Polypropylene (PP) is a widely used plastic due to its durability, versatility, and cost-effectiveness. However, not all PP types are the same. One distinct form, isotactic polypropylene (iPP), offers unique properties that make it advantageous for specific applications. In this article, we’ll dive into the differences between isotactic PP and regular PP, discussing how iPP’s structure contributes to its enhanced characteristics and varied uses.
1. What is Isotactic Polypropylene?
Isotactic polypropylene (iPP) is a variant of polypropylene distinguished by the regular arrangement of its molecular structure. In iPP, the methyl groups are aligned on the same side of the polymer chain, creating a highly crystalline structure. This uniformity, achieved through specialized production processes, results in enhanced mechanical properties, such as increased stiffness, thermal resistance, and chemical resistance.
Isotactic PP is synthesized using specific catalysts, like Ziegler-Natta or metallocene catalysts, which control the polymer chain’s alignment. Due to its crystallinity, iPP is more rigid and has a higher melting point compared to other forms of PP. This structure makes isotactic PP an ideal choice for applications requiring strength, durability, and thermal stability.
.jpg)
Isotactic polypropylene (iPP)
2. Comparing Isotactic PP With Regular PP
Isotactic polypropylene has many advantages over regular PP due to its crystalline structure. To understand how iPP differs from standard PP, let’s examine their structures, physical properties, and performance.
2.1. Structural Differences
-
PP: Polypropylene is a thermoplastic made from propene or propylene monomer that is durable, rigid, and crystalline. It's a hydrocarbon resin with a linear structure. Polypropylene's chemical formula is (C3H6)n. Polypropylene plastic is one of the most affordable plastics on the market today.
- Isotactic PP: Has all methyl groups on the same side of the polymer chain, resulting in a highly organized, crystalline structure.
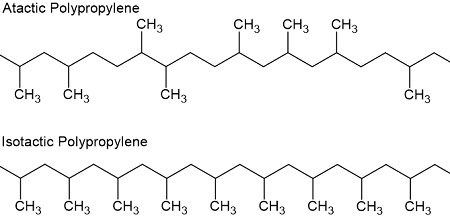
Structural Differences Between PP and iPP
Read more: PP Plastic: Everything you need to know
2.2. Melting Point
-
PP: The typical melting point of PP falls between 160°C to 170°C (320°F to 338°F). However, this can vary based on factors such as isotacticity and crystallinity.
- Isotactic PP: iPP, characterized by a regular molecular structure, generally exhibits a higher melting point compared to atactic PP, which has a more disordered molecular arrangement.
2.3. Chemical Resistance
-
PP: Has moderate chemical resistance, but is less reliable in extreme conditions compared to iPP.
- Isotactic PP: Its structure provides superior resistance to chemicals, acids, and bases, making it an ideal choice for containers or packaging that might come into contact with these substances.
2.4. Physical Properties
-
PP: Regular polypropylene (PP), particularly in the form of random copolymers, has a less ordered structure, which results in greater flexibility and slightly softer properties compared to isotactic polypropylene (iPP). This flexibility makes it easier to process and mold, suitable for applications needing elasticity, like plastic bags and packaging films. Although regular PP offers some chemical resistance, it may not be as robust as iPP under high-stress conditions.
- Isotactic PP: iPP has a highly ordered molecular structure, giving it a high crystallinity level. This arrangement results in a stiffer and more rigid material with excellent tensile strength, making iPP ideal for products that need durability and shape retention, like pipes, containers, and automotive parts. iPP is also highly resistant to chemicals, moisture, and heat, further boosting its durability for industrial applications.

Physical Properties Of Isotactic Polypropylene
2.5. Optical Clarity
-
PP: Regular PP is less crystalline, especially in its random copolymer form. This allows it to offer higher transparency and better optical clarity, making it ideal for applications requiring a clear view of products such as packaging materials, clear bottles, and food storage containers. The more flexible and less ordered structure of regular PP enables better light transmission, enhancing its suitability for uses where product visibility or aesthetic appeal is essential.
- Isotactic PP: iPP, due to its highly crystalline structure, generally has lower optical clarity compared to regular PP. The orderly arrangement of polymer chains in iPP enhances strength and rigidity but often leads to a more opaque or cloudy appearance in the final product. This makes iPP suitable for applications where transparency isn't a primary concern but where durability and strength are crucial, like in automotive parts or industrial containers.
3. Applications of Isotactic PP
The unique properties of isotactic polypropylene make it suitable for a wide range of applications across various industries.
3.1. Automotive Industry
Isotactic PP is ideal for automotive components due to its strength, durability, and heat resistance. It’s commonly used in parts like bumpers, dashboard panels, battery cases, and other interior and exterior parts that need to be strong and withstand wear and tear. Its rigidity helps these parts hold their shape under pressure, while its resistance to chemicals makes it a good fit for environments where it may be exposed to fuels, oils, or other substances.

Isotactic Polypropylene Used For Automotive Industry
3.2. Packaging Industry
In packaging, iPP is valued for its stiffness, which helps it protect products effectively. Its chemical resistance also ensures that food, items, and other products remain safe. iPP is often used for rigid containers, bottle caps, and even some types of films. The high melting point of iPP allows it to be used in packaging that must endure hot filling processes or high-temperature storage conditions.
3.3. Electronics Industry
With its insulating properties and stability, iPP is commonly used in electronic components and electrical appliances. Its ability to withstand thermal stress makes it a reliable choice for insulation and protective casings for wires, cables, and electronic parts.
3.4. Consumer Goods
Many consumer goods use isotactic PP for its durability, impact resistance, and safety. This includes items like furniture, toys, storage containers, and household items. iPP's strength and resistance to wear and tear make it a practical choice for products designed for regular use.

Consumer Goods Made From Isotactic PP
4. Conclusion
In short, isotactic polypropylene (iPP) stands out as a specialized form of polypropylene with unique advantages due to its crystalline structure. Its increased strength, durability, and resistance to heat and chemicals make it preferable in industries ranging from automotive to medical and packaging. Compared to regular PP, iPP’s distinct properties open doors to applications that demand high reliability and performance.
5. About EuroPlas’ PP Products
EuroPlas offers high-quality polypropylene products, including isotactic PP, tailored to meet industry standards. With advanced manufacturing and strict quality control, EuroPlas ensures that the company’s PP products are suitable for applications across automotive, medical, packaging, and other sectors. Here’s the list of our PP compound and the suggested applications:
- PP filler masterbatch: Improve several properties of end-products: brightness, opacity, shrinkage reduction,...
- PP glass fiber compound: You can use it for car doors, kettle handles, rice cooker covers, etc.
- PP glass bead compound: It's suitable for home appliances, interior, and automotive decoration.
- PP talc compound: Outdoor equipment, motorcycles, and car interiors are common applications.
- PP BaSO4 compound: It's ideal for sanitary ware, water purifiers, vacuum cleaners, rice cookers, etc.
- PP conductive compound: You can use it for household appliances, pumps, pipes, ESD film, etc.
- PP flame retardant compound: It has better flame retardancy, which is ideal for household electrical and electronic equipment.
For more information and samples, please contact us HERE!