strength, and impact resistance. These attributes position it as the preferred material for more demanding applications.
Impact Resistance of Nylon 11 exhibits greater flexibility and overall strength compared to Nylon 12. Its exceptional strength combined with a high elongation at break makes it the most impact-resistant nylon 3D printing material.
Nylon PA11, renowned for its outstanding mechanical properties, is a favored choice in consumer goods markets for items like cases and containers, as well as in the sports and automotive industries. It has also found valuable applications in the medical sector, serving as an ideal material for prosthetics, insoles, snap fits, and living hinges due to its durability and flexibility.
Since PA11 is derived exclusively from vegetable oil, it consumes fewer non-renewable resources during production and, consequently, has a reduced environmental footprint overall.
.jpg)
Nylon 11: More Flexibility, Competitive Edge
4. Nylon 12: Superior Heat Resistance
Nylon PA12 stands out for its superior UV and heat resistance, maintaining remarkable stability even in the face of extreme temperature fluctuations. This material is known for its high strength, stiffness, exceptional resistance to stress-induced cracking, and consistent long-term performance.
Nylon PA12 boasts an impressive heat deflection temperature of 182 degrees Celsius (at 0.42MPa). It excels in retaining its dimensional stability and resisting polymer matrix degradation even under elevated temperatures and increased radiation levels. Consequently, it is commonly employed in functional components where resistance takes precedence over durability. Environments containing fats, oils, and solvents exemplify situations where a part's resistance is of paramount importance.
In addition to high-temperature endurance, PA12 can withstand substantial temperature fluctuations and exhibits robust resistance to stress-induced cracking. It maintains exceptional strength even in sub-freezing conditions.
Although less environmentally friendly, Nylon PA12 offers more reliable 3D printing results compared to PA11, supports a wider range of surface finishing options, and is a more cost-effective material to manufacture, making it a preferred choice for rapid prototyping.
.jpg)
Nylon 12: Superior Heat Resistance
5. Learn about EuroPlas PA-GF Technical Compound
EuroPlas PA-GF is a high-strength and heat-resistant technical compound plastic. It is made from polyamide (PA) plastic and glass fibers (GF) blended together to create a material with outstanding durability and rigidity. EuroPlas PA-GF is widely used in applications that demand high strength, such as automotive manufacturing, electronic equipment, and industrial machinery.
EuroPlas PA-GF is a product of EuroPlas Vietnam LLC, a leading manufacturer and supplier of technical compound plastics in Vietnam. The company has over 20 years of experience in the production of technical compound plastics, and their products are used by customers worldwide.
EuroPlas PA-GF is a high-quality product manufactured to international standards. It has high durability, excellent heat resistance, and is easy to process. EuroPlas PA-GF is an excellent choice for applications that require high durability.
.jpg)
Learn about EuroPlas PA-GF Technical Compound
Here are some applications of EuroPlas PA-GF:
- Automotive Manufacturing: Used to produce automotive components such as engine covers, gears, and axles.
- Electronic Equipment: Used to manufacture electronic components such as motherboards, computer cases, and screens.
- Industrial Machinery: Used to produce industrial machinery parts such as gears, shafts, and machine casings.
- Construction: Used to manufacture construction materials such as water pipes, windows, and doors.
- Household Appliance Manufacturing: Used to produce household appliances such as stoves, refrigerators, and washing machines.
EuroPlas PA-GF is a high-quality product manufactured to international standards. It has high durability, excellent heat resistance, and is easy to process. EuroPlas PA-GF is an excellent choice for applications that require high durability.