Injection molding is a versatile and cost-effective method that can produce a wide variety of products. However, there are several different types of injection molding techniques, each with its own unique characteristics and applications. In this article, we will explore the various types of injection molding that you need to know about. Follow now!
1. What is injection molding?
Injection molding is a widely used manufacturing process that involves the creation of plastic parts and products by injecting molten material into a mold or cavity, where it cools and solidifies to take the shape of the mold.
Injection molding involves feeding thermoplastic pellets into a hopper, heating and melting them in a barrel with a rotating screw, and then injecting the molten plastic into a mold cavity. After filling the mold, the plastic cools to solidify the product, and it is ejected from the mold. The entire cycle's duration depends on factors like part size, material, and mold design, with shorter cycles being more efficient.
Read more: What is injection molding? How does it work?
2. Types of injection molding
2.1. Conventional injection molding
Conventional injection molding is the most common and widely recognized form of injection molding. In this process, plastic pellets are heated until they become a molten material. The molten plastic is then injected into a mold, where it cools and solidifies into the desired shape. Conventional injection molding is known for its precision and the ability to produce complex and intricate parts.
2.2. Overmolding
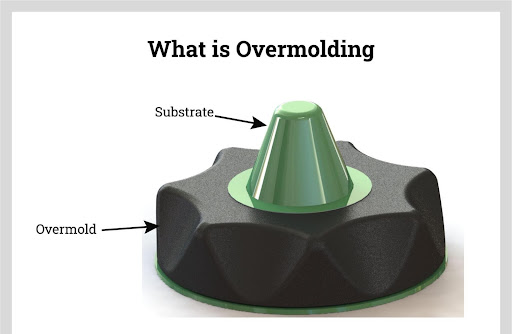
What is overmolding?
The overmolding process is a special process in the plastic injection industry in which a basic part or original product is created by molding plastic onto another material. This method creates a final product with two or more layers, usually an outer layer of plastic and an inner backing of another material. This technique is commonly used to create products with soft or ergonomic grips, like toothbrush handles or tool grips. Overmolding can add functionality, improve aesthetics, and enhance the comfort of a product.
2.3. Insert molding
Before the plastic material is injected into the mold, pre-fabricated components are inserted, such as metal pins or threaded parts. This is called the insert molding technique. The molten plastic surrounds and bonds with these components during the molding process. Insert molding is widely used in the production of electrical connectors, automotive parts, and medical devices.
2.4. Two-shot injection molding
Two-shot injection molding is a special process in the plastic injection industry in which two different types of plastic are used to create the finished product. This process is typically performed on special plastic injection machines designed to accommodate two different plastic feed positions and have multiple nozzles. How two-shot injection molding works is as follows:
- In the first pressing, an initial amount of resin is loaded and pressed into a part of the product.
- The mold or core of the machine then moves to create another space to extrude a second amount of plastic, creating a second layer of plastic or another part of the product.
- These two layers of plastic combine to create a finished product.
2.5. Gas-assisted injection molding
Gas-assisted injection molding (GAIM) is a method that uses compressed air to create plastic products with complex shapes and structures. Gas-assisted injection molding is commonly used in the production of products such as automotive parts, furniture, and home appliances, where weight, aesthetics, and structural properties play an important role. The process is similar to conventional plastic injection molding, but with an important, specific additional step:
- The thermoplastic is pressed into a mold.
- When the mold has been extracted, a quantity of compressed air is supplied into the plastic product through nozzles inside the mold.
- The pressure of compressed air pushes the plastic into areas inside the product, creating "pits" or "concave shapes" inside the product.
2.6. Micro injection molding
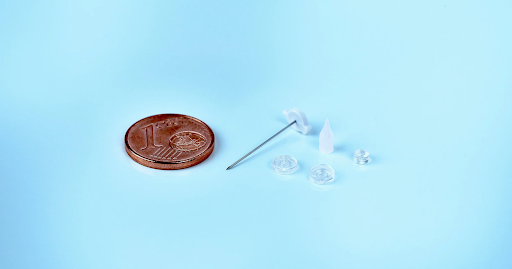
Injection molding in the micro range
Micro injection molding is a specialized method in the plastic injection industry to produce small and complex plastic products, often very small in size, especially in the field of precision technology and medicine. This method uses extremely precise plastic injection machines to create products with extremely small sizes and details.
2.7. Liquid silicone rubber (LSR) molding
Liquid silicone rubber injection molding is a special plastic injection process that uses liquid silicone rubber instead of conventional plastic to create products with high flexibility and heat resistance. The LSR molding process is similar to the conventional plastic molding process but with the difference of using liquid silicone instead of thermosetting resin. LSR molding is often used in the production of products such as medical parts, electronic products, and products that require elasticity, heat resistance, and grease resistance.
2.8. Reaction injection molding (RIM)
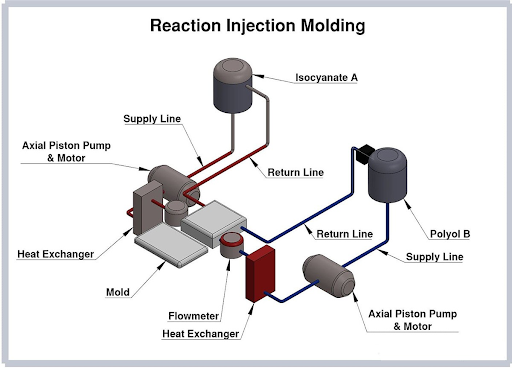
Reaction injection molding process
Reaction injection molding is an industrial manufacturing method for creating products by reacting chemical compounds. This injection molding technique is similar to conventional injection molding, except that it uses thermosetting polymers, which require a curing reaction to occur in the mold. This method typically uses two or more different liquids or chemicals, usually a polymer compound, to create the product by reacting them together in an injection mold or mold. Reaction injection molding is often used to create products with complex structures and special properties, such as automotive parts, medical products, and products with high strength or performance requirements. good insulation.
2.9. Hot runner molding
Hot runner molding is an innovative and efficient technique within the realm of injection molding. Unlike conventional methods, hot runner molding eliminates the need for a sprue and runner system by employing a heated manifold system to deliver molten plastic directly into the mold cavity. This results in several significant advantages, including reduced material waste, improved product quality, shorter cycle times, and enhanced flexibility in part design. Maintaining the plastic material in a molten state minimizes the risk of defects and ensures that molds can be filled immediately when needed, leading to cost savings over time. Hot runner molding is widely applied in industries that demand high precision, such as automotive, medical, packaging, and consumer goods, offering a more sustainable and efficient approach to plastic part manufacturing.
2.10. Thermoplastic injection molding
Thermoplastic injection molding is a flexible manufacturing process that shapes molten thermoplastics into complex parts in precisely designed molds. Thermoplastic is a type of plastic that can withstand heat without deforming or changing properties in high-temperature environments and can solidify many times without changing its quality. This technique is prized for its ability to consistently create complex and detailed components. Thermoplastic injection molding is suitable for applications in products for automobiles, electronics, medical, and consumer goods. This is a quick and cost-effective method of producing large quantities with short lead times, ensuring quality standards are met.
2.11. Thin-wall injection molding

Thin-wall injection molding products
Thin-wall injection molding is a specialized technique for creating plastic parts with extremely thin walls. It's known for its rapid cycle times and is commonly used in industries where lightweight, yet strong components are essential, such as packaging and consumer electronics. The process demands precision in material selection, mold design, and process control to ensure both structural integrity and aesthetic quality in the final products.
2.12. Metal injection molding
Metal injection molding (MIM) is an advanced process that combines plastic injection molding with metal durability. Finely powdered metal mixed with a binder is injected into a mold, followed by debonding and high-temperature sintering to form precise, dense metal parts. MIM is used in aerospace, medical, automotive, and electronics for intricate metal components, providing a cost-effective and low-waste solution for small, complex parts.
3. Conclusion
Injection molding is a versatile manufacturing process with various techniques that cater to different product requirements. Understanding the various types of injection molding is essential for selecting the most suitable method for your specific application. Each method has its own advantages and limitations, making it crucial to choose the right one to achieve the desired product quality, cost-effectiveness, and functionality. Whether you're in the automotive, medical, consumer goods, or electronics industry, the knowledge of different injection molding techniques is paramount for successful product development and manufacturing.
Read more:
Common plastics for injection molding that you need to know
4. Plastic products are used for injection molding at EuroPlas

Color masterbatch is widely used for injection molding
Color masterbatch is a crucial component in the injection molding process when it comes to adding color to plastic products. The use of color masterbatch in injection molding offers several advantages, including precise color control, ease of handling, reduced waste, and cost-effectiveness. It allows manufacturers to achieve consistent and vibrant colors in their plastic products, making it suitable for a wide range of applications, from consumer goods and packaging to automotive parts and medical devices. Additionally, the use of masterbatch simplifies the color changeover process in injection molding and improves production efficiency.

Filler masterbatch products at EuroPlas
Filler masterbatch plays a crucial role in the world of injection molding, offering a cost-effective and versatile solution to enhance the properties of plastic items. By incorporating a concentrated blend of inert fillers into the plastic material, this masterbatch brings about a multitude of advantages. It not only strengthens the plastic, improving attributes like tensile strength and impact resistance but also reduces costs by reducing the need for expensive resins. Furthermore, it contributes to weight reduction, making it an ideal choice in applications where lighter components can lead to improved efficiency. The dimensional stability it provides minimizes warping and shrinkage, ensuring precise and consistent product dimensions. In addition, certain fillers can bolster heat resistance, making them suitable for applications in high-temperature settings.

Eco-friendly material for injection molding - Bio filler
Bio filler is gaining traction in injection molding, offering an eco-friendly alternative to traditional filler materials. Derived from renewable sources, such as agricultural waste or wood fibers, these fillers improve the biodegradability of plastic products, reduce carbon footprints, and contribute to a more sustainable, circular economy. They can also enhance mechanical properties and reduce weight, making them valuable in various industries. At EuroPlas, BiOMates is a biodegradable filler made from bioplastic, modified CaCO3 powder and dispersion aids. Over time, EuP has successfully developed diverse bio filler product lines, serving many uses: BiOMates 01, BiOMates 02, and BiOMates 03. Each product line has a unique structure to suit the customers’ requirements.
If you are looking for a variety of plastic types to serve the injection molding process to create quality, highly aesthetic finished products, suitable for many different needs, EuroPlas is a great choice. We are one of the leading plastic injection molding manufacturers, have been manufacturing plastic pellets for over 15 years, and have produced high-quality plastic pellets with high mechanical properties and durability. Contact us now for detailed advice.