Thermosetting plastics are used in various industries thanks to their dimensional stability, durability, and flexibility. Each type of thermosetting plastic is suitable for different applications, depending on its ability to resist heat.
Let’s figure out which plastics are considered thermosetting and their melting points right below!
Read more: Thermosetting vs Thermoplastic: Which one to choose?
1. Overview Of Thermosetting Plastics
Thermosetting plastics, also known as thermosetting resin or thermosetting polymers, are liquid at room temperature and solidify upon heating or chemical addition. They are made using resin transfer molding (RTM) or reaction injection molding (RIM). During the curing process, permanent chemical bonds are formed. These bonds or crosslinks alter the composition of the material and lock molecules in place, preventing it from melting and reverting to a liquid state.
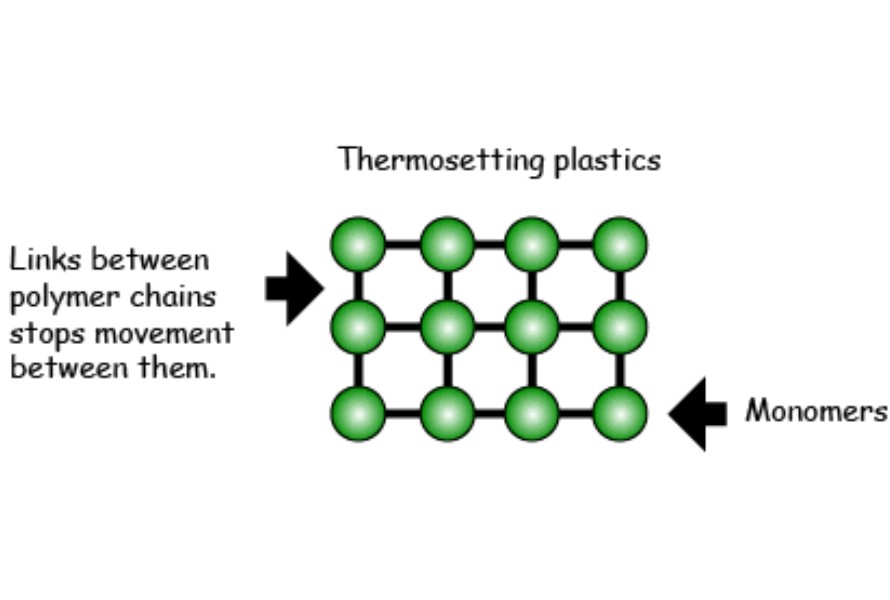
Thermosetting plastics are perfect for use in chemical processing equipment, electronic housings, and other applications where heat is an issue. They have many advantages, such as:
- Ability to be molded to a variety of tolerances
- Strong dimensional stability
- Low thermal conductivity
- Excellent electrical insulation qualities
- Great heat resistance at high temperatures
- Flexibility in product design
- Corrosion and water resistant
- A wide range of colors and surface finishes
- Cost-effectiveness
2. Which Plastics Are Considered Thermosetting?
Common types of thermosetting plastics include:
2.1. Bakelite
Bakelite, featuring simple moldability and electrical insulating qualities, is a versatile material used in many different products. In the electrical industry, it is frequently utilized for wire insulation, switches, boards, and sockets. Because of its distinctive color production, bakelite can be used to create a variety of cookware items as well as colored bracelets and bangles.
2.2. Duroplast
Duroplast is a lightweight, sturdy thermoset material, similar to Bakelite but with cotton or wool fibers for reinforcement. It is utilized in toilet seats and car bodies to cut down on the price of steel. However, it poses a risk to the environment because it is difficult to break down and releases harmful gasses when burned.
2.3. Epoxy
Another thermosetting plastic on our list is epoxy. Due to its resilience to heat and corrosion, this reactive thermosetting resin finds significant application in the aerospace sector. It is also used in structural adhesives, electrical components, and metal coatings.

2.4. Cyanate Ester
Cyanate Ester is brittle and performs better in water absorption, dielectric loss, and stability at high temperatures than epoxy. It's frequently used with epoxy or other thermosetting compounds for more durable products. Because of its exceptional structural and mechanical qualities, it is employed in electronic chip adhesives, electrical device encapsulation, and the aerospace industry.
2.5. Melamine-Formaldehyde
It’s a low alkaline combination of Melamine and Formaldehyde. The material features exceptional heat and chemical resistance and is commonly utilized in wood items. Paper, paint, plastics, flame-resistant textiles, particleboards, laminates, cookware, and floor tiles can all be made with melamine resins since they are fire-retardant. Additionally, it aids in the production of fabrics that withstand flames.
2.6. Polyimide
This thermosetting plastic is well-known for its thermal and chemical properties. It boasts mechanical strength and water resistance and is frequently employed in the manufacture of sockets, bushings, and bearings.
2.7. Polyurethane
Strong foam materials like polyurethane can be used to insulate a variety of automobile and electrical components, including door panels, bumpers, windshields, steering wheels, and gaskets. However, polyurethane is prone to microbial diseases and can turn yellow when exposed to sunlight frequently.
2.8. Polyester
Polyester is a tough and long-lasting thermosetting plastic created when polyhydric alcohol reacts with a defective organic acid. Its chemical and water resistance allow it to be used in a wide range of applications, including parts for electrical components, tanks, pipes, ducts, and boat building.
2.9. Silicone
With its robust three-dimensional network structure, silicone resin is adaptable to many different applications. This thermosetting material can produce films that are resistant to sunlight and offers robust coatings with excellent dielectric characteristics and heat and water resistance. It’s durable and reliable, making it suitable for silicone fluids, coatings, sealants, art, and the electrical industry. Besides, its biocompatibility is also ideal for the production of medical equipment.

2.10. Urea-Formaldehyde
The interaction of urea with formaldehyde in water with a pH of more than 7 produces urea-formaldehyde, a thermosetting substance. It has a semi-crystalline structure and solidifies at high temperatures. Common applications of this thermosetting plastic include fiberglass matting, wood products, air filtration coating, particle board adhesive, and decorative goods lamination.
2.11. Vinyl Ester
This material is a blend of vinyl acids and epoxy resin. It’s commonly used in the petrochemical and chemical industries as well as the maritime industry since vinyl acid facilitates its cross-linking and the material offers great heat and water resistance.
2.12. Vulcanized Rubber
Vulcanized rubber is a non recyclable, hardened substance utilized in many different industries. It features superior abrasion resistance and electrical and thermal insulation qualities. Because of its high tensile strength, which lowers the risk of tire punctures, it is especially well-liked in the manufacture of car tires. It is also used in insert molding to protect metal and iron products.

3. Melting Points Of Thermosetting Plastics
Here is the table of melting points of thermosetting plastics:
| Bakelite |
80 - 100 °C |
| Duroplast |
140 - 180 °C |
| Epoxy |
115 - 120 °C |
| Cyanate Ester |
79 - 106 °C |
| Melamine-Formaldehyde |
100 - 110 °C |
| Polyimide |
247 - 388 °C |
| Polyurethane |
71 - 221 °C |
| Polyester |
295 °C |
| Silicone |
450 °C (when combustion occurs) |
| Urea-Formaldehyde |
95 - 105 °C |
| Vinyl Ester |
88–99 °C |
| Vulcanized Rubber |
160 - 180 ℃ |
4. How Does The Melting Point of Thermosetting Plastic Affect Its Applications?
Melting points of thermosetting plastics play an important role in the production of many applications.

- Automotive: Plastics that can tolerate high temperatures and mechanical stress are essential to automobile components because they guarantee reliability and safety.
- Electronics: Plastics used in electronics need to have exact melting points in order to survive heat cycling and soldering temperatures without breaking down.
- Manufacturing: Knowing melting points makes it easier to choose plastics that work well for particular production techniques like blow molding, extrusion, and injection molding, resulting in effective material processing.
- Medical: In order to guarantee compatibility with sterilization procedures and human tissue, thermosetting plastics with regulated melting points are used in implants and medical equipment.
- Packaging: Plastics used in food packaging must have particular melting points so they can endure heat sealing or microwave heating without warping or releasing toxic compounds.
- Product design: Designers use melting points to ascertain the maximum temperature at which thermosetting plastic components can be used, guaranteeing their efficiency and longevity under anticipated operating circumstances.
5. Conclusion
Thermosetting plastics come in various types with different melting points. Since each application requires a certain quality of heat resistance, knowing the melting points of these materials will help businesses choose the most suitable and durable ones. We hope our list of thermosetting plastics above will lift the heavy job for you.
6. Explore Engineering Plastic Compound From EuroPlas
Engineering plastic compound from EuroPlas is a full-function-in-one-material solution for end-products. We offer various options with improved mechanical properties for end products, such as stiffness, impact resistance, reduced shrinkage, and enhanced thermal resistance ability.

If you want to know more about our products and best deals, contact us now!