In the world of engineering plastics, PA6 and PA66 are considered the “two giants” thanks to their balance of strength, toughness, and processability. Both belong to the polyamide (nylon) family and are widely used in automotive, electrical & electronics, mechanical engineering, and high-performance consumer goods. According to Mordor Intelligence (2024), the global polyamide market is expected to surpass USD 25 billion by 2029, with PA6 and PA66 holding the largest share. This proves that knowing and selecting the right polyamide is a true competitive advantage.
However, when comparing PA6 vs PA66, significant differences emerge — from molecular structure and mechanical performance to production cost. Understanding these distinctions not only helps manufacturers choose the right material but also optimizes product design, reduces costs, and enhances reliability.
1. Overview of PA6 and PA66
1.1. What is PA6?
PA6, also known as Nylon 6, is produced by the ring-opening polymerization of caprolactam. It is a semi-crystalline plastic with good mechanical strength, wear resistance, and excellent impact performance.
Key features of PA6:
- Tough and impact-resistant → ideal for flexible parts.
- Easily processed → suitable for injection molding and extrusion.
- More cost-effective than PA66, making it common in mass-market products.
Typical applications: gears, bushings, lightweight housings, and household goods (e.g., cookware handles, vacuum cleaner parts).
1.2. What is PA66?
PA66, or Nylon 66, is synthesized through the condensation of hexamethylene diamine and adipic acid. It is also a semi-crystalline material, but with a higher density of hydrogen bonding compared to PA6, resulting in greater stiffness and thermal stability.
Key features of PA66:
- Higher rigidity than PA6, especially at elevated temperatures.
- Excellent dimensional stability, less deformation over time.
- Better chemical resistance, especially to oils and solvents.
Typical applications: automotive engine components (radiator end tanks, housings), electrical and electronic parts (switches, sockets), and high-load engineering components.
2. Chemical Structure of PA6 and PA66
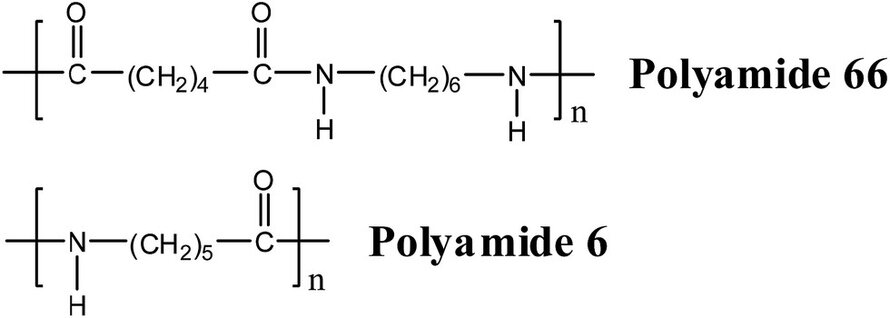
Chemical Structure of PA6 and PA66
The chemical structure of Polyamide 6 (PA6), commonly referred to as Nylon 6, is characterized by its arrangement of repeating amide groups (-CONH-) within the polymer chain. This fundamental structure places PA6 within the family of nylon polymers, which are known for their versatility and strength. The presence of these amide linkages gives PA6 its distinctive properties, including a semi-crystalline structure.
Polyamide 66 (PA66), commonly known as Nylon 66, is derived from the polycondensation reaction between adipic acid and hexamethylenediamine, also known as hexamethylene diamine adipate. This reaction results in the formation of a polymer chain composed of repeating units, with each unit consisting of six carbon atoms (hexamethylene) linked by amide groups.
The chemical formula for Nylon 66, represented as (NH-(CH2)6-NH-CO-(CH2)4-CO-)n, illustrates the arrangement of the polymer chain. In this structure, the amide groups (-NH-CO-) alternate with hexamethylene segments (-(CH2)6-), forming a backbone that extends through the entire length of the polymer chain. The repeating units are connected by covalent bonds, with 'n' representing the number of repeating units present in the polymer chain. The resulting chemical structure of PA66 exhibits a high degree of symmetry and regularity, contributing to its exceptional mechanical properties and thermal stability.
Read more: Nylon 66: What is it? Properties, benefits, and applications
2. Comparing the Key Properties of PA6 and PA66
When considering
the differences between Polyamide 6 (PA6) and Polyamide 66 (PA66), it's essential to examine their key properties, as they can significantly impact their suitability for various applications. Here's a comparative analysis:
2.1. Melting Point
- PA6: The melting point of PA6 is approximately 223°C.
- PA66: PA66 boasts a higher melting point of around 255°C, indicating superior heat resistance compared to PA6.
2.2. Strength and Stiffness
- PA6: While PA6 offers good tensile strength, it generally falls short compared to PA66 in terms of strength and stiffness.
- PA66: PA66 demonstrates excellent tensile strength and stiffness, making it suitable for applications requiring high mechanical performance and structural integrity.
2.3. Moisture Absorption
- PA6: Nylon PA6 tends to absorb more moisture than PA66, which can impact its dimensional stability, particularly in humid environments.
- PA66: PA66 exhibits lower water absorption, contributing to better dimensional stability and performance in environments with high humidity levels.
2.4. Chemical Resistance
Both PA6 and PA66 demonstrate good resistance to various chemicals, including oils, fuels, and solvents. However, PA66 may offer slightly better resistance due to its higher melting point and denser molecular structure.
3. Processing and Production Cost
3.1. Processing PA6
One of the advantages of PA6 is its ease of processing. With a lower melting temperature (~220°C), injection molding and extrusion can be carried out more efficiently, saving energy. PA6 also requires less complex tooling, which reduces cycle times.
Production costs with PA6 are generally lower because:
- The raw material price is cheaper.
- Processing conditions are less demanding.
It can be easily combined with fillers and additives (CaCO₃, glass fiber) to further optimize costs.
3.2. Processing PA66
On the other hand, PA66 has a higher melting temperature (~260°C), which makes its processing more challenging:
- Higher barrel and mold temperatures are required, leading to increased energy consumption.
- Longer cycle times compared to PA6.
- Tooling must withstand higher heat to avoid deformation.
In addition, PA66 raw material costs are higher. However, in return, PA66 delivers greater mechanical strength and dimensional stability, which is critical for high-performance industrial applications.
4. Applications of PA6 and PA66
Diverse applications of PA6 and PA66 engineering plastics
Polyamide 6 (PA6) and Polyamide 66 (PA66) find extensive applications across various industries due to their remarkable properties and versatility. Let's see applications in each specific field below:
4.1. Automotive
- PA66: Widely used in the automotive industry for manufacturing engine covers, intake manifolds, fuel lines, radiator end tanks, and airbags due to its strength, heat resistance, and chemical resistance.
- PA6: Utilized for producing engineering components such as gears, bearings, and bushings in automobiles, leveraging its mechanical strength and wear resistance.
4.2. Electrical & Electronics
- PA66: Employed in electrical connectors, switches, sockets, and housings owing to its excellent electrical insulation properties, providing reliability and safety in electrical and electronic devices.
- PA6: Used in electrical applications requiring toughness and puncture resistance, such as cable ties and insulating materials.
4.3. Consumer goods
- PA66: Utilized in consumer goods like luggage, backpacks, footwear, and household appliances due to its toughness, flexibility, and aesthetic appeal.
- PA6: Applied for consumer products such as toothbrushes, combs, and utensils due to their durability and resistance to chemicals.
4.4. Industrial
- PA66: Employed in industrial applications for manufacturing components like gears, bearings, rollers, and bushings, thanks to its wear resistance and low friction coefficient.
- PA6: Used in industrial applications for producing films, sheets, and packaging materials, leveraging its toughness and puncture resistance.
In general, PA6 and PA66 play integral roles across a wide spectrum of industries, from automotive and electrical to consumer goods and industrial applications, owing to their exceptional properties and performance characteristics. Whether it's enhancing structural integrity in automobiles or providing reliable insulation in electrical devices, these polyamides continue to be indispensable materials in modern manufacturing processes.
Read more: How many types of nylon? Properties & Common uses
5. PA6 and PA66: Choosing the Right Material
Choosing between PA6 and PA66 requires a thorough understanding of the unique properties of these two materials, and whether they are suitable for each product's specific needs. While PA6 offers excellent adaptability and cost savings, PA66 offers outstanding heat resistance and mechanical strength. The final decision depends on factors such as operating conditions, performance requirements, product operating environment, budget constraints, etc.
6. Conclusion
By comparing the chemical structures, key properties, and common uses of PA6 and PA66, this article has highlighted the critical considerations necessary for selecting the optimal material. Whether for automotive components, electrical and electronics applications, consumer goods, or industrial uses, etc, understanding these differences ensures that enterprises can leverage the strengths of each polyamide to achieve the best possible outcomes in their projects.
7. About EuroPlas’ PA6 and PA66 products
EuroPlas stands as a premier manufacturer renowned for crafting top-tier filler masterbatch, bio-plastic, plastic additives, engineering plastic compounds, etc. Among its esteemed offerings are the Polyamide 6 (PA6) and Polyamide 66 (PA66) compounds, pivotal materials extensively utilized across diverse industries.

PA66, PA6 Glass Fiber Compound at EuroPlas is the perfect choice for your product
PA66, PA6 Glass fiber compound is a mixture of PA resin and glass fiber reinforced. With a composition boasting 30-50% glass fiber, this compound delivers unparalleled toughness, wear resistance, and chemical resilience. Ideal for an array of applications ranging from gears and bearings to household electrical components, it offers stability, electrical insulation, and ease of molding.
There are some features of PA66, PA6 glass fiber compound at EuroPlas:
- Combines multiple functions into a single material.
- Directly processable without additional materials.
- Tailored to meet specific end-product requirements.
- Enhances stiffness, reduces shrinkage, and fortifies strength.
- Improves impact resistance and thermal durability.

Quality PA6, PA66 Blend Compound products at EuroPlas
PA6, PA66 blend compound comprises PA6/PA66 resin, elastomer, and impact strength modifiers. This blend capitalizes on the strengths of both PA6 and PA66, offering a versatile solution prized for its elasticity and high-impact strength. Widely embraced in the automotive and motorcycle sectors, it finds utility in roller bearings, office equipment, and various gear-related components.
You can see some significant advantages of our PA6, PA66 blend compound here:
- Integrates multiple functions into a singular material.
- Directly processable without additional materials.
- Customizable to suit diverse end-product specifications.
- Exhibits superior elasticity and impact strength, augmenting mechanical properties and thermal capability.
EuroPlas’ PA6 and PA66 compounds are indispensable choices in industries ranging from automotive and electronics to industrial manufacturing. Highly appreciated for their mechanical prowess, heat resistance, and chemical resilience, those engineering plastic compounds serve as integral components in engine parts, electrical connectors, and high-performance gear systems.
For expert consultation on technical plastic compound solutions tailored to your unique application, contact EuroPlas today!