Automotive plastic materials have become the backbone of modern vehicle design. Once dominated by metals, today’s cars rely heavily on plastics for lighter weight, greater fuel efficiency, and increased flexibility in design. But what are the most commonly used plastic materials in cars? How are they applied, and why are they essential? In this article, we’ll walk you through the key types of automotive plastics, their properties, applications, and the challenges ahead.
1. Why Automotive Plastic Materials Matter
1.1. The Rise of Plastics in Cars
The transformation of the automotive industry from metal-heavy designs to lightweight, plastic-integrated structures has been driven by economic, environmental, and performance demands. According to the American Chemistry Council, plastics make up approximately 50% of a vehicle’s volume but only about 10% of its weight.
Plastics were initially introduced to replace heavier components and offer manufacturers a cost-effective and energy-efficient material. Over time, their versatility led to wider adoption across interior, exterior, and under-the-hood components.
1.2. Advantages of Using Automotive Plastic Materials in Cars
Plastics aren’t used just because they’re lighter. Their advantages extend across several performance categories:
- Fuel efficiency: Reducing vehicle weight by 10% can improve fuel economy by 6–8%, according to the U.S. Department of Energy.
- Cost reduction: Injection molding and thermoforming allow quick and affordable part production.
- Design flexibility: Plastic components can be shaped into complex forms that would be impossible or expensive with metal.
- Corrosion resistance: Unlike steel or aluminum, plastics don’t rust.
- Noise and vibration dampening: Plastics help improve cabin comfort.
- Safety: Energy-absorbing plastic parts improve crashworthiness.
.jpg)
Automotive plastic materials have become the backbone of modern vehicle design.
2. Types of Automotive Plastic Materials and Their Properties
Different areas of the vehicle require plastics with different characteristics, such as flexibility, heat resistance, or impact strength. Below are the most common plastic materials used in the automotive industry today:
2.1. PP
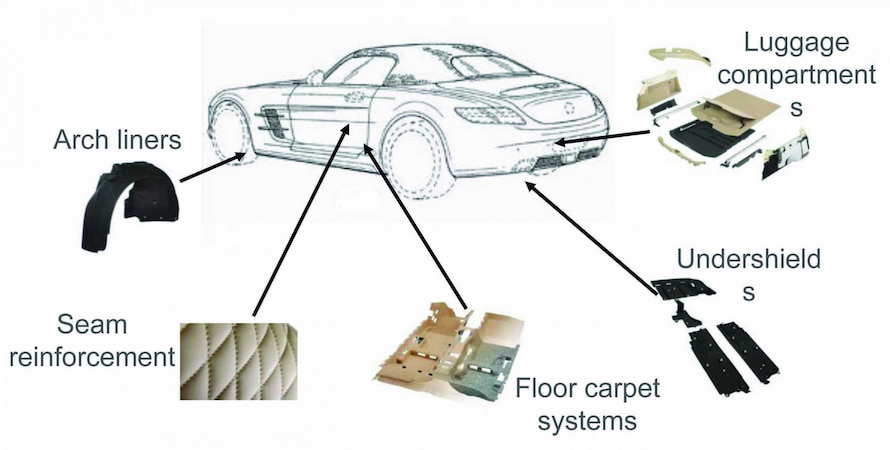
- Properties: Lightweight, chemically resistant, tough, flexible
- Applications: Bumpers, battery housings, carpet fibers
- Example: Most car bumpers today are made of PP because it can absorb minor impacts without permanent deformation.
Read more:
2.2. PUR
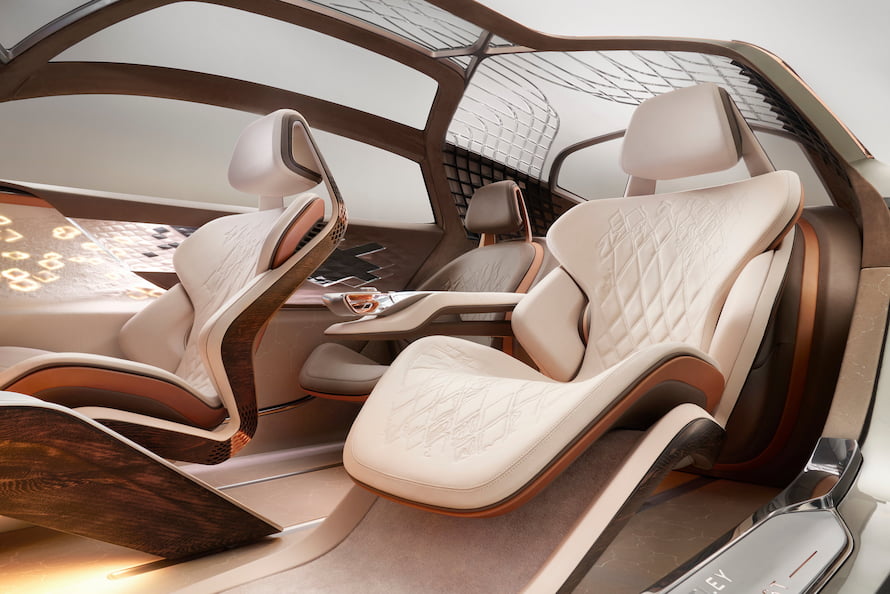

- Properties: Flexible, shock-absorbing, insulating
- Applications: Seat cushions, soundproof panels, bumpers
- Example: Automotive seat foam is often made from PU for maximum comfort and form retention.
2.3. PVC
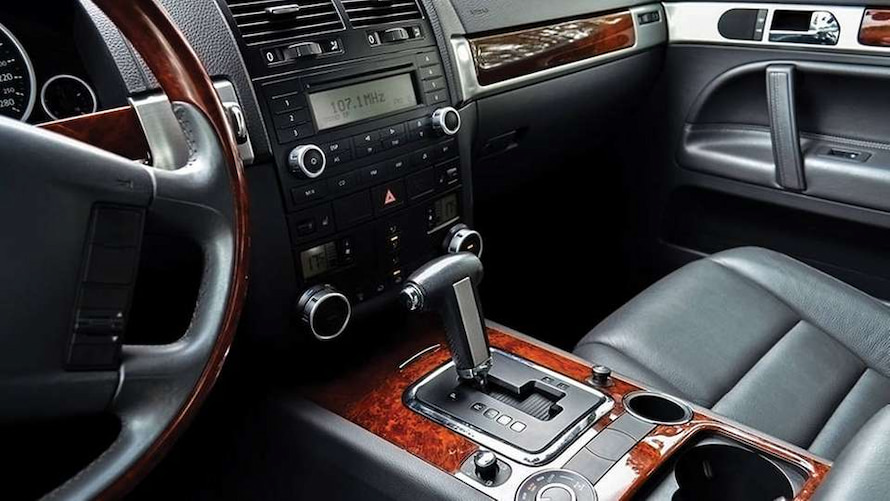

- Properties: Strong, durable, chemical-resistant
- Applications: Interior door panels, wiring insulation, seals
- Example: PVC is used in car doors for its resistance to wear and weather exposure.
2.4. ABS
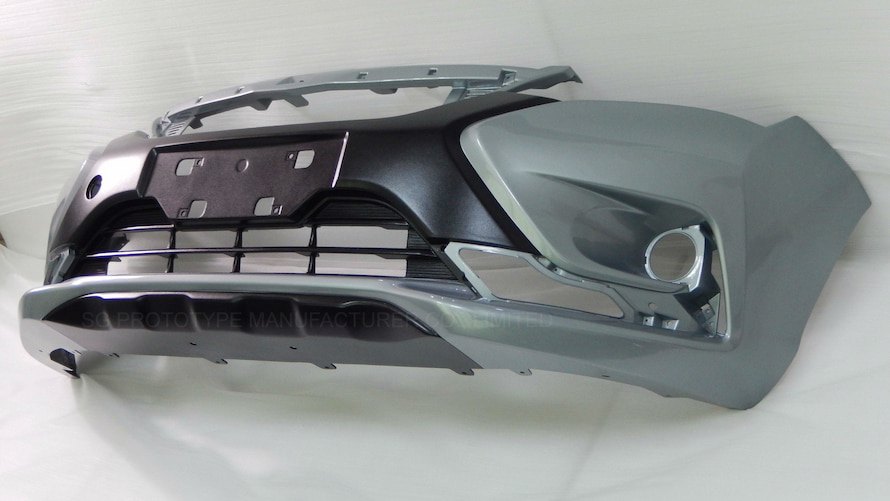

- Properties: High strength, impact resistance, glossy finish
- Applications: Dashboards, trim panels, control bezels
- Example: The dashboard of many economy vehicles uses ABS to combine safety and aesthetics.
Read more: Advantages of ABS Compound in Automotive Applications
2.5. PA

- Properties: High melting point, strong, wear-resistant
- Applications: Gears, fuel system parts, under-hood components
- Example: Nylon is widely used in engine compartments because of its ability to withstand high temperatures.
2.6. PS
.jpg)
Polystyrene (PS) is a thermoplastic material that is popular for its lightweight and versatile nature.
Polystyrene (PS) is a thermoplastic material that is popular for its lightweight and versatile nature. , Therefore, it becomes the top choice for a variety of automotive applications. One of the most common applications for PS in the automotive industry is as a material for exterior parts. This includes body-side moldings, bumpers, grilles, and other trim pieces.
PS is an efficient and cost-effective material, becoming an attractive choice for mass-production applications. PS insulating properties are applied to manufacture interior components such as dashboards and door panels because of their ability to dampen sound and vibrations. Another important benefit of PS is its ability to be recycled. PS can be recycled and reused in other applications, hence, becoming an environmentally friendly material.
However, one of the downsides of PS is its susceptibility to damage from UV radiation, which can cause it to degrade over time. This can be mitigated by using additives and coatings, but it is still a consideration when choosing PS for automotive applications.
2.7. PE

- Properties: Chemical resistant, tough, flexible
- Applications: Fuel tanks, inner liners, wire coverings
- Example: PE is often used in fuel systems where corrosion and flexibility are key.
2.8. POM

POM is considered an ideal automotive plastic material
POM is considered an ideal material with high stiffness, high resistance to wear, good dimensional stability, chemical resistance, and resistance to impact and fatigue. It is a popular choice for manufacturing many different automotive components including:
- Fuel system components: due to POM's excellent chemical resistance to fuels, oils, and solvents.
- Interior components: due to POM's excellent dimensional stability, low friction coefficient, and good wear resistance.
- Exterior components: due to POM's high stiffness, impact resistance, and weather ability.
- Engine components: due to POM's excellent resistance to wear, fatigue, and creep.
2.9. PC

Some common applications of PC in the automotive industry include dashboard and interior trim.
Polycarbonates (PC) are a group of thermoplastic polymers containing carbonate groups in their chemical structures. Some common applications of PC in the automotive industry include:
- Headlight lenses
- Window and windshield glazing
- Dashboard and interior trim
- Exterior body panels
2.10. PMMA

PMMA, or polymethyl methacrylate, is a transparent thermoplastic that has many uses in the automotive industry. It is used for exterior and interior parts such as headlamp lenses, taillight lenses, and instrument panels.
PMMA has a high level of transparency, allowing for excellent light transmission. This material is also highly resistant to weathering, withstand prolonged exposure to sunlight and other environmental factors without yellowing, hazing, or cracking. Worth mentioning, PMMA is highly scratch-resistant, then becomes the first choice for use in automotive applications where surfaces may be exposed to frequent handling and abrasion.
Lastly, PMMA can be easily molded into a wide range of shapes and sizes, allowing for greater design flexibility and creativity in automotive applications. This makes it a popular choice for instrument panels, where designers need to balance functionality with aesthetic appeal.
2.11. PBT

PBT, or polybutylene terephthalate, is commonly used in the automotive industry due to its excellent mechanical and electrical properties. PBT is a member of the polyester family and is created by combining terephthalic acid or dimethyl terephthalate with 1,4-butanediol. Some of its applications in automotive are:
- Electrical components: connectors, switches, relays, and sensors.
- Under-the-hood parts: engine covers, oil filter housings, and radiator end tanks.
- Exterior parts: front grilles, mirror housings, and wheel.
- Interior parts: door handles, seat belt components, and airbag housings.
PBT has a high strength-to-weight ratio, which is suitable for automotive applications where parts need to be both strong and lightweight. Additionally, PBT has good resistance to many chemicals, including oils, fuels, and brake fluids. This makes it a suitable material for automotive components that are exposed to these substances.
In terms of dimensional stability, PBT can maintain its shape and size in varying temperatures and humidity levels. This is important for automotive parts that need to function properly in different weather conditions. PBT also has low water absorption, which makes it less susceptible to degradation and corrosion caused by water exposure. This is important for parts that are exposed to moisture and need to last a long time without corroding or degrading.
2.12. PET

PET (polyethylene terephthalate) is a type of polyester thermoplastic material. In the automotive industry, PET is used in the form of fibers, films, and foams. PET films are used for laminating glass windows to reduce shattering in case of accidents, and to protect headlights and tail lights from scratches and UV radiation. PET foams are used as a lightweight and durable material for vehicle interior parts such as door panels, instrument panels, and headliners.
PET is used in the automotive industry for various applications due to its desirable properties. Firstly, PET is a strong and rigid material, with good resistance to impact and chemicals, which is suitable for applications such as car interior panels, door panels, and trim. PET is also easy to process, allowing for efficient and cost-effective manufacturing of automotive parts.
Besides, PET provides great innovation and design. External plastic vehicle cladding enables designers to develop cutting-edge ideas that may not be feasible when working with metal. Utilizing plastics also results in lower production and manufacturing expenses, which are then passed on to the customer. Furthermore, unlike metal, which rusts when scratched, a PET bumper or plastic vehicle door cladding is considerably simpler to repair or replace when dented or scraped. In terms of sustainability, PET is a highly recyclable material, which is important in the automotive industry as there is a growing focus on sustainability and reducing the environmental impact of manufacturing.
2.13. ASA

ASA (Acrylonitrile Styrene Acrylate) is a copolymer of Acrylonitrile, Styrene, and Acrylate used in the automotive industry for exterior components such as body panels, spoilers, grilles, and trim parts.
ASA has excellent weathering properties and is highly resistant to UV radiation. This material also has good impact strength, good thermal stability, good surface finish properties, and chemical resistance properties. All of these benefits help ASA is increasingly preferred in the automotive industry and suitable for coming into contact with chemicals, such as fuel lines, reservoirs, and tanks.
3. Benefits of Using Automotive Plastic Materials
Plastics in cars aren’t just about weight reduction—they offer a wide range of practical and economic advantages.
3.1. Lightweight for Better Fuel Efficiency
As mentioned earlier, reducing vehicle weight by 10% can lead to up to 8% improvement in fuel economy (source: U.S. Department of Energy). With global emissions regulations tightening, lightweighting through plastics is a key solution.
3.2. Cost-Effective Production
Plastics can be injection molded into complex shapes, often combining multiple functions in a single part. This reduces the number of components, assembly time, and labor costs.
3.3. Design Versatility
Unlike metal, plastics can be colored, textured, and shaped without secondary operations. This is particularly useful for:
- Sleek dashboard designs
- Integrated clips and brackets
- Complex geometries in tight spaces
3.4. Safety and Noise Control
Many plastics are engineered to absorb energy during collisions, reducing injury risk. Additionally, materials like PU and PVC help insulate the cabin from outside noise and vibrations.
4. The Future of Automotive Plastic Materials
4.1. Bio-Based and Recycled Plastics
Manufacturers are investing in alternatives to petroleum-based plastics:
- Bioplastics from sugarcane, corn, or cellulose
- Recycled polyamide, polypropylene, and others used in non-critical parts
4.2. Advanced Composites
- Glass fiber-reinforced PP or PA: Offers better strength at lower weight
- Carbon fiber-reinforced plastics: Now used in high-end sports cars and EVs
4.3. Electric Vehicles and Sustainability
EVs demand even more plastic innovation:
- Thermal management of batteries using PC and PBT
- Lightweight body panels to improve range
- Flame-retardant materials for safer electronics housing
5. Conclusion
Automotive plastic materials are integral to modern car design. Their role spans structural, aesthetic, and safety functions. From bumpers to battery casings, plastics enable lightweight, affordable, and efficient vehicles. As the industry continues to evolve—toward electric, connected, and sustainable mobility—plastic innovation will remain at the heart of automotive progress.
6. Looking for automotive plastic materials manufacturers?

Looking for automotive plastic materials manufacturers?
As the world's No. 1 filler masterbatch manufacturer, EuroPlas is proud to offer a unique plastic material solution that helps customers' factories optimize production costs and improve their competitiveness on the market. Our engineering plastics compound is a full-featured solution for finished plastic products in a single input material.
Advantages of EuroPlas' compound plastic products:
- Bring the full features of the finished product in a single input material
- Can directly process finished products without mixing any other materials
- Specialized design according to finished product characteristics
- Improve mechanical properties for finished products: increase hardness, impact resistance
- Reduce shrinkage and increase heat resistance
If you want to learn more information about EuroPlas compound plastic products, do not hesitate to contact us for the earliest advice and support!