Plastics have transformed from materials used mainly for soft items to essential components in various applications, including construction. This shift prompts an important question: what accounts for the newfound strength and durability of modern plastics? This article examines the key differences between traditional and modern plastic, highlighting the innovations that enhance their resilience. Join us as we explore how advancements in material science are reshaping the future of plastic applications.
Read more: Processing Aids: What you need to know
1. What are the Differences between Old Plastic and Modern Plastic?
When we think of plastic, a myriad of objects comes to mind, from shopping bags to intricate electronic components. However, the evolution of plastic materials has led to significant differences between traditional and contemporary plastics, particularly in terms of composition, properties, and applications. Understanding these distinctions is essential for appreciating the advancements that have shaped the plastic industry.
1. 1 Composition and Origins
Old plastics, such as celluloid, were primarily derived from natural sources and created to replace materials like ivory in products such as billiard balls. Made from nitrocellulose and camphor, celluloid aimed to mimic the desirable qualities of natural materials while addressing environmental concerns. However, these early plastics often lacked versatility and durability.
In contrast, modern plastics are largely composed of synthetic or semi-synthetic polymers. The introduction of fully synthetic plastics, like Bakelite, marked a significant shift, enabling a wider range of applications and formulations tailored to specific needs.
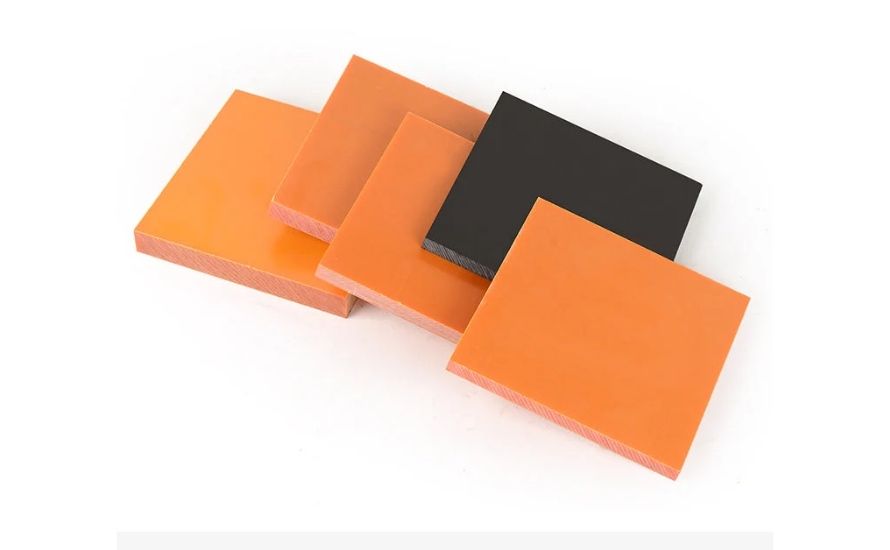

1.2 Properties and Performance
The physical properties of old and modern plastics differ markedly. Early plastics, including celluloid, were susceptible to cracking and degradation, limiting their effectiveness in demanding conditions. Modern plastics, however, are engineered for enhanced durability, flexibility, and resistance to heat, chemicals, and UV radiation.
This improvement results from advanced polymer science and the use of performance-enhancing additives. For example, materials like polycarbonate and polyethylene are designed to endure significant wear and tear, making them ideal for various applications, from automotive components to outdoor gear.

1.3 Applications and Versatility
The range of applications for plastics has expanded dramatically due to advancements in material science. Old plastics were often restricted to specific uses, such as billiard balls or piano keys, due to performance limitations.
In contrast, modern plastics are utilized across diverse industries, including automotive, aerospace, medical, and consumer goods. Their versatility allows them to be molded into complex shapes and designs, facilitating innovative products that were previously unimaginable. Technologies like 3D printing have further revolutionized plastic applications, enabling the creation of custom components with intricate geometries.
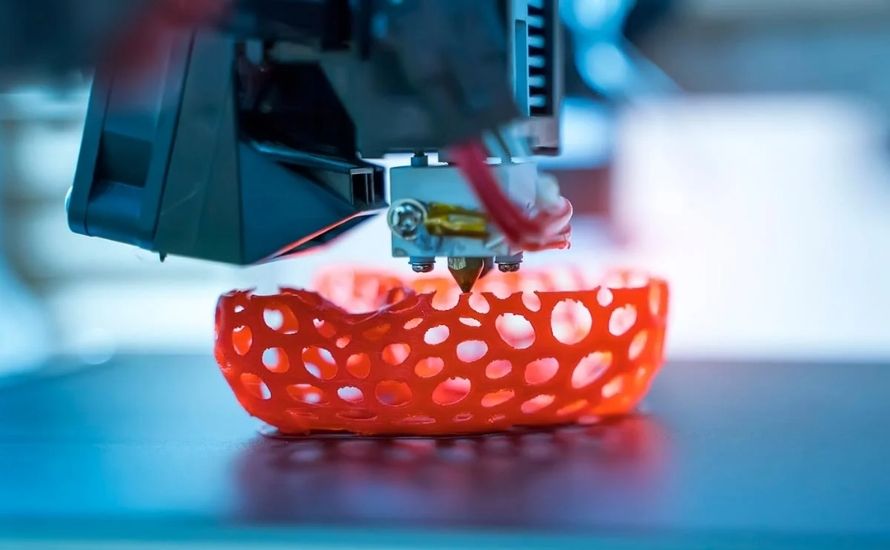

Read more: The Future of Bioplastic Polymers in 3D Printing Technologies
1.4 Environmental Considerations
Old plastics, while sometimes developed with sustainability in mind, often posed significant environmental challenges due to their production and disposal. The rise of synthetic plastics has introduced new concerns related to pollution and waste management.
In response, the industry is increasingly exploring biodegradable alternatives and recycling solutions. Modern advancements emphasize sustainability, focusing on creating eco-friendly plastics that minimize environmental impact. Innovations such as bioplastics, derived from renewable resources, represent a shift towards more sustainable practices, addressing both ecological concerns and consumer demand for environmentally responsible products.

2. Why is Modern Plastics Now More Durable?
The durability of modern plastics is a result of various factors that enhance their strength and flexibility. Understanding these elements provides insight into why modern plastics are significantly more resilient than their predecessors.
2.1 Intricate Molecular Structures
Modern plastics are characterized by long chains of polymers that provide exceptional strength and flexibility. These intricate structures allow plastics to withstand significant wear and tear while maintaining the necessary pliability to absorb impacts. This combination of strength and flexibility is crucial for a wide range of applications, ensuring that plastics can perform effectively under various conditions.
2.2 Custom Fabrication
Custom plastic fabricators can create specialized products that meet precise requirements, ensuring that the resulting plastic is optimized for its intended use. This targeted approach not only enhances the performance of the plastic but also contributes significantly to its overall durability. By focusing on specific needs, manufacturers can develop plastics that excel in particular applications, thereby increasing their reliability and effectiveness.

2.3 Technological Advancements
Advances in polymer science and processing techniques have played a pivotal role in enhancing the strength of modern plastics. Our growing understanding of the molecular behavior of polymers, combined with innovative processing methods, has led to the development of robust and reliable plastic materials. Ongoing experimentation continues to push the boundaries of what plastics can achieve, resulting in materials that are both durable and versatile.

3. Conclusion
In summary, the differences between old and modern plastics are profound, encompassing changes in composition, properties, applications, and environmental considerations. As we continue to innovate and refine plastic materials, the industry moves toward more sustainable and versatile solutions, ensuring that plastics remain an integral part of our daily lives while addressing the challenges of the future. Understanding these differences not only enriches our appreciation of plastic as a material but also highlights the importance of responsible usage and development in the ongoing evolution of this essential resource.
4. About EuroPlas
EuroPlas stands at the forefront of the filler masterbatch manufacturing industry, equipped with state-of-the-art machinery, including extruders, blown film machines, and injection molding machines. Our advanced testing facilities, featuring plastic thermal deformation testing machines, impact testing machines, and tensile strength testing machines, ensure that every product meets the highest quality standards. As the world’s leading manufacturer of filler masterbatch, EuroPlas is dedicated to providing tailor-made plastic material solutions that empower our clients to enhance their competitiveness in a rapidly evolving market.

Discover the unparalleled quality and innovation that EuroPlas offers. Elevate your production capabilities with our bespoke materials designed to meet your specific needs. Don’t miss the opportunity to transform your business -
contact us today to explore how we can partner together for success.