Nowadays, one of the consumers’ concerns is corporate social responsibility related to CO2 emissions, fossil fuel depletion, and other environmental issues. Therefore, the demand for bioplastic is increasing day by day. One plain proof is that some of the world's famous brands like Walmart are using biodegradable plastic rather than plastic from petroleum. So in today's article, let's find out what bioplastics are, their pros and cons as well as their application in real life.
1. What are bioplastics?
1.1. Differentiating between disintegrating plastics and biodegradable plastics
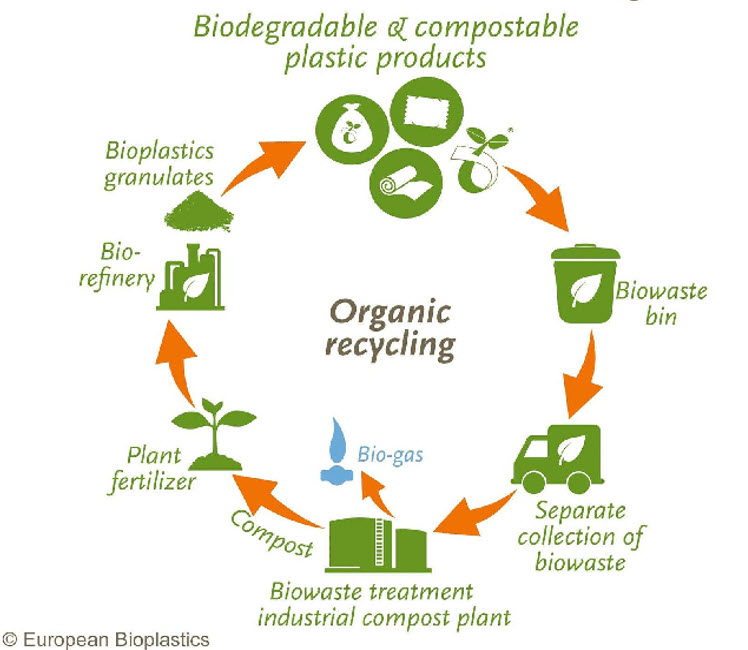
Bioplastics include disintegrating plastics and biodegradable plastics. In fact, many people may mistake disintegrating plastics for biodegradable plastics and assume that any type of bioplastics will completely decompose in the environment. So, what are the differences between them?
- Disintegrating plastics include the process of destroying the polymer molecular chains. Mixing plastic with additives (OXO degradable system) makes the polymer structure unstable, resulting in the molecular chain being destroyed but not completely decomposed.
- Biodegradable plastics include the process of complete decomposition when discharged to the conditions of moisture, light, and microbiology ... when being decomposed, it will be converted into other structures.
To distinguish biodegradable plastics from disintegrating plastics, we can use solvents. Put the plastic film in the solvent called CH2Cl2, if the film is completely dissolved in the solvent, it is biodegradable plastics. If the film does not dissolve, it is disintegrating plastics or PE, PP plastic.

The structure of biodegradable plastic is similar to common plastics such as polyethylene, polypropylene, and polystyrene. In addition, the technologies used to process biodegradable plastics are similar to those used for common plastics, including extrusion, injection molding, blown films, and thermoforming.
1.2. What are bioplastics made of?

Bioplastics are made from renewable sources such as polylactic acid (PLA) and Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA), extracted from crops and vegetables such as corn, palm oil, soya, and potatoes. Besides, bioplastics can be synthesized from fossil fuels like aliphatic-aromatic co-polyester (PBAT). The mixing of biodegradable polyester and starch is called starch/synthetic biodegradable polymer blends.
Related: What are bioplastics made from?
The following materials are what is used to make bioplastic:
1.3. What are the properties of bioplastics

Depending on the purpose of uses, manufacturers will produce bioplastic with the appropriate properties for final products. The major functions of bioplastics are:
- Biodegradable within a short time period after use (normally 12 months), thus causing no harmful effects on the environment
- High stiffness
- Good elongation
- Low melt flow index
- High impact strength
- Great gloss
- - Keep moisture on the surface, resulting in longer food preservation
- Anti UV, oxidation and moisture
2. What are some of the advantages and disadvantages of bioplastics?
2.1. What are the advantages of bioplastics?
Bioplastics will preserve the exhausting fossil fuel.
The production of bioplastics emits a smaller carbon footprint compared to traditional plastics.
Fast decomposition which happens in weeks to months.
Better for health (PLA and PHB) so they are suitable for the production of food packaging.
2.2. What are the disadvantages of bioplastics?
Are bioplastics a good alternative to traditional plastics? Not really. Because every coin has two sides and so do bioplastics. Below are some disadvantages of bioplastics we should take into consideration:
Because the main resources of bioplastics are crops, the fertilizers and pesticides used in growing the crops and the chemical processing needed to turn organic material into plastic will emit pollutants to the environment.
The land required for growing crops competes with land for food production.
The price of bioplastics is more expensive than that of traditional plastics.
Some bioplastics require a specific disposal procedure and industrial composting which needs advanced machines and facilities. If the local authorities can not filter bioplastics from traditional plastics and put all of them in landfill, the biodegradability will be somewhat reduced.
3. What can you make from bioplastic
The biodegradable plastic market has grown rapidly over the past 10 years, but it shares a relatively small amount. Biodegradable plastics such as starch and modified starch, polylactic acid, and aliphatic-aromatic co-polyesters, are currently used in a wide variety of niche applications, particularly for the production of rigid/flexible packaging, bags, sacks, and food contact products.
Currently, bioplastics are used to produce the following products:
3.1. 100% biodegradable & compostable shopping bags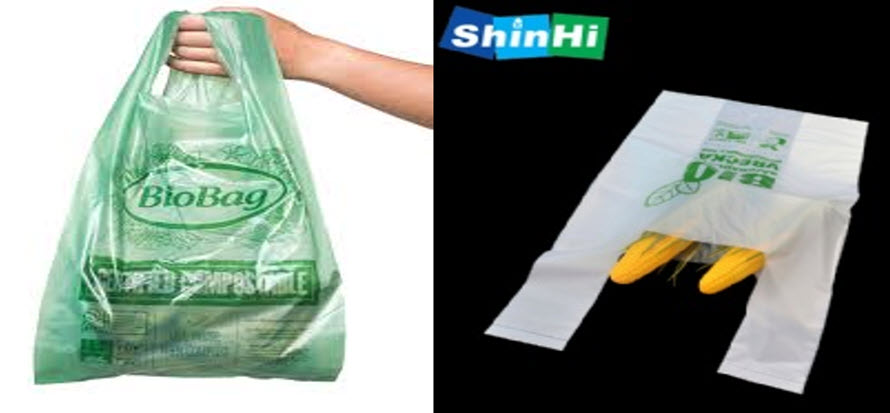 
3.2. 100% biodegradable T-shirts

Source: vollebak.com
3.3. 100% biodegradable trash bags

3.4. 100% biodegradable tablecloth

3.5. 100% biodegradable gloves

3.6. 100% biodegradable knives/spoons/forks
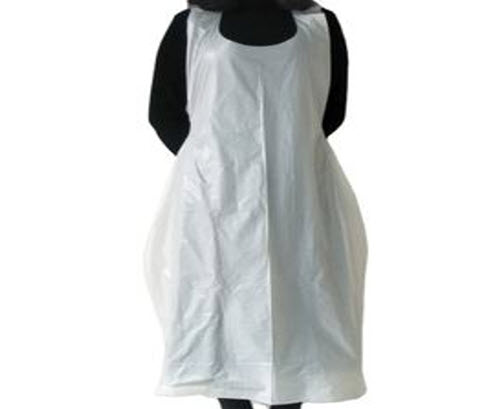
3.7. 100% biodegradable aprons

3.8. 100% biodegradable laminating film

3.9. 100% biodegradable trays

3.10. 100% biodegradable dog poop bags

3.11. 100% biodegradable films

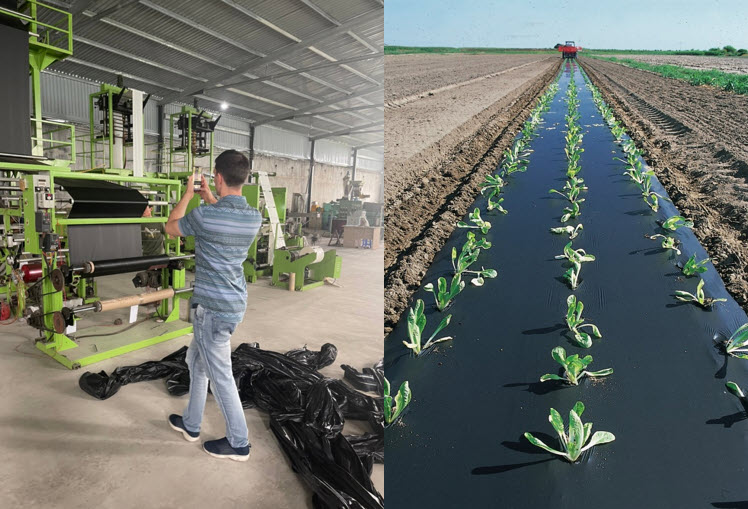
3.12. 100% biodegradable mulch

3.13. 100% biodegradable bottles

4. Where to buy bioplastic materials?
Understanding the market demand for biodegradable plastic materials, EuP has developed bioplastic compound and bio filler products which are solutions to replace traditional plastics. Currently, EuP's products have been successfully exported to markets such as the US, Europe, Japan, and China...
4.1. Biocompounds
BIONEXT 152 is a compound of modified PLA resin with 25% CaCO3 powder. This product is the best fit for injection molding of cups, spoons, and forks.

The most outstanding feature of BIONEXT 152 is completely biodegradable and environmentally friendly:
- High stiffness
- High impact strength
- Great gloss
- Easy for processing
BIONEXT 102 is a bioplastic compound based on modified PLA with CaCO3 powder, used for extrusion products such as straw extrusion. BIONEXT 102 is widely used to replace PE and PP plastics.
BIONEXT 102 is a fully biodegradable material with the following characteristics:
- High stiffness
- Low melt flow index
- High impact strength
- Easy for processing
BIONEXT 400 is a bio compound based on PBAT resin mixed with modified corn starch. This is a completely biodegradable plastic compound that can be applied to blown films for shopping bags, rolling films, food wrapping films, etc. Thanks to the ability to retain moisture on the surface and prevent oxygen absorption, fruits and vegetables are preserved longer.

BIONEXT 500 is a compound based on modified PBAT plastic and reinforced CaCO3 powder. It’s used for blown film products such as shopping bags, rolling film, and food bags.
This product replaces the traditional packaging products made from PE.
Features of BIONEXT 500:
- High stiffness
- Good elongation
- Easy for processing
- Great dispersion
BIONEXT 600 is a bio compound based on PLA, PBAT, talc powder, and special additives. This product is used to produce agricultural mulch film due to its UV resistance, anti-oxidation, and mildew which prevent a lot of environmental damage. After completing its life cycle, BIONEXT 600 plays the role of fertilizer for plants.

BIONEXT 700 is a bio compound based on PLA, PHA, PBS, and special plasticizers. The materials is applied for creating transparent packaging for the seafood, and garment industry which requires avoiding oxygen absorption and food oxidation. BIONEXT 700 is a fully biodegradable bio compound.
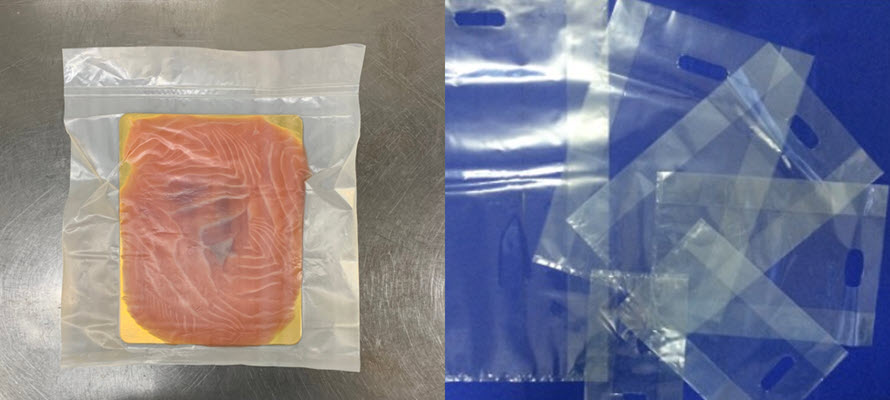

4.2. Biofiller
We have successfully researched and developed biodegradable filler and obtained the world's first degradable certificate. Taking the advantages of the Vietnam's natural materials, this product offers a cost-effective solution for the bioplast packaging and blowing industry.


BIO MATES 01 is a combination of biodegradable plastic fillers mixed with surface-modified CaCO3 powder and additives. BIO MATES 01 is suitable for plastic substrates such as PBAT, PBAT and starch compound, PBAT and PLA blend. This product helps to reduce the cost of the end product and acts as an anti-block and anti-slip additive for PBAT films. EuP’s BIO MATES 01 obtained the certificate of biodegradation from OK COMPOST INDUSTRY.

BIO MATES 02 is a combination of biodegradable plastic mixed with surface-modified BaSO4 and additives. EuP’s BIO MATES 02 obtained the biodegradation certificate from OK COMPOST INDUSTRY.
Features of BIO MATES 02:
- Optimize cost when mixing with several types of bio resins, such as: PBAT, PBAT compound, PBAT & PLA blend
- Increase the film glossiness
- Films are more transparent than when using CaCO3

BIO MATES 03 is a combination of biodegradable plastic mixed with surface-modified TALC and additives. EuP’s BIO MATES 03 obtained the biodegradation certificate from OK COMPOST INDUSTRY.
Features of BIO MATES 03:
- Optimize cost for bioplastic end-products processing
- Increase the stiffness for films
- Films are more transparent than when using CaCO3
- Play as anti-blocking and slipping agent for PBAT films
If you want to get more details about our products, please fill in this form or contact us via email/phone number. We are more than happy to help!