Technical plastic processing is not just about shaping products from plastic, but also an art that combines materials science, manufacturing techniques, and practical experience. To obtain high-quality technical plastic products that meet the stringent requirements of durability, precision, and aesthetics, practitioners need to master the basic principles and important notes. This article will provide an overview of the key factors to consider when processing technical plastics, from material selection to mold design and quality control, helping you shape the right direction and achieve success in this field.
1. What is Engineering Plastic?
Engineering plastics are plastic materials that possess superior properties compared to standard plastics, including mechanical, chemical, optical, and thermal properties. They have dimensional stability, low flammability, and reduced shrinkage. Engineering plastics are often thermoplastic materials, easily processed into complex shapes, suitable for structural applications requiring high detail such as mechanical parts or automotive interiors. Engineering plastic is not a specific type of plastic with a fixed composition but is customized according to the technical requirements of the final product.
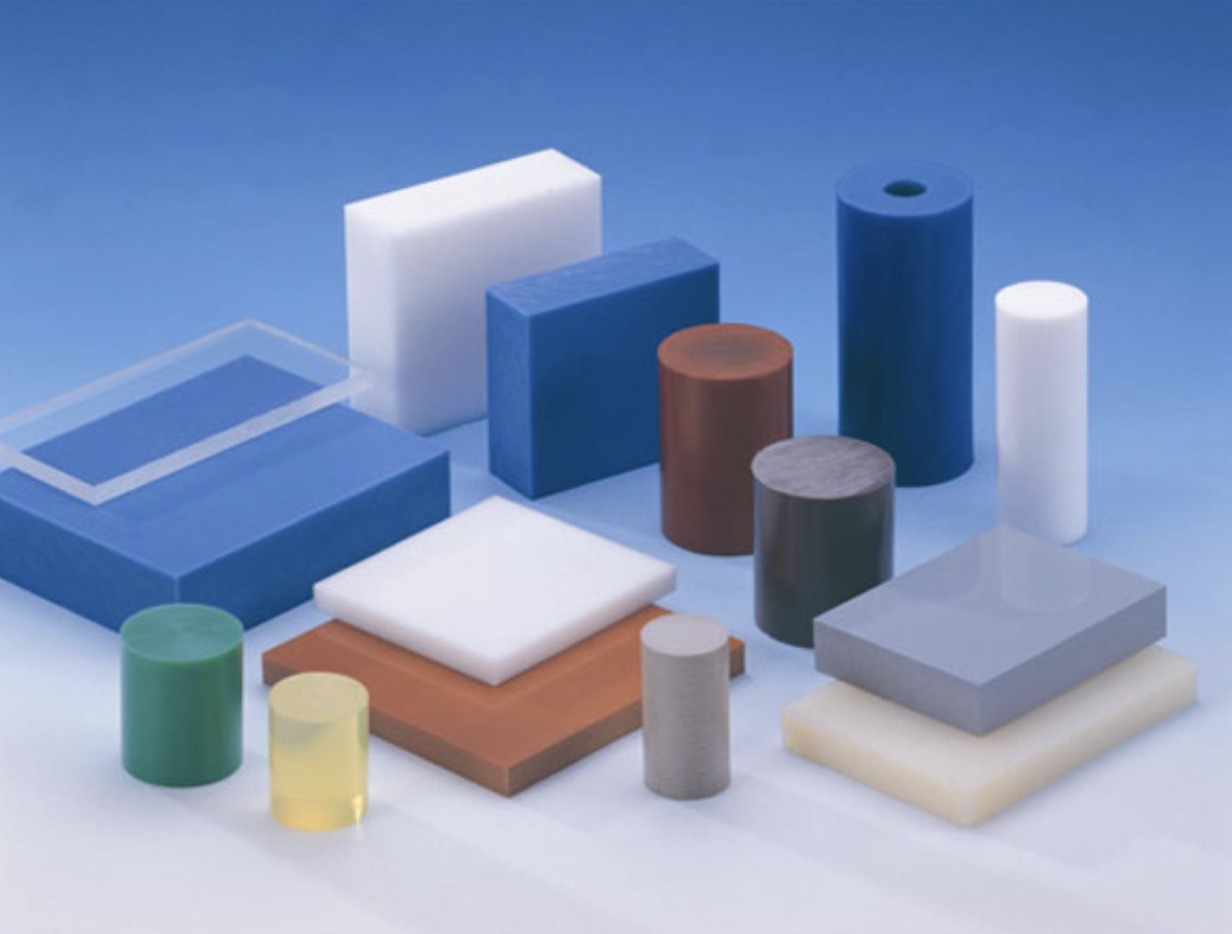

See more: Engineering plastic materials properties - All you should know
1.1. Properties
Engineering plastics possess special physical and chemical properties, making them superior in technical applications.
- Strength: High tensile strength, flexural strength and impact strength.
- Ductility: Ability to bend without breaking.
- Hardness: Resists deformation under the action of force.
- Electrical properties: Good electrical insulation or conductivity depending on the application.
- Heat resistance: Maintains properties at high temperatures.
- Optical properties: Transparent, translucent, or непрозрачный depending on the type of plastic.
- Chemical resistance: Resistant to the effects of acids, bases, solvents and other chemicals.
- Chemical stability: Does not react with other substances under normal conditions.
- Flame resistance: Some engineering plastics are flame retardant or self-extinguishing.
- UV resistance: Resists degradation due to the effects of ultraviolet rays.
1.2. Advantages and disadvantages
Engineering plastics have the following advantages and disadvantages:
- High mechanical strength: Withstands better loads and impacts.
- Good chemical resistance: Resists corrosion from many types of chemicals.
- Good heat resistance: Can operate at higher temperatures than conventional plastics.
- High dimensional stability: Less deformed by temperature or humidity.
- Some types of engineering plastics are more difficult to process.
- Higher cost than conventional plastics.
- May require special equipment and processing procedures.
1.3. Application
Engineering plastics are widely used in many different industries due to their superior properties.
Automotive Industry: Engineering plastics are used to manufacture parts such as bumpers and car bodies. Polypropylene (PP) is one of the most popular plastic resins in this application, offering a balance between strength, heat resistance, and flexibility.

Electronics Industry: Engineering plastics are used to manufacture computer cases, smartphones, and other electronic devices. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is the most commonly used plastic resin for these applications, providing high durability and aesthetics, while being easy to process.

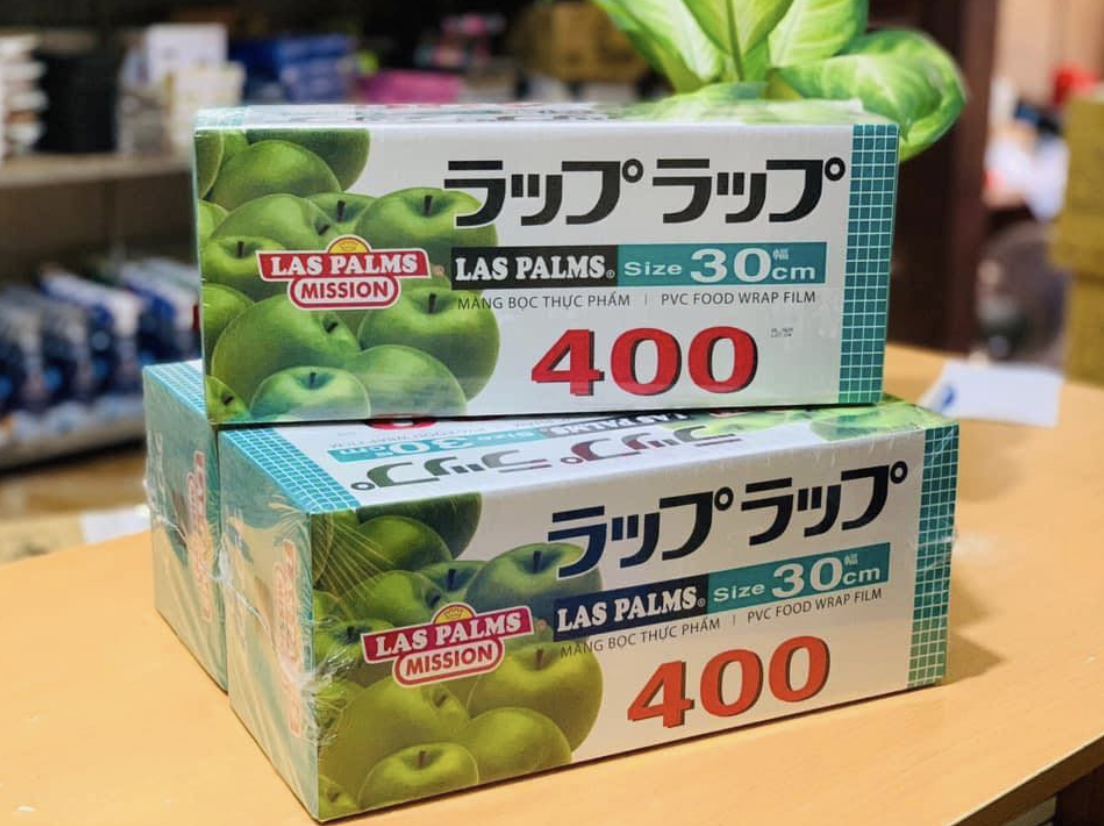
Food Packaging Industry: Engineering plastics are used to manufacture packaging such as water bottles, food containers, and food wrap. Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) is the most commonly used plastic resin in this field, with high transparency, good impact resistance, and excellent odor retention properties.

Construction Industry: Engineering plastics are used to manufacture water pipes, windows and doors. Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) is the most widely used plastic resin in the production of water pipes, with excellent corrosion resistance, easy installation, and reasonable cost.

Medical Industry: Engineering plastics are used to manufacture devices such as syringes, infusion tubes, and surgical instruments. Polypropylene (PP) is the most commonly used plastic resin in this field, with chemical resistance, non-toxicity, and high stability.
Other Applications: Engineering plastics are also used in the aerospace industry to manufacture parts that require high precision, durability, and lightweight. They are also used to make molds in garment factories, electrical insulation technical machine parts in industry, high-tech electronic circuit boards in the electronics industry, anti-static and waterproof liners and partitions, and support in advertising, interior and construction.
See more: Plastic compounds vs standard plastics, which one is better?
2. Important Factors to Pay Attention to When Processing Engineering Plastics
When processing engineering plastics, process control is a key factor to ensure product quality. Technicians need to have in-depth knowledge of technical parameters and the ability to adjust machinery when necessary. In addition, checking the operating procedures of each part of the plastic molding machine is also very important, including mold temperature and pressure. Common challenges in plastic processing include material inconsistency, machine failure, temperature control issues, environmental impacts, and the risk of contamination.

To overcome these challenges, it is necessary to apply strict quality control processes, preventive maintenance, invest in advanced technology, apply sustainable production measures, and ensure strict hygiene control processes. In addition, the following factors should be noted to ensure product quality and production efficiency:
- Choose The Right Material: Each type of engineering plastic has its own properties, suitable for different applications. It is necessary to choose the type of plastic that meets the technical requirements of the product.
- Accurate Mold Design: Molds play an important role in shaping the product. It is necessary to design accurate molds, ensuring tightness and effective cooling systems.
- Control of Processing Temperature: Processing temperature greatly affects the properties of the product. It is necessary to control the mold temperature, molten plastic temperature and ambient temperature.
- Adjust Injection Pressure: Injection pressure needs to be adjusted to suit the type of plastic and product shape. Too high pressure can cause residual stress, while too low pressure can lead to incomplete products.
- Injection Speed: The injection speed needs to be controlled to ensure that the plastic flows evenly into the mold and avoid air bubbles.
- Cooling Time: Cooling time is sufficient for the plastic to solidify and shape the product. Too short a cooling time can lead to product deformation.
- Post-processing: After processing, the product may need to be further processed such as cutting excess material, polishing or painting to achieve complete quality.
- Dust and Temperature Control: Ensure effective control of dust and temperature during processing to protect machinery and ensure product quality.
3. Conclusion
Engineering plastic processing plays an important role in the manufacturing industry, creating diverse products. To achieve high efficiency, it is necessary to control the quality of raw materials, operate machinery stably, and maintain optimal temperature. Sustainable production measures and hygiene control also need to be emphasized to reduce environmental impacts and ensure product safety. Thanks to that, production efficiency can be improved and the stringent requirements of the market can be met.
EuroPlas provides engineering plastics, including PBT GF-FR compounds, PA6, PA66 blends, PC flame retardant compounds, ABS fiberglass compounds, and ABS antistatic compounds. These products are designed to provide customers with complete material solutions, capable of operating effectively in many different applications.
EuroPlas's compound base plastic includes engineering plastics such as ABS, PC, HIPS, POM, PBT,... Common reinforcing agents used in EuroPlas's engineering plastic compounds include glass fibers and beads, conductive carbon, barium sulfate, antistatic additives and flame retardant additives.
EuroPlas engineering plastic compound is an optimal solution thanks to its flexibility, high quality and ability to integrate many functions into a single material. This helps simplify the production process and improve the performance of the final product. Please contact EuroPlas now for fast consulting and additional detailed information!