In the vast realm of synthetic materials, PVC plastic stands out as one of the most widely used polymers. With over a century of development, PVC has become an indispensable part of modern life, from construction to healthcare, automotive to household goods. The diversity of PVC types is not only evident in their physical and chemical properties but also in their adaptability to a multitude of applications.
This article delves into the world of PVC plastics, exploring their characteristics, advantages, and unique applications in both everyday life and advanced industrial sectors.
1. Overview of PVC Plastic
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) - one of the most common plastics globally, finds extensive applications across various industries and daily life. PVC is a synthetic polymer produced through the polymerization of Vinyl Chloride Monomer (CH2=CHCl). Its versatile properties allow for customization, resulting in a diverse range of PVC types to cater to a multitude of applications.
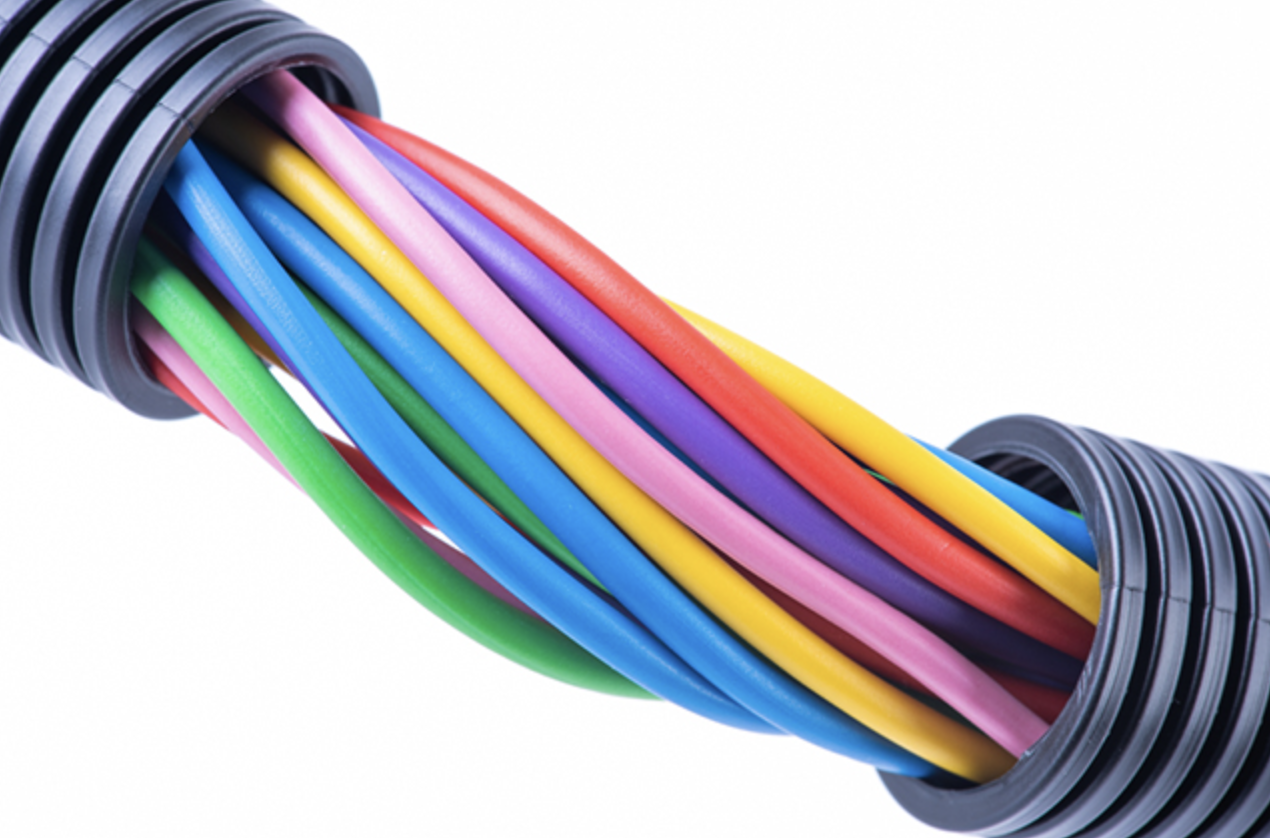

Fundamentally, PVC can be categorized into two primary groups:
- Rigid PVC (uPVC): Characterized by its hardness, durability, and stability.
- Flexible PVC: More pliable due to the addition of plasticizers.
This versatility enables PVC to be used in a wide array of applications, from pipes and windows to electrical cables and toys.
PVC's notable advantages include inherent flame resistance, high durability, and excellent corrosion resistance. These attributes make PVC an ideal choice for applications in construction, healthcare, and the automotive industry. Moreover, PVC offers relatively low production costs and is recyclable, contributing to its sustainability.
However, the use of PVC also presents environmental challenges. The production and processing of PVC can generate hazardous substances like dioxins. Additionally, certain additives used in PVC, especially plasticizers, can pose health risks if not properly controlled.
See more:
PVC stabilizers: Boosting product durability
Plastic Additives for PVC - Useful Information to Know
2. A Comprehensive Guide to PVC Types and Their Characteristics
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is one of the most widely used plastics globally, finding diverse applications across various industries. Each type of PVC possesses unique properties, making it suitable for specific applications. Here's a detailed breakdown of common PVC types and their salient features:
2.1. Rigid PVC - uPVC
Rigid PVC, also known as Unplasticized PVC or uPVC, is the most common type of PVC.
- Color: Typically white or cream.
- Key characteristics: uPVC exhibits high rigidity, durability, excellent corrosion and fire resistance, chemical resistance, and electrical insulation properties.
- Applications: Widely used in the construction industry for manufacturing pipes, windows, and frames due to its durability and weather resistance.
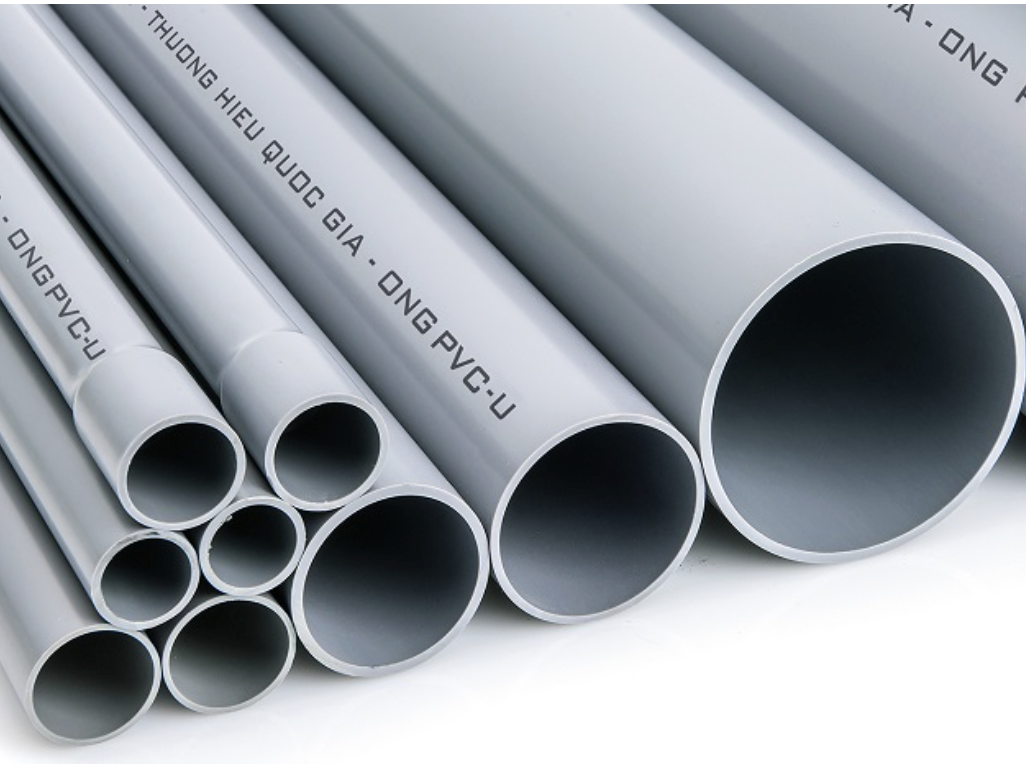

2.2. Flexible PVC
Flexible PVC, or Plasticized PVC, is produced by adding plasticizers to rigid PVC to enhance its flexibility.
- Color: Can be dyed in various colors.
- Key characteristics: Flexible PVC offers good elasticity, softness, durability, ease of bending and stretching, and excellent water resistance.
- Applications: Commonly used in the production of electrical cables, vinyl fabrics, medical gloves, and products requiring flexibility.
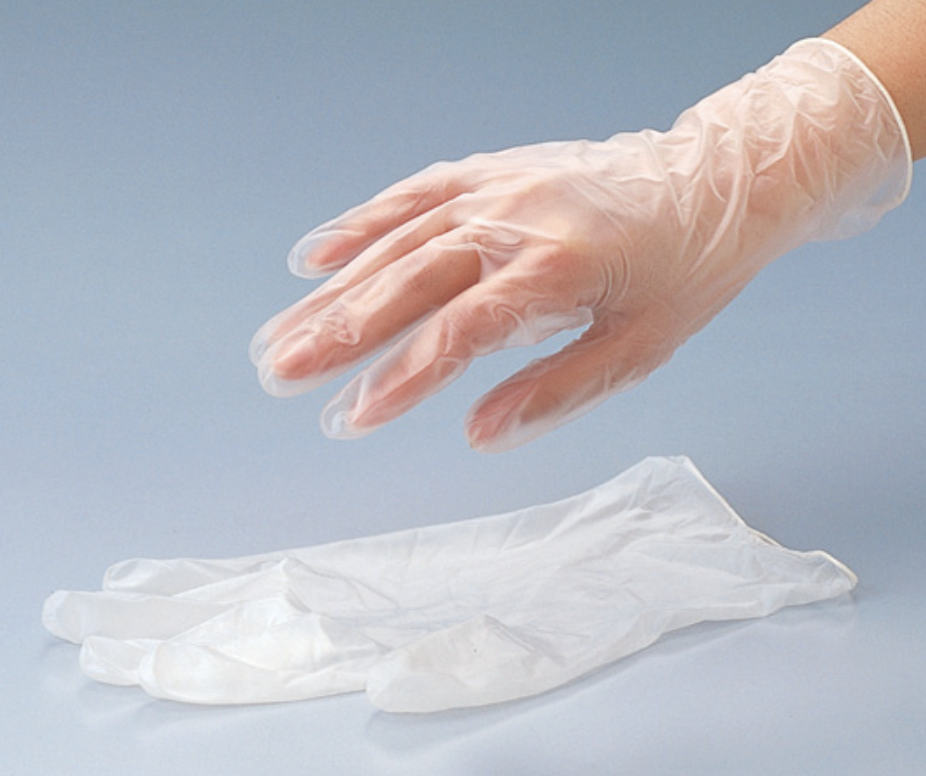

2.3. Other PVC Types
CPVC - Chlorinated PVC: A thermoplastic produced by chlorinating PVC. CPVC is typically light yellow, can withstand higher temperatures than regular PVC, and is primarily used in hot water systems and industrial applications.
PVC-O - Oriented PVC: An improved PVC with high strength and lighter weight compared to regular PVC. PVC-O is usually light blue and primarily used in high-pressure piping systems.
Foamed PVC: A lightweight PVC with excellent thermal and acoustic insulation properties. Foamed PVC is typically white or light-colored and widely used in advertising, packaging, and construction.
Recycled PVC: Produced from recycled PVC products. Recycled PVC is often grey or dark-colored and used in various applications, contributing to reducing the environmental impact of the plastics industry.

In conclusion, each type of PVC offers distinct properties, making it suitable for specific applications in various industries and aspects of modern life. The versatility and wide range of applications of PVC make it a crucial material in various sectors. However, the use of PVC also poses environmental challenges. Many countries are encouraging the use of recycled PVC and developing more environmentally friendly production and recycling methods. Research and development of new, safer, and more environmentally friendly PVC types is a growing trend in the global plastics industry.
3. Applications of PVC in Life
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) finds numerous applications in our daily lives and various industries. Let's delve into the specific applications of different PVC types:
3.1. Applications of Rigid PVC
Construction: Rigid PVC is widely used for manufacturing window and door frames, offering durability and excellent insulation properties. PVC piping systems for water supply and drainage are preferred due to their corrosion resistance and longevity.
Electrical: Rigid PVC is used as a sheath for cables and conduits, ensuring safety and efficiency in electrical distribution.
Healthcare: Rigid PVC is used for manufacturing medical bottles and containers due to its stability and resistance to contamination.

3.2. Applications of Flexible PVC
Fashion Industry: Flexible PVC is used for producing waterproof footwear, raincoats, and durable handbags.
Interior Design: Flexible PVC is utilized in making upholstery for sofas, curtains, and floor coverings that are waterproof and easy to clean.
Electronics: Flexible PVC is used for cable sheathing and manufacturing flexible insulating components.
Healthcare: Flexible PVC plays a crucial role in manufacturing infusion tubing, blood bags, and medical gloves, thanks to its flexibility and ability to be sterilized.
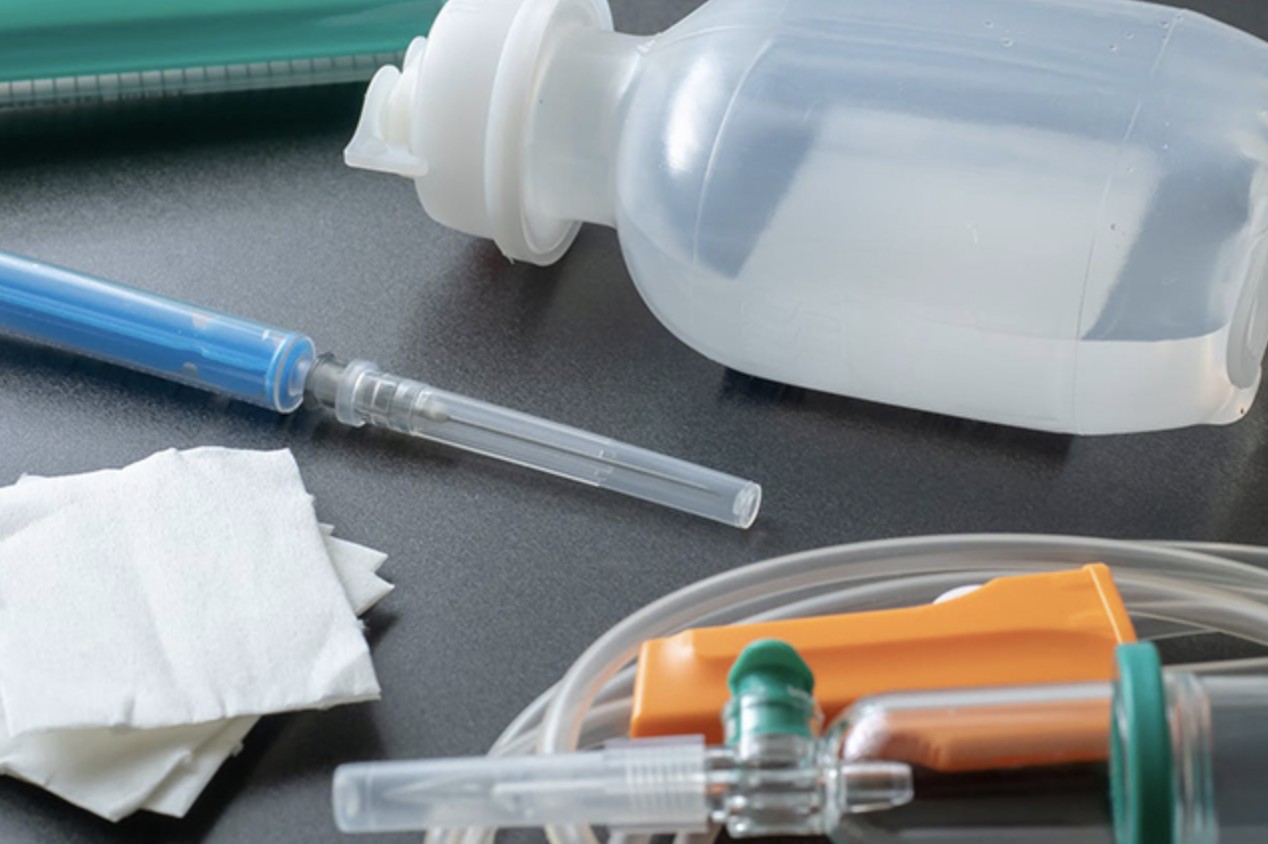
3.3. Applications of Other PVC Types
CPVC (Chlorinated PVC): Primarily used in hot water piping systems and fire protection systems due to its high temperature resistance. It is used for manufacturing hot water pipes in residential and industrial settings, as well as in automatic sprinkler fire suppression systems.
PVC-O (Oriented PVC): Found in high-pressure piping systems, especially in urban water supply and large-scale agricultural irrigation systems.
Foamed PVC: Widely used in advertising, construction, and packaging. It is used for making signs, lightweight billboards, as insulation material for walls and ceilings, and for manufacturing lightweight, shock-resistant packaging boxes.
Recycled PVC: Contributes to environmental conservation and is used to produce products like floor tiles, wall panels, traffic cones, and agricultural products like seedling trays and irrigation pipes.
The diverse applications of PVC reflect its versatility and adaptability. From rigid PVC used in construction and industry to flexible PVC in healthcare and fashion, each type of PVC plays a distinct role. The development of specialized PVC types like CPVC, PVC-O, and foamed PVC has opened up new application possibilities, meeting the growing demands of various sectors. However, alongside its benefits, the use of PVC also presents environmental challenges, prompting the plastics industry to continuously innovate and develop more sustainable solutions.
4. Conclusion
The diverse applications of PVC reflect its versatility and adaptability. From rigid PVC used in construction and industry to flexible PVC in healthcare and fashion, each type of PVC plays a distinct role. The development of specialized PVC types like CPVC, PVC-O, and foamed PVC has opened up new application possibilities, meeting the growing demands of various sectors. However, alongside its benefits, the use of PVC also presents environmental challenges, prompting the plastics industry to continuously innovate and develop more sustainable solutions.
5. About EuroPlas
EuroPlas, as a leading global supplier of filler masterbatch products, has established its position in the global plastics industry. EuroPlas not only provides high-quality products but also continuously innovates and develops. EuroPlas' focus on developing advanced solutions for the packaging and textile industry has met the growing and diverse needs of the market.
For detailed and accurate advice on EuroPlas'products, please fill out the contact form on our website. EuroPlas is committed to responding to all inquiries promptly, ensuring that your needs are met efficiently and professionally. With years of industry experience and a deep understanding of plastic types and their applications, EuroPlas is confident in providing optimal solutions tailored to the specific requirements of each project.