In today's modern industry, plastic molding plays a pivotal role in mass-producing a diverse range of plastic products, from everyday household items to sophisticated technological components. This article delves into the technical aspects, applications, and evolving trends of plastic molding, providing a comprehensive overview of this critical technology.
1. What is Injection Mould?
Injection Mould is a sophisticated engineering process that involves using specially designed molds to shape and form plastic products through Injection Mould. Essentially, a plastic mold consists of a system of precise cavities where molten plastic is injected, cooled, and solidified to create the final product.

Injection Mould not only produces products but also ensures the consistency and quality of mass-produced plastic items. By maintaining uniform structures and dimensions, molds guarantee the quality and uniformity of products in large quantities.
Injection Mould plays a crucial role in manufacturing industries:
- Mass production: Injection Mould enable the production of a large number of products with high precision and consistency.
- Product diversity: From small components like buttons to large parts like car dashboards, Injection Mould can create almost any shape and size.
- Cost optimization: Although initial costs are high, Injection Mould significantly reduce the production cost per unit in the long run.
- Quality and durability: Modern Injection Mould allow for strict control over the production process, ensuring the quality and durability of products.
See more: Types Of Injection Mould Machines You Need To Know
2. The Structure of a Injection Mould
Injection Mould is composed of two primary components:
- Fixed mold (cavity): This stationary part is attached to the Injection Mould machine. It is connected to the nozzle system to deliver molten plastic into the mold cavity.
- Movable mold (core): This part can move to close and open the mold. When the mold is closed, it applies pressure to the molten plastic, forcing it to fill the cavity. When the mold opens, the finished product is ejected.
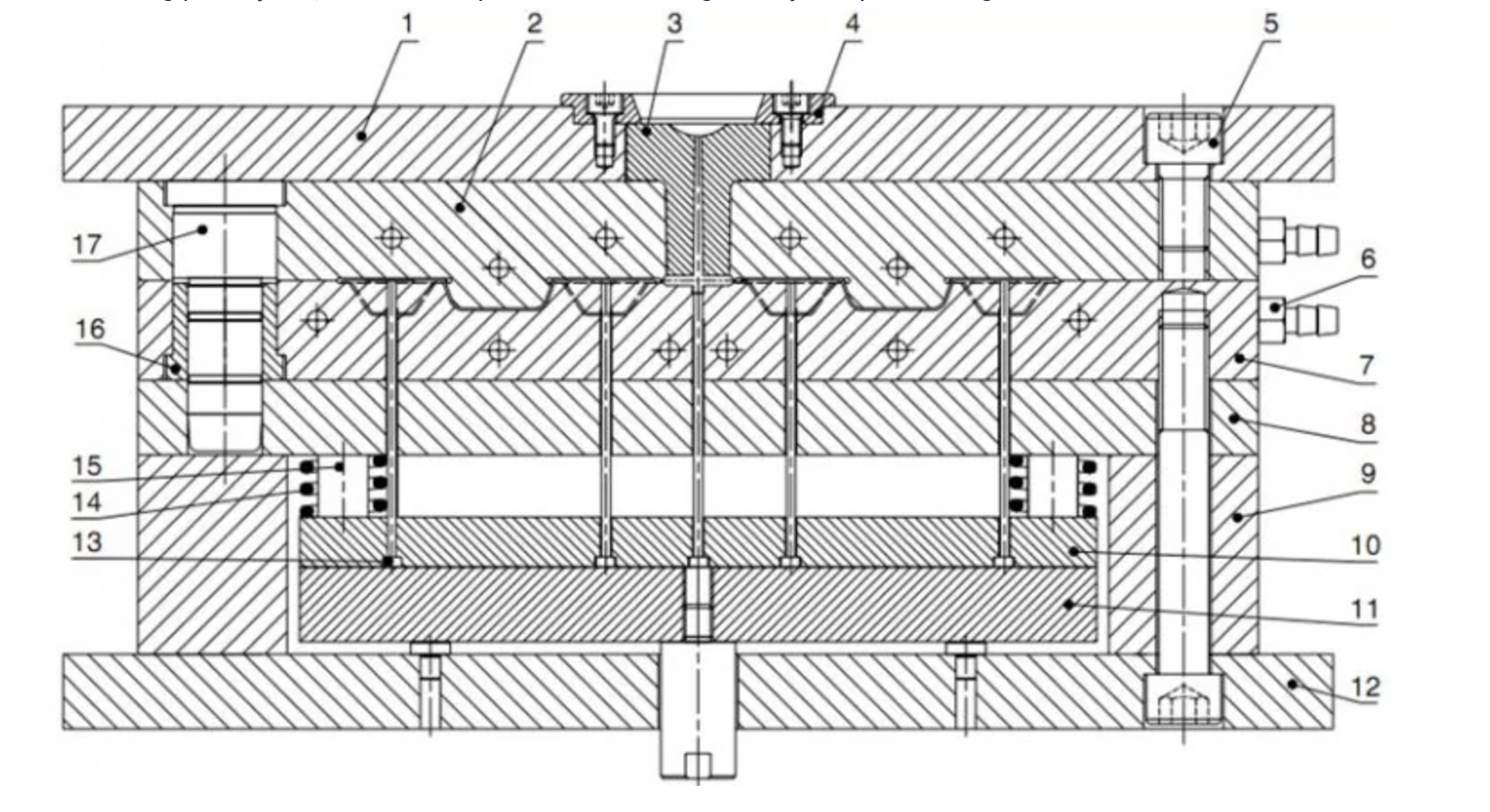
Additionally, Injection Mould include other crucial components such as:
- Locator pins: Ensure precise alignment of the mold components.
- Cooling system: Regulates the mold temperature during the molding process.
- Clamping plates: Secure the mold halves together.
- Ejection system: Includes ejector pins and plates that push the molded part out of the cavity.
- Core and cavity plates: Determine the shape and dimensions of the molded product.

Each component is manufactured with high precision, often using specialized materials like tool steel or special alloys to ensure durability and longevity under harsh working conditions.
3. The Operating Principle of Injection Mould
The operation of a Injection Mouldmachine involves a complex sequence of steps:
- Preparation: Plastic pellets are fed into the hopper of the Injection Mould machine, and the mold is heated to the appropriate temperature.
- Mold closing: The movable mold closes, clamping the fixed mold together.
- Injection: Molten plastic is injected into the mold cavity through a nozzle and runner system. High pressure is maintained to ensure the cavity is completely filled and to compensate for shrinkage as the plastic cools.
- Cooling: Cooling water circulates through channels in the mold, gradually reducing the temperature and allowing the plastic to solidify.
- Mold opening: The movable mold opens, creating a space for the molded part to be ejected.
- Ejection: The ejection system pushes the part out of the cavity. In some cases, robots may be used to remove the part.
- Return: The ejection system returns to its original position.
- Cycle repeat: The mold closes, and the cycle repeats for the next part.
The entire molding cycle can take from a few seconds to several minutes, depending on the size and complexity of the part.
4. Types of Injection Mould
Injection Mould come in various types, each suited for specific production requirements:
4.1. Two-plate mold:
Construction: Consists of a fixed and a movable plate.
Advantages: Simple, cost-effective, suitable for a wide range of products.
Applications: Manufacturing simple products like containers and bottle caps.
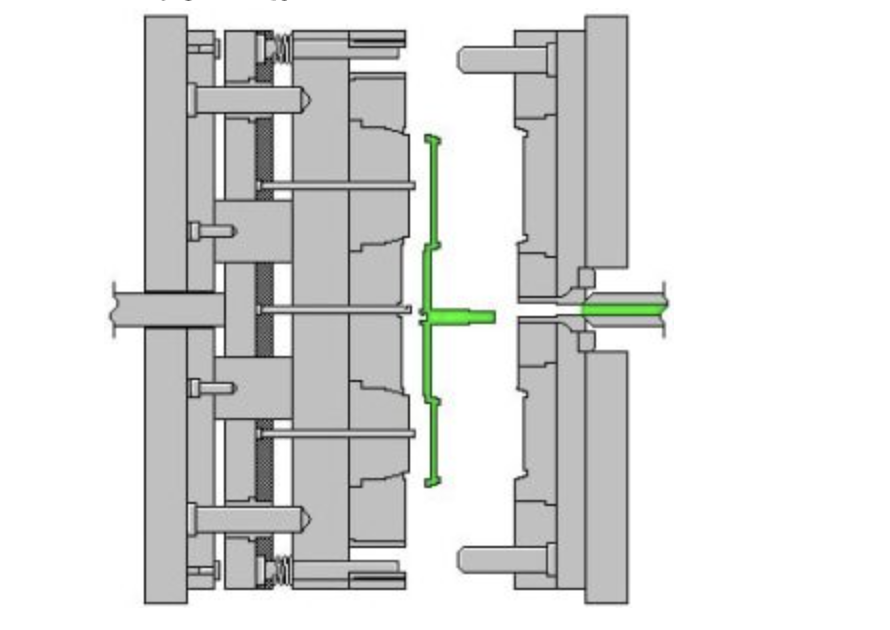
4.2. Three-plate mold:
Construction: Includes an intermediate plate between the fixed and movable plates.
Advantages: Enables automatic separation of the runner system from the product.
Applications: Producing small parts that require a center gate, such as buttons and electronic components.

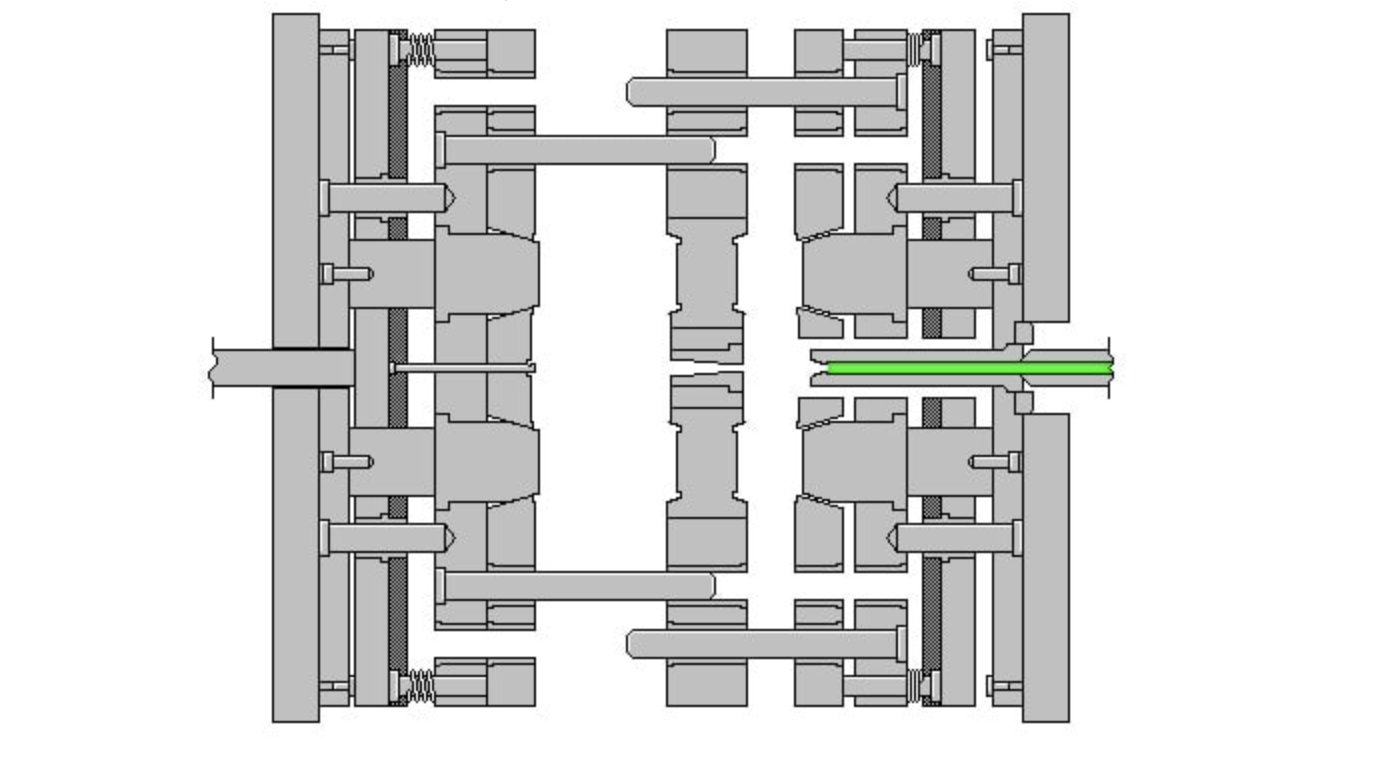
4.3. Multi-cavity mold:
Construction: Features multiple cavities stacked on top of each other.
Advantages: Increases production efficiency and reduces clamping force.
Applications: Mass production of small products like bottle caps and straws.
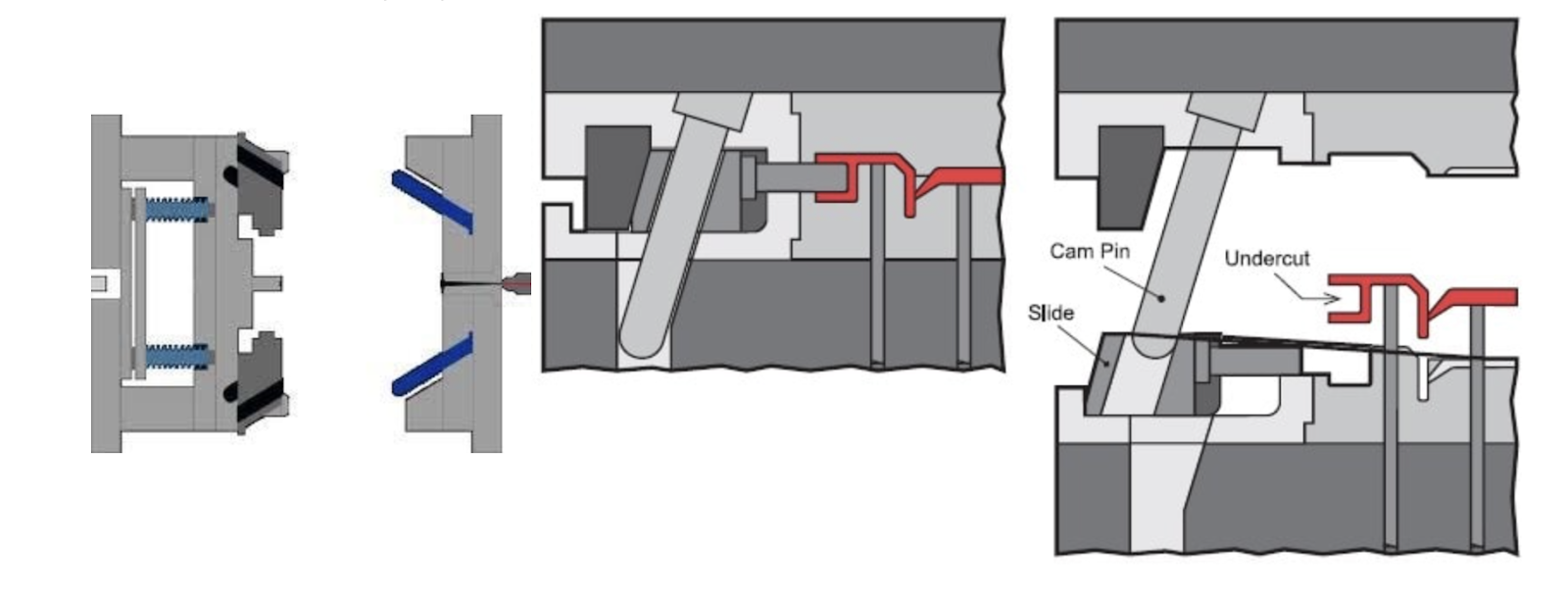
4.4. Side-gated mold:
Construction: Includes a mechanism for side gating.
Advantages: Allows for the creation of parts with undercuts or side holes.
Applications: Manufacturing complex products like computer cases and automotive components.
5. Conclusion
Injection Mould is a complex and continually evolving technology that plays a pivotal role in the modern plastics manufacturing industry. From its detailed structure to its operating principles, every aspect of plastic molding is meticulously designed to ensure maximum production efficiency and product quality.
With advancements in technologies such as artificial intelligence, 3D printing, and smart sensors, the future of the Injection Mould industry promises groundbreaking innovations that will further enhance production efficiency and the sustainability of plastic products.
A thorough understanding of the structure, operating principles, and various types of plastic molds provides a comprehensive overview of the plastic product manufacturing process. By selecting the appropriate mold type based on specific production requirements and product characteristics, manufacturers can optimize production processes and product quality.
6. About EuroPlas
EuroPlas has established itself as a world-leading supplier of filler masterbatch products. With years of experience and a team of highly skilled engineers, EuroPlas is committed to assisting customers in selecting and applying the most suitable filler masterbatches for their specific production needs.
If you are interested in learning more about filler masterbatch products and how to utilize them to enhance production efficiency, please contact EuroPlas's team of consultants.
Upon receiving your inquiry, EuroPlas's experts will promptly analyze your specific needs and contact you to provide in-depth advice, helping you make the most informed decisions for your production project. EuroPlas is dedicated to providing optimal solutions that contribute to improved production efficiency and product quality for your business.