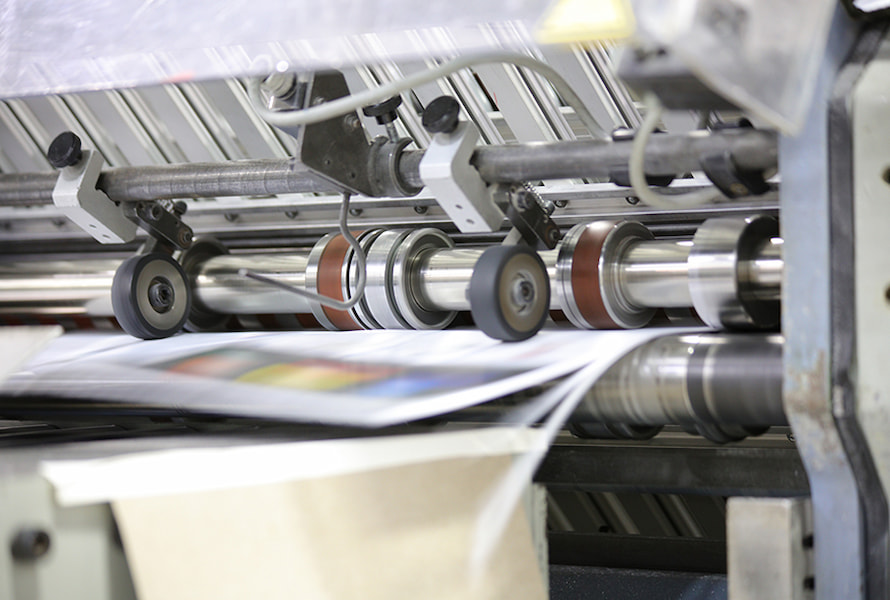

Printing on plastic is a crucial aspect of modern manufacturing and packaging. From plastic bottles and containers to labels and packaging, printing on plastic serves a variety of purposes. However, printing on plastic requires specialized techniques and expertise to ensure the best results. So how to print on plastic? In this article, we will explore 7 of the most common methods for printing on plastic, how they work, their advantages, and applications.
1. What plastics can you print on?

Different types of plastics can be used for printing, depending on the desired properties and application. PVC, polycarbonate, and PETG are among the most preferred options.
1.1. PVC
PVC (polyvinyl chloride) is a widely used thermoplastic, known for its durability, toughness, and resistance to chemicals, abrasion, and weather. PVC filaments have become popular in printing because they are easy to handle, have low cost, and have a wide range of colors. However, it can be not easy to work with and doesn’t always produce the highest quality prints.
1.2. Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate is a high-performance engineering thermoplastic, known for its strength, transparency, and high-temperature resistance. It’s easier to work with and produces better results than PVC. However, it is expensive compared to other filaments, which can limit its usage.
1.3. PETG
PETG (glycol-modified PET) is a glycol-modified version of PET (polyethylene terephthalate), a common plastic used in beverage bottles, food containers, and textiles. PETG is known for its flexibility, transparency, and resistance to impact, chemicals, and UV light.
In addition, there are a number of other plastic materials that are also used in printing, typically ABC, PLA, TPU, or even Nylon.
1.4. Polyethylene (PE) - LDPE and HDPE
- Smooth Surface: Allows ink to adhere easily, especially with flexographic or rotogravure printing.
- Stable Mechanical Properties: LDPE and HDPE have high tensile strength and good water resistance, which helps maintain print quality over time.
- Heat Resistance: Polyethylene can withstand high temperatures without distorting during the printing process.
Read more: PE plastic - Everything you need to know
1.5. Polypropylene (PP)
- High Strength and Chemical Resistance: PP resists chemical effects and environmental impacts, which helps prints stay vibrant longer.
- Corona Treatment: PP surfaces can be easily treated to enhance ink adhesion, particularly with flexographic and rotogravure printing.
- Light and Flexible: Suitable for various shapes and complex plastic products.
Read more: PP Plastic: Everything you need to know
1.6. Polystyrene (PS)
- Hard and Brittle Surface: The brittle nature of polystyrene ensures ink adheres well and doesn’t bleed.
- Good Light Transmission: Ideal for transparent products, resulting in sharp, clear prints.
Read more: Everything you need to know about polystyrene
1.7. Acrylic (PMMA)
- Excellent Transparency: Acrylic is highly transparent, perfect for high-definition and precise printing.
- Easy to Process: Can be laser-cut and shaped, allowing for complex designs.
- UV Protection: Helps in preserving print quality by shielding it from UV light.
Read more: PMMA Plastic: What is it?
1.8. ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene)
- Smooth and Tough Surface: ABS has a smooth surface that is easy to process and print on.
- High Durability: ABS’s durability ensures that printed products withstand physical impacts.
- Heat and Chemical Resistance: Protects ink layers from environmental factors and weather.
Read more: ABS sheet plastic - 5 most widely-used applications
2. How to print on plastic? Common methods to print on plastic
2.1. Digital InkJet printing
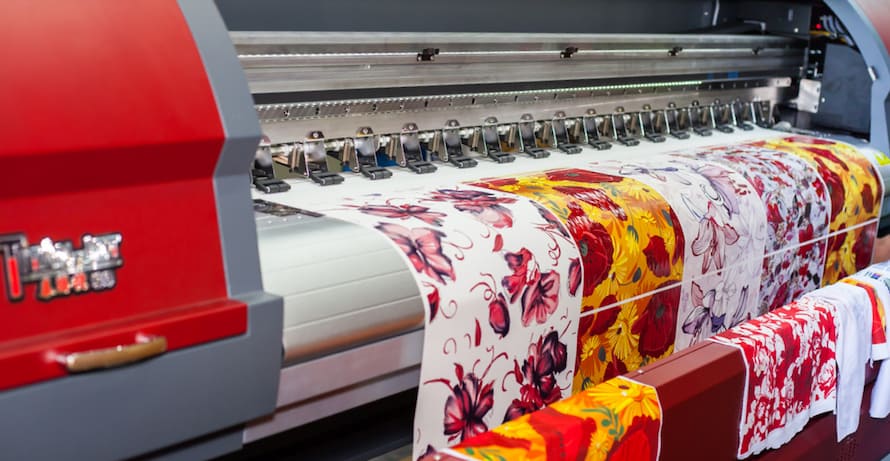

Digital InkJet printing is a process utilizing inkjet technology to print high-quality images onto plastic surfaces. This printing technology uses a digital file containing the image or text to be printed, which is processed by a printer that uses inkjet nozzles to deposit ink onto the plastic substrate.
The process of Digital InkJet printing involves the following steps:
- Preparing the digital file containing the image or text to be printed. This file is created using computer software and is saved in a format that is compatible with the InkJet printer.
- Printing the image: The inkjet nozzles in the printer head are activated, and droplets of ink are ejected onto the plastic substrate to create the image or text. The ink droplets are deposited onto the substrate in a precise pattern that corresponds to the digital file.
- Drying the ink: The ink is dried using a combination of heat and airflow, which ensures that the printed image is smudge-proof and water-resistant.
Digital printing does not involve the usage of a printing plate, in contrast to conventional printing techniques. This enables quicker turnaround times and lower prices. Moreover, digital printing provides more versatility since it can be utilized to create small quantities of items with bespoke printing.
Digital InkJet printing is also a customizable printing method, as it allows for variable data printing, meaning that each item printed can have different content or images. With the development of personalized or customized items such as gift cards, ID cards, and loyalty cards, digital InkJet printing is increasingly preferred.
2.2. Screen printing
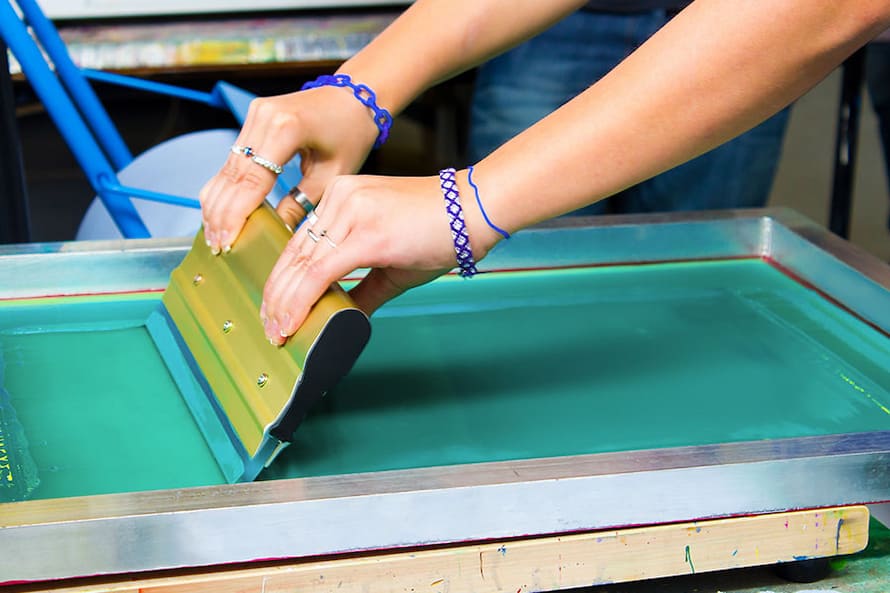

Screen plastic printing is a printing process that involves transferring ink through a stencil or mesh screen onto a plastic substrate.
How does it work?
- Preparing the artwork or design that will be printed.
- Creating the stencil: Once the artwork is ready, a stencil is created by either exposing a photosensitive emulsion-coated screen to the design or by cutting the design out of a vinyl sheet. The stencil is then attached to a frame to create the screen.
- Preparing the ink: The ink used for screen printing is typically a specialized ink that is designed to adhere to plastic substrates. The ink is mixed with a catalyst or hardener to ensure that it dries quickly and adheres to the plastic surface.
- Printing the image: The screen is placed on top of the plastic substrate, and ink is applied to the top of the screen. A squeegee is then used to pull the ink through the stencil and onto the plastic substrate. The ink is then dried using a combination of heat and air.
Screen printing can provide a durable and long-lasting print. It is often used for printing substrates because the specialized inks used for screen printing adhere well to the plastic surface. In the long term, screen printing is also a cost-efficient technique. After the initial setup is complete, printing products in large quantities is rather rapid and simple. So, it's safe to say the more you print, the cheaper the unit cost becomes.
2.3. Flexo printing
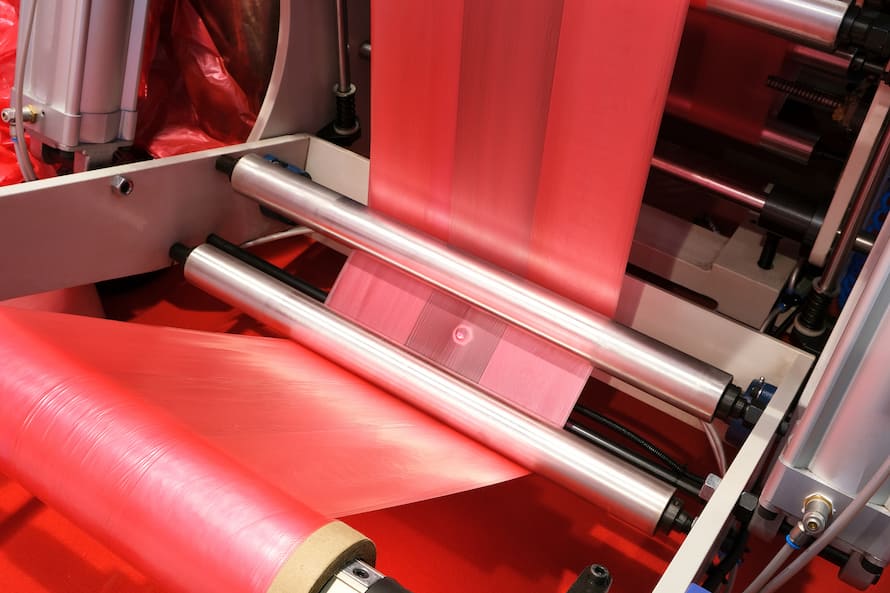

Flexo printing is a direct printing process in which printing is carried out with flexible print forms (printing plates) made of photopolymer.
- Prepress preparation: The printing plate is made by creating a relief image on a flexible material such as rubber or photopolymer.
- Ink preparation: The ink used in flexo printing is specialized to adhere well to plastic substrates and is mixed with a solvent or water-based carrier to create a liquid ink that can be applied to the printing plate.
- Flexo printing: The plastic substrate is fed through the flexo printing press, which consists of several printing stations. Each station has a printing plate cylinder, an ink fountain, and an impression cylinder. As the substrate passes through each station, ink is transferred from the plate cylinder to the substrate, creating the desired image or text.
- Drying and finishing: The printed plastic substrate is passed through a drying chamber to evaporate the solvents from the ink. After drying, the substrate is cut to size and finished according to the requirements, such as laminating, embossing, or die cutting.
Flexo printing is popular in the printing industry because it can produce high-quality images at high speeds. It is used to print a wide range of products, including labels, packaging, bags, and more.
Additionally, it is versatile and can be used to print on a variety of plastic substrates, including flexible and rigid plastics. Flexo printing is also capable of producing high levels of detail and color vibrancy, helping it become one of the most preferred options for printing logos, graphics, and other images onto plastic substrates.
2.4. UV Litho printing
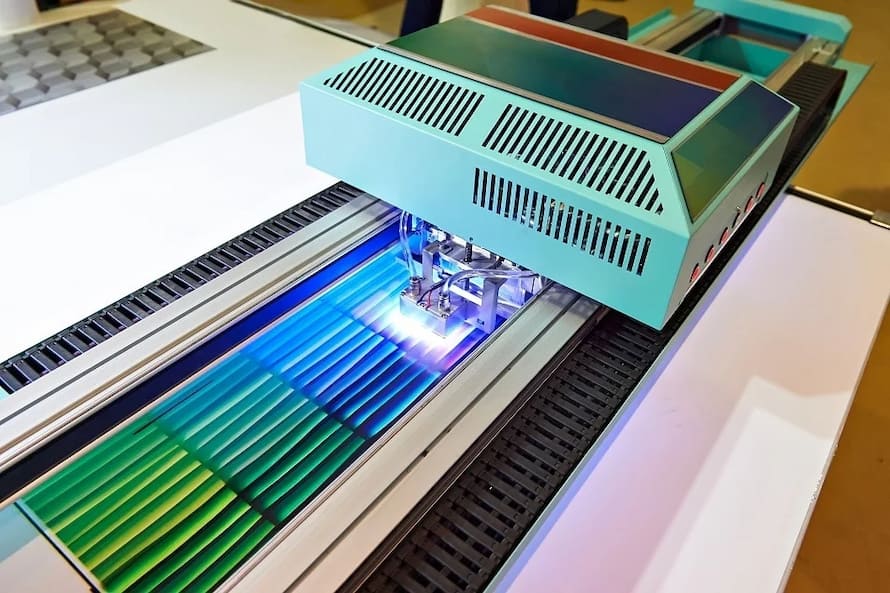

UV Lithography, also known as UV offset printing, is a digital printing method that uses ultraviolet light to cure or dry ink, coatings, adhesives, aluminum, foam, or acrylic.
How does it work?
- Pre-press preparation, including designing the artwork and preparing files for printing
- Application of photosensitive coating to an aluminum printing plate
- Exposure of the plate to UV light to create a relief surface
- Preparation of UV litho ink by mixing pigments, binders, and additives
- Loading of the ink onto the printing press
- Application of ink to the plate using rollers
- Transfer of ink from the plate to the plastic substrate as it passes through the press
- Instant curing of ink by UV light, creating a durable and long-lasting image
- Inspection of the substrate for quality, and finishing touches, such as varnishing, laminating, or die-cutting, are added as needed.
One of the significant advantages of UV Litho printing is the ability to produce high-quality images with fine details. The UV ink used in this printing method is highly pigmented and produces vibrant colors that resist fading. Another advantage of UV Litho printing is its fast drying time. The UV lamp cures the ink instantly, which means that the printed substrate can be immediately handled and processed.
UV Litho printing has a wide range of applications, including printing on packaging, labels, and other plastic products. It is commonly used in the cosmetic, pharmaceutical, and food industries, where high-quality images and durability are essential. UV Litho printing is also popular for printing on products that require special effects, such as metallic finishes or embossed textures.
2.5. Pad printing
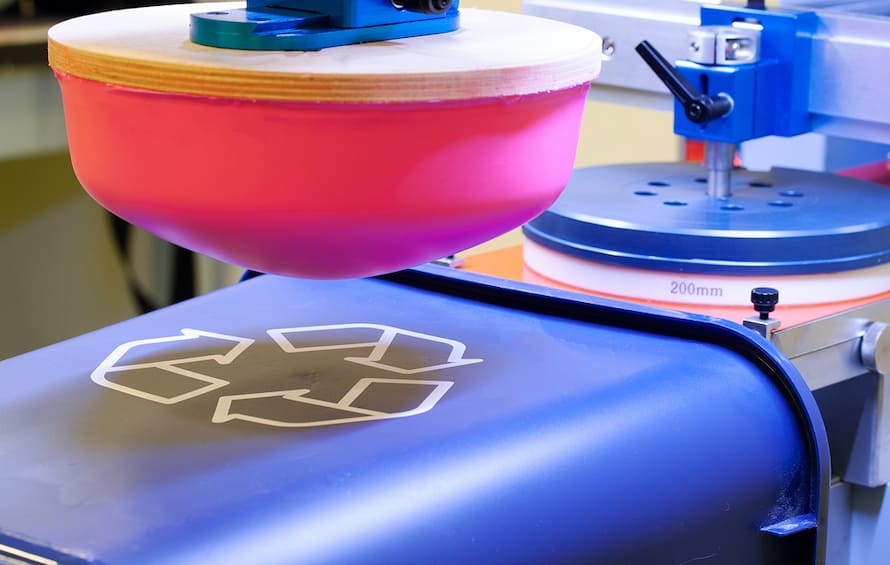

Pad printing, also called tampography or tampo printing, is an indirect offset (gravure) printing process that transfers a two-dimensional image from a laser-engraved (etched) printing plate (also known as cliché) to a three-dimensional object using a silicon pad.
The following is a detailed step-by-step process for pad printing:
- Plate etching: Next, a printing plate is created by etching the design into a metal or polymer plate.
- Ink preparation: The ink used in pad printing is typically solvent-based or UV-curable ink.
- Ink transfer: A doctor blade is used to remove excess ink from the printing plate, leaving ink only in the etched areas. The pad is then pressed onto the plate, picking up the ink from the etched design.
- Print transfer: The pad is then positioned over the plastic substrate, and the ink is transferred from the pad to the substrate using a stamping motion. The pad conforms to the contours of the plastic surface, allowing for high-precision printing.
- Curing: Finally, the ink is cured to ensure adhesion and durability. This may involve heating the printed plastic parts or exposing them to ultraviolet light.
Pad printing is preferred thanks to its ability to print on curved or irregular surfaces, which is not possible with other printing methods. The flexible rubber pad can conform to the contours of the plastic surface, ensuring that the print is even and consistent. Another advantage of pad printing is its ability to print fine details and intricate designs.
2.6. Laser printing
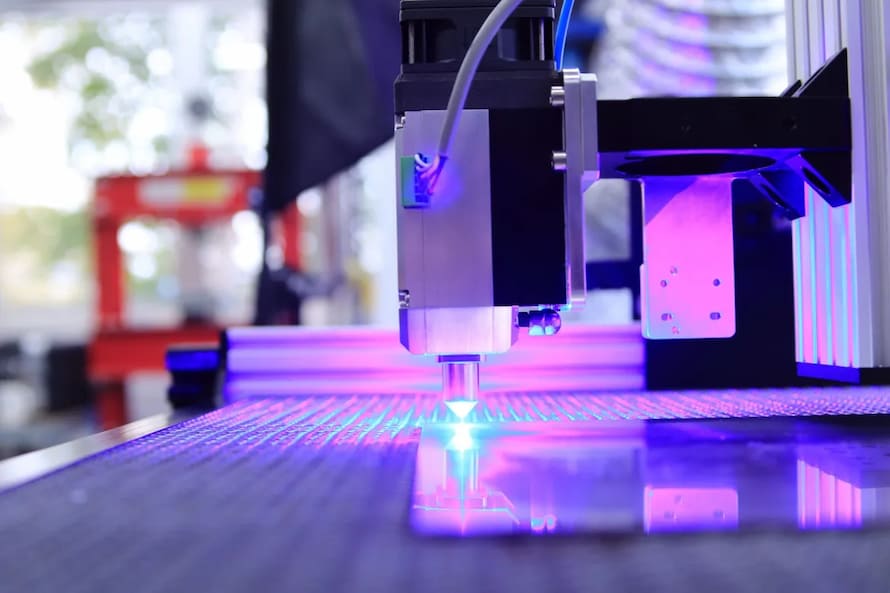
Laser printing of plastic, or plastic engraving, is a non-contact printing process during which components are labeled or marked with the aid of a laser.
Process of Laser printing
- A computer-controlled laser printer is used for the printing process. The design or image to be printed is loaded onto the computer that controls the laser printer.
- The plastic material is then placed on a flat surface, and the laser printer is set up and adjusted to the correct settings for the specific plastic material being used.
- The laser printer uses a focused laser beam to selectively heat and melt the surface of the plastic material, creating the desired design or image.
- The laser beam moves across the surface of the plastic material, tracing the design or image as it goes. This is controlled by the computer that is connected to the laser printer.
- Once the printing is complete, the plastic material is allowed to cool, and any excess or loose material is removed.
Laser printing provides high-quality, precise, and detailed prints with sharp and clear lines, even on small or intricate designs. It is also non-contact, which means there is no physical contact with the plastic material, reducing the risk of damage to the material.
Another advantage of laser printing is that it is a clean and environmentally friendly process. Lastly, laser printing produces less waste material compared to other printing methods, as only the surface of the plastic material is melted, rather than creating additional layers of ink or other substances.
2.7. Hot Stamping
.jpg)
Hot stamping or foil stamping is a printing method of relief printing in which pre-dried ink or foils are transferred to a surface at high temperatures.
Here are the steps involved in the hot stamping printing process:
- Die Engraving: The design is engraved onto a metal die, which will be used to transfer the design onto the foil and then onto the plastic material.
- Foil Selection: The next step is to select the appropriate foil that will be used for the hot stamping process. Foils come in a variety of colors and finishes, including metallic, glossy, and holographic.
- Surface Preparation: The plastic material is prepared for hot stamping by applying a heat-activated adhesive or coating onto the surface to be printed.
- Foil Transfer: The foil is placed onto the surface of the plastic material and then pressed onto the foil and plastic material, transferring the design from the foil onto the plastic.
- Die Removal and Cooling: Once the design has been transferred onto the plastic material, the hot die is removed. The plastic material is cooled down.
One of the key benefits of hot stamping is its versatility. It can be used to print on a wide range of materials, including plastics, paper, leather, and fabrics. This makes it a popular choice for a variety of applications, from labeling and packaging to automotive and aerospace industries. Another advantage of hot stamping is its durability. The prints are resistant to fading, scratching, and other forms of wear and tear. Hot stamping also offers the ability to create highly detailed designs, including fine lines, text, and intricate patterns.
In short, printing on plastic is a vital aspect of modern manufacturing and packaging, and there are several methods available to achieve high-quality results. Whether you choose Flexo, UV Litho, Pad printing, Laser printing, Hot Stamping, Digital InkJet, or Screen printing, understanding the processes, benefits, and applications of each method can help you choose the right one for your specific needs.
3. EuroPlas - Where provides different plastic solutions
As the world's No. 1 filler masterbatch manufacturer, EuroPlas is proud to offer unique plastic material solutions, helping customers' factories optimize production costs and improve business competitiveness. EuroPlas provides various plastic solutions such as bioplastics and bio fillers, color and filler masterbatch, engineering plastic compounds, and other plastic additives. Please contact EuroPlas to raise your questions, or if you have specific needs for your next project.