Plastic products are used everywhere. However, the durability of each product is different depending on the intended use and quality of the product. This article will analyze the main causes affecting the life cycle of plastic products as well as reveal methods to prolong the use life.
Related:
- What are antioxidant plastic additives and their applications in the plastic industry?
- Anti-aging additives - Effective ways to improve plastic products’ quality
- What are primary and secondary antioxidants in polymer?
- UV stabilizers for plastics - everything you need to know
I. Plastic life cycle
The life cycle of plastic, also known as the shelf life of plastic, is calculated from the time the plastic is used until it is no longer usable or discarded. People divide the life cycle of plastic into 4 categories as shown in the table below:
|
Period
|
Examples
|
|
Very short to short
|
Single used plastic, plastic packaging
|
|
Medium
|
Cups, cosmetic containers, food containers, kitchen utensils
|
|
Long
|
Electronic products. toys
|
|
Very long
|
Car interiors, pipes
|

Just like humans, plastic that goes through a long period of exposure to the environment will age. They change both mechanically and physically. Some manifestations of aging plastics are that they are discolored, unsightly, broken, cracked, and deformed compared to the original. The consequence of this phenomenon is that plastic products lose their aesthetics and are unsafe for users. We will learn more about the phenomenon of aging in plastics shortly.
II. The aging of plastic
Plastic aging, also known as oxidation, is the change in properties of plastic after a period of use in a bad direction.
What causes plastic aging?
- Physical impact: Temperature, cutting force due to screw, repeated heat processing, etc. make plastic chains less stable, combined with rotating screw can cause chain break. This process generates free radicals. Free radicals are ions, molecules containing unbound free electrons, with strong chemical reactivity.
- Chemical impact: Oxygen, denatured additives, moisture, chemicals ... from the surrounding environment can also generate free radicals.
- Aging during machining:
+ Cut the chain due to the screw
+ Multiple heat processing
+ Decomposition additives
+ Oxidation of plastic chain
- Aging during use:
+ Exposure to direct heat
+ Exposure to moisture
+ Light from the surroundings
+ Exposure to dust, dirt, chemicals, etc.
Oxidation cycle of plastic
The two main factors that cause oxidation in the plastic chain are free radicals and Peroxide/Hydroperoxide. Peroxide/hydroperoxide are substances in the form of R-O-O-R, which easily decomposes when given energy (heat, light), forming new free radicals. A typical example is hydrogen peroxide H2O2. The peroxide radical has the form –O-O-R.
1 plastic oxidation cycle includes
- Initiation: The process by which impurities generate free radicals due to physical and chemical effects. As a result, free radicals, peroxides are formed.
- chain development: The process by which free radicals attack sites with low activation energy, to form new products. The consequence is:
+ Generate new free radicals
+ Create chain break
+ New substances are more durable
- Cutting the chain: Free radicals combine to create stable products. This determines the change in the properties of the plastic chain. Plastic has changed its mechanical properties and color.
The aging of some common plastics
|
Types of plastics
|
Causes
|
Results
|
|
Polystyrene (GPPS, HIPS)
|
Phenyl radicals are highly reactive, especially in the presence of sunlight
|
PS plastic is often less durable, easy to discolor.
|
|
ABS (Acrylonitrile – Butadiene – Styrene)
|
The chain contains a double bond of butadiene, a phenyl radical of styrene, and a cyanide photophilic group.
|
ABS plastic often changes color quickly
|
|
PE, PP
|
The chain usually contains tertiary carbon
|
PE, PP plastic is often less durable, especially PP
|
|
PET
|
Rarely oxidizes in dry environments, more easily oxidized in humid environments
|
PET plastic is relatively durable
|
|
BPA - PC
|
The carboxyl group works, but the whole chain is very cumbersome
|
PC plastic is relatively durable
|
III. How to prolong the life of plastic?
Plastic manufacturers will use plastic aging resistance additives to increase the shelf life of plastic products, minimizing the effects of the aging process. Additives combine many components, ensuring comprehensive and effective operation. Anti-aging additives are usually divided into 2 types:
1. Chain Breaker CB
Chain break additive is effective when resisting oxidation during processing and product use. The group of commonly used chain break additives includes Phenolic, Amine, HAS.
|
Group
|
Substant
|
Type
|
Application
|
|
CB-D
|

|
Phenolic
|
PP, PE, HIPS, PMP, PVC, ABS,…
|
|

|
Phenolic
|
Polyurethane, polypropylene, polyester
|
|

|
Amine
|
Polyolefins, PAs, styrenics
|
|
CB-A
|
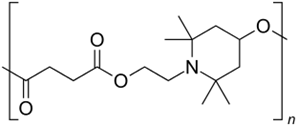
|
HAS
|
PP, PE, PS, ABS
|
2. Peroxide decomposition additive
The peroxide decomposition additive helps to increase the antioxidant effect during the use of the product. The group of commonly used peroxide-degrading additives includes Phosphite and Sulfur groups.
|
Type
|
Substant
|
Application
|
|
Phosphites Ester
|

|
PE, PP, PS, Polyesters, PVC, thermoplastic
|
|

|
PP, PE
|
|
Sulfur Compounds
|
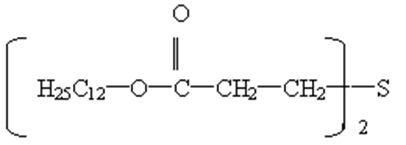
|
PP, PE, PVC, ABS
|
|

|
Polyurethanes
|
Using anti-aging additives has the effect of limiting degradation in finished plastic products due to the impact of physical and chemical factors, helping the finished product to be more durable and have a longer service life. If you are looking for a suitable additive for your plastic product, do not hesitate to contact our team of consultants today for advice and samples!