The environmental impact of single-use plastic straws has become a growing concern in recent years. To address this issue, more and more businesses are switching to eco-friendly alternatives such as compostable straws. What are compostable straws made of, and how are they produced?
In this blog, we will take a closer look at the materials and manufacturing process behind compostable straws. Let’s get started!
Related:
- What is Biodegradable Packaging? Biodegradable Packaging Advantages and Disadvantages
- Top 5 polymer additives for agricultural films
- Create a bioplastic business plan in 4 steps
- Potato starch bioplastic pros and cons - Top secret may surprise you
1. What are compostable straws made of
1.1. Definition:

Compostable straws are made from natural materials that can decompose into organic compounds in a relatively short time frame, typically within 180 days or less.
These straws are designed to be environmentally friendly and an alternative to traditional plastic straws, which can take hundreds of years to decompose and contribute to plastic pollution in the environment.
1.2. Components:
What is a compostable straw made of? Compostable straws are made of natural components that are biodegradable and can break down into organic compounds over time. The materials used to make compostable straws may vary depending on the manufacturer, but typically include:
- Polylactic acid (PLA): A bioplastic made from renewable resources like cornstarch, sugarcane, or cassava. This biomaterial is biodegradable and can decompose under the right conditions.
- Paper: Compostable straws made from paper are typically made from plant-based fibers like wood pulp, bamboo, or bagasse, a byproduct of sugarcane production. These straws are coated with plant-based wax to make them waterproof.
- Wheat straw: A byproduct of wheat harvesting that is typically discarded, but can be used to make straws and other biodegradable products. Wheat straw-based straws are biodegradable and break down quickly in the environment.
- Bamboo: A fast-growing, renewable resource that requires no pesticides or fertilizers and can be used to make biodegradable straws. Bamboo straws are durable and can be reused multiple times.
Overall, the components of compostable straws are chosen for their biodegradability, renewability, and environmental sustainability.
1.3. Benefits:
Here are some of the advantages of using compostable straws:
- Reduce plastic pollution: Traditional plastic straws are one of the top items found in ocean and beach cleanups. They can take hundreds of years to decompose, and in the meantime, can harm marine life when ingested or entangled. Compostable straws, on the other hand, break down much more quickly and do not release harmful chemicals into the environment. By using compostable straws instead of plastic, individuals and companies can reduce their contribution to plastic pollution.
- Minimize waste: Compostable straws can be discarded in compost bins or facilities, where they will break down naturally and contribute to soil health. This reduces the amount of waste that ends up in landfills and helps to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Composting also creates nutrient-rich soil that can be used to grow more plants and reduce the need for chemical fertilizers.
- Support sustainable agriculture: Some compostable straws are made from renewable resources such as corn or wheat, which can support local farmers and reduce dependence on non-renewable resources. By using compostable straws, individuals and companies can contribute to a more sustainable agricultural system.
- Encourage innovation: The development of compostable straws and other eco-friendly products encourages companies to invest in research and development for more sustainable materials and practices. This can lead to the development of new and better ways to reduce waste and protect the environment.
- Improve brand reputation: Using compostable straws can demonstrate a company's commitment to sustainability and environmental responsibility, which can be appealing to environmentally conscious customers. It can also be a way for individuals to show their personal commitment to reducing their environmental impact.
Ultimately, biodegradable straws provide a more sustainable and environmentally friendly option than conventional plastic straws. Individuals and businesses may have a positive influence on the environment and help create a more sustainable future by using biodegradable straws.
2. Materials for producing compostable straw from EuroPlas

BiOMates is a type of bioplastic filler made from sustainable and renewable raw materials such as starch, cellulose, and others. It is used as a filler in plastics to enhance the biodegradability of bioplastic end-products.
The BiOMates are biodegradable within 12 months. In addition, they act as an anti-block and slipping agent in blown film, making them ideal for use in single-use plastic extrusion, injection molding, and biodegradable film.
By using BioMates, companies can reduce their carbon footprint and contribute to the creation of a more sustainable future. These products provide an eco-friendly solution for the plastic industry and help to reduce the environmental impact of plastic waste.
EuroPlas offers three types of bio-filler products, collectively known as BioMates 01, 02, and 03, each with different compositions to meet specific customer requirements.

EuroPlas also offers a range of bioplastic compounds under the name BioMates. These compounds are made from renewable sources such as cornstarch, rice straw, bamboo, and other plant-based materials, making them a more sustainable alternative to traditional petroleum-based plastics.
Bioplastic compounds are complete plastic materials and can be used to create products without the need for additional materials.
EuroPlas offers different grades of bioplastic compounds, such as BiONext 102 and 152, each with different properties and functions. BiONext 102 is eco-friendly and flexible, while BiONext 152 is bio-based and biodegradable.
The characteristics of bioplastic compounds include being biodegradable within 12 months after use, having outstanding mechanical properties, and being able to be tailor-made based on the end-products requirements. Additionally, the use of bioplastic compounds reduces the carbon footprint of bioplastics, making them a more environmentally friendly option.
EuroPlas' BioMates bioplastic compounds have a diverse range of applications, including compostable straws, shopping bags, dental picks and floss, mulch films, single-use plastic utensils, thermoformed trays, food packaging film, and rolling film. By using bioplastic compounds, companies can contribute to the reduction of plastic waste and preserve the environment for future generations.
3. Plastic straw manufacturing process
3.1. Extrusion
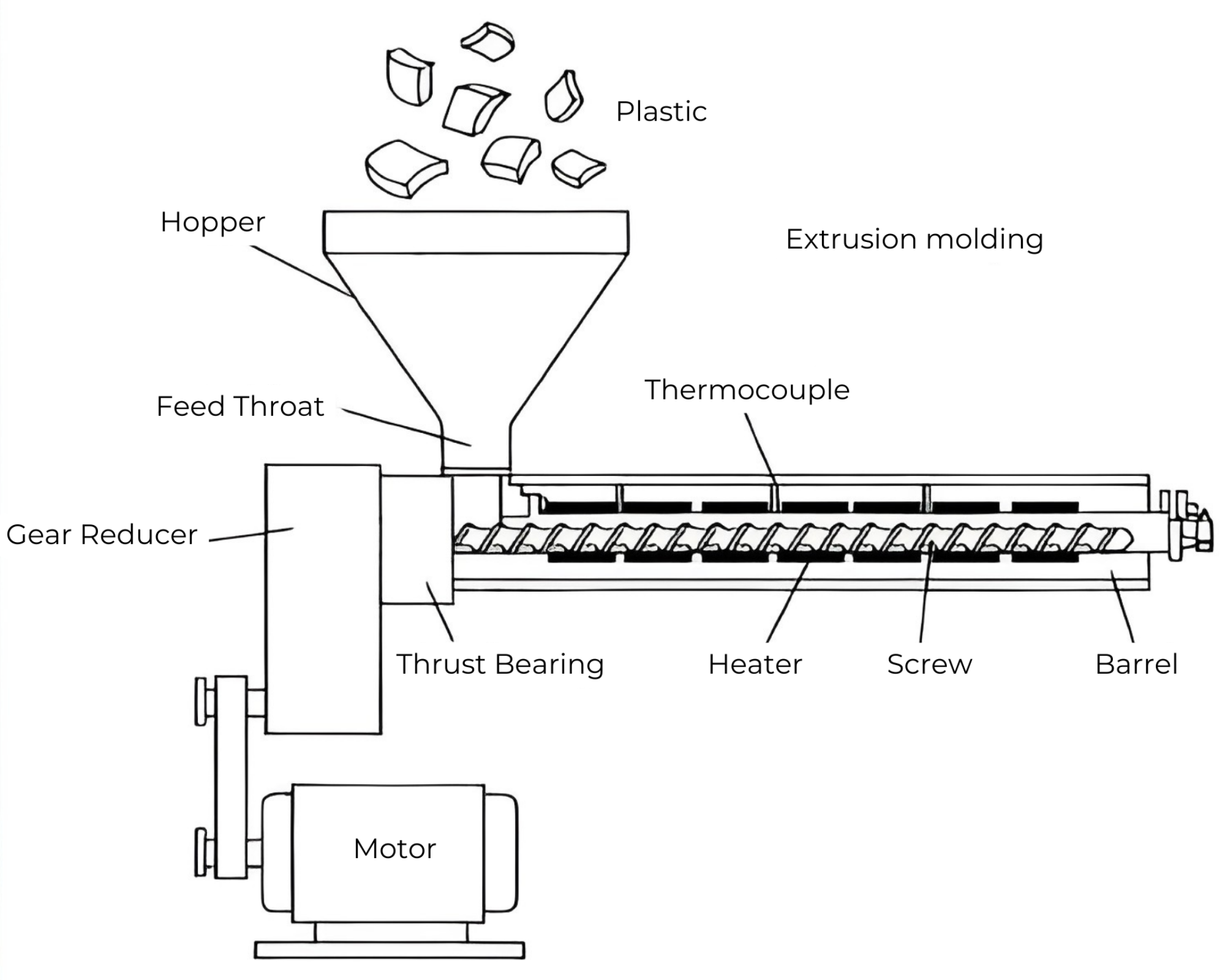
In the straw manufacturing process, the melted plastic pellets are transformed into hollow tube shapes using a second extrusion molder. The pellets are fed into a hopper at one end of the machine and are pushed through a long channel by a screw mechanism powered by a motor through a gear reducer. The second extruder is equipped with a different type of die that shapes the plastic into a tube. As the screw rotates, it moves the plastic resin down the barrel, which is heated, causing the resin to melt and become more flowable.
The screw fits within the barrel with only a few thousandths of an inch clearance, and it is machined from a solid steel rod. The surfaces of the screw that almost touch the barrel are hardened to resist wear. This close tolerance ensures good movement and heat transfer as the resin travels down the barrel. By the time the plastic resin reaches the end of the barrel, it has completely melted, and it can be easily forced out through the die's opening.
3.2. Cooling & Cutting
After exiting the die, the melted resin forms into a long and continuous tube shape, which will ultimately become the straw. At this stage, the straw is still quite fragile and requires careful handling to maintain its shape. To aid in this process, a puller is used to gently move the straw along and ensure it retains its shape. Additionally, in some manufacturing processes, the straw is pulled through sizing plates, which serve to further control and refine its diameter. These plates are essentially sheets of metal with precisely drilled holes, through which the straw is threaded.
Once the straw has been pulled through the sizing plates, it is directed through a cooling stage. In most cases, the straw is passed through a water bath, which cools and solidifies the plastic. Some manufacturers may also use a metal rod, called a mandrel, which is chilled and used to freeze the internal diameter of the straw to a specific size. Once the plastic has been cooled and hardened, it is ready to be cut to the appropriate length by a knife assembly.
3.3. Special Operations (optional)
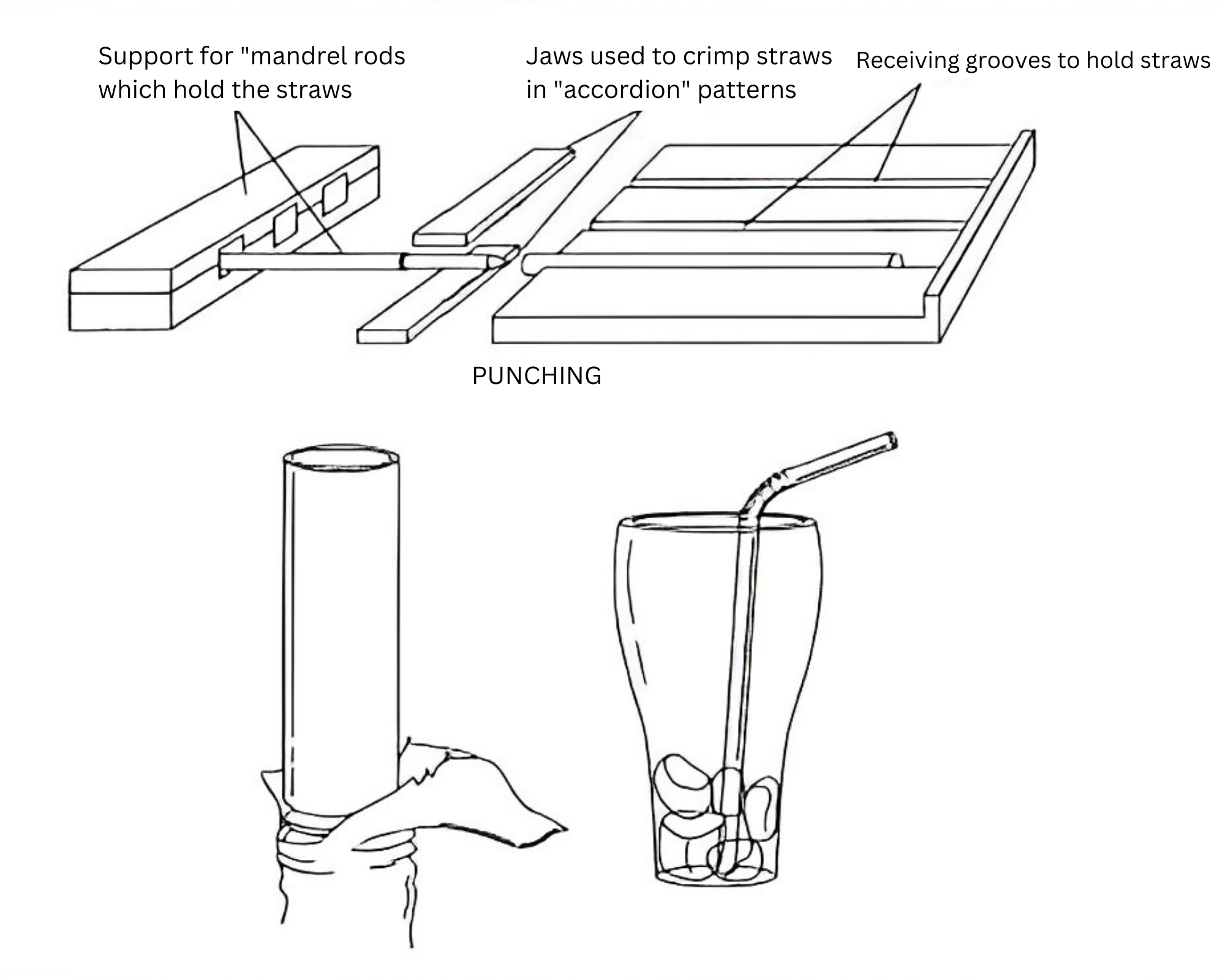
Straws that require unique designs may undergo additional manufacturing steps. "Crazy" straws, for instance, which contain a series of loops and turns, require special molding equipment to be bent into shape. On the other hand, bendable straws, which can be flexed in the middle, are produced using a special device that creates grooves in the straw, allowing it to flex.
This process takes place in two steps, the first of which involves picking up the straw for manipulation. This is accomplished by laying the straws across a flat plate with slots cut into it, which the straws will naturally roll into and remain. The plate is adjacent to a metal plate with a series of pins extending from it, which are aligned parallel to the slots.
Once the straws have settled into the slots, the pins can be easily inserted into them, allowing the straws to be lifted and moved in any orientation by manipulating the pin plate. The steel pins used to hold the straws have a series of parallel rings cut into them. As the straws are wrapped around the pins, they are gripped by a pair of semi-circular steel jaws that have a complementary set of rings. The jaws crimp a series of rings into the straw to create the desired bend pattern. Once completed, the straws are then ready for the last step - packaging.
3.4. Packaging
After the manufacturing process, straws are typically packaged in individual paper sleeves to keep them sanitary. One commonly used method involves loading the finished straws into a supply funnel. The funnel empties into a wheel with straw receiving grooves cut in it around its outer edge. The straws drop out of the hopper and are picked up one at a time by this rotating wheel, which moves them along to a second wheel connected to a vacuum source.
Sheets or packaging material, such as paper wrap, are fed onto this second wheel from a supply roller. The vacuum holds the paper in place while the first wheel feeds straws onto the paper. Another layer of paper is then guided over the first, and the assembly passes through a sealing roller. The two layers of paper are then crimped together using pressure or another sealing method.
The sealed sheet of straws is then transported along a conveyor to a punching region, where a die cuts out individual straws. The die-cut pieces then move along another conveyor to a collection area. The individual straws can then be bundled together and packed in boxes or pouches for shipping.
Packaging straws individually in paper sleeves is an effective way to keep them clean and sanitary for use. The packaging process described above can be automated and done on a large scale for mass production.
4. EuroPlas compound engineering plastic
EuroPlas is a pioneer in the plastic materials market in general and the filler masterbatch market in particular. Engineering plastic compound is one of the latest innovations at EuroPlas. This is a perfect combination of fossil resin, reinforcements and special additives based on the characteristics of end-products. With outstanding advantages, plastic engineering compounds are widely applied in several industries, such as household appliances, electrical engineering, electronics,..., especially high-tech industries, such as automotives, electronics,…
Currently,
EuroPlas supplies a wide range of engineering plastic compounds, such as PP compound, ABS compound, PC compound, PA compound,...
For detailed information and samples, please contact
HERE