To choose the right plastic, it is very essential to know about the difference between PBT and PET. Each of the plastics possesses its own properties that serve specific applications in these industries. This article examines their impressive properties, outstanding applications and optimal ways to choose appropriate material to help to determine the best choice for your project needs. Let's explore to make the discovery of which of these materials has the best fit for your requirement!
1. Overview of PBT vs PET

PET has got to be pioneering when it comes to the material's recyclability and safety properties
Currently, PBT vs PET are being recourse by a very important thermoplastic in today's industrial applications.
PBT was the engineering semi-crystalline plastic, which used terephthalic acid and butanediol polymerization. Because of the absorbability of low moisture, PBT became a very durable material for many products in different fields. The rapid increase in industries demanded lightweight yet strong materials has provided a market for PBT.
Read more: Beyond the Basics: The PBT Family You Need to Know
Meanwhile, PET is derived from ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid. Their impressive properties and recycle ability are recognized widely making PET one of the best options in both rigid and flexible applications. Currently, consumer preference for products that pose less undesired environmental effects is the biggest factor propelling PET development.
Read more: What is Polyethylene terephthalate (PET)?
By comparing PBT vs PET, manufacturers can better understand the unique characteristics of the materials to select materials suitable for their respective applications and changes in industry trends.
2. Comparing Properties of PBT vs PET
Understanding the differences in properties between PBT vs PET is a crucial factor in the production process. By comparing the key properties, manufacturers would be able to optimize the production processes of the products, which, in turn, ensures the performance, cost, and durability of the products produced. Here are some key properties that showcase differences in PET vs PBT.

PBT vs PET are being recourse by a very important thermoplastic in today's industrial applications
2.1. Mechanical Strength
This property is particularly important for materials in products that are subject to loading or stress. When comparing PBT with PET, PET gives a higher tensile strength, making it better suited for packaging and structural components that need stiffness and durability. PBT, although strong, the tensile performance is not equal to PET in high-stress application cases; hence, PET is the better choice when products need maximum strength.
2.2. Thermal Stability
It plays an important role at high temperatures, such as those exposing components of automobiles or electrical systems. PBT has exhibited improved thermal stability where heat stays on for a longer period without losing its properties. In comparison, PET has good performance in moderate temperatures so it is not really suited to continuously long high temperatures. Thus, it is most appropriate to use PBT for heat-resistant applications.
2.3. Chemicals Resistance
This ability ensures the longevity of a material to oils, solvents, and chemicals, primarily in the automotive and industrial environments. In PBT vs PET, both plastics exhibit excellent chemical resistance, but PBT excels with respect to resistance against hydrolysis in humid or wet ambient conditions. Consequently, PBT is preferred in applications involving frequent exposure to chemicals.
2.4. Moisture Absorption
The low moisture absorption is critical to dimensional stability under humid conditions. Comparative assessment of PBT vs PET reveals that PBT absorbs more moisture than PET. Thus, the applications where moisture exposure should be otherwise avoided, would be more suited to apply PET, e.g., packaging of foods and beverages.
2.5. Easy to Process
Processability, in general, governs the intricacy with which products are manufactured to have elaborate designs and high precision. Analyzing PBT vs PET, one will find that PBT is easier for molding, because it has a lower temperature for processing, as well as more suitable flow properties. PET is somewhat more torturous to process, but gives a better surface finish and clarity. It can be said that manufacturers should carefully consider finished product requirements to choose the appropriate one.
2.6. Sustainability
Sustainability becomes crucial dimensions in material choice, particularly in packaging and consumer products. PET is a far better environmentally sound option because it has been recycled widely around the world. There are many technological methods to recycle PET to be parts for new products, while PBT is and often is recycled less. Although PBT can be recycled in some cases, it is rare in recycle streams too. In other words, for sustainable applications, PET is the better choice.
2.7. Cost-Effectiveness
This is the parameter which however has to be taken into concern by the manufacturers wanting to optimize the balance between material performance and budget. Judging the performance for PET vs PBT, PET is generally much cheaper since it is readily available and usually has established recycling systems. Moreover, PET has become cost-efficient for mass production in many industries. In contrast, PBT is slightly more expensive because of good heat and chemical resistance but may counter the cost in maintenance after a long time. For budget-effective projects, PET often wins the race. However, manufacturers need to consider PBT when aiming to use it in a harsh environment.
3. Applications of PBT vs PET
Acquaintance with the applications of PBT vs PET is crucial for both the consumers and manufacturers. Their applications should be recognized to make the selection of the material for improving efficiency, durability, and economic advantages. Here are some principal applications that reflect the strengths and utility of these materials.
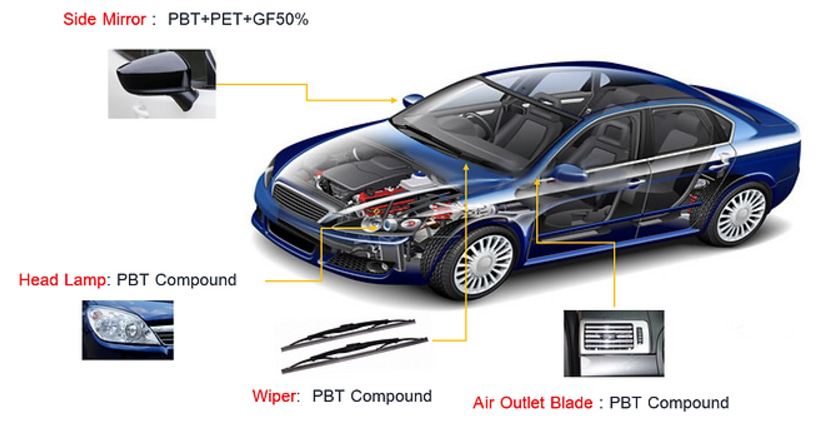
PBT is widely used for manufacturing components in the automotive industry
| PBT vs PET |
PBT |
PET |
| Applications |
- Automotive Components: PBT is widely used for manufacturing components in the automotive industry, such as those used in fuel systems, connectors, and gears. It absorbs loads well due to its high dimensional stability and thermal resistance even in severe conditions. For example, it can be applied for windshield wiper housing and sensors, where it will have to endure stress and heat constantly.
- Electrical and Electronic Devices: PBT extends its good use also in electrical and electronic applications due to insulation capability and resistance to moisture. It brings us circuit breakers, switches, and lamp sockets fulfilling people's unique safety and stability concerns. For instance, PBT has great performance even in humid conditions and is therefore suitable for outdoor electrical systems.
- Industrial Machinery: PBT is one of the main parts of industrial machinery products, such as conveyor belts, gears, and pulleys. It is reliable in a harsh environment according to high strength and resistance to chemicals. For instance, in a factory where PBT components have a harsh chemical environment, they tend to retain their structure over time.
- Household Appliances: In home appliances, PBT is commonly applied to parts susceptible to high temperature and physical stress, such as components in coffee machines and housings for hairdryers. Being thermally stable and tough, PBT is the best suited material for these applications. It is very easy to see the PBT role in toasters and kettles to ensure safe operation.
- Medical Devices: Some conditions regarding sterilization and biocompatibility make PBT suitable for some medical applications. It is very common in surgical instruments, handles and diagnostic devices. The properties make sure that PBT products meet the rigorous hygiene standards required in the healthcare ground.
|
- Packaging: There is rarely any alternative to PET in the packaging industry. Particularly for food and beverages, PET is the top choice. Apart from being lightweight and transparent and recyclable, it delivers optimal protection and visual appeal. Some common applications such as flexible packaging films, water bottles, food trays, and squeezable bottles.
- Textiles: PET acts as a vital raw material in the textile industry for the making of tough and moisture-resistant fabrics. These are produced for different applications, including clothing, upholstery, and industrial fabrics. An example for the textile produced mainly from PET is sportswear, which is praised for its durability and versatility.
- Consumer Goods: Consumers use PET to manufacture different goods such as storage containers, kitchenware, and toys. Due to its clarity, strength, and cost-effectiveness, PET is appropriate for beautiful and long life goods. It is commonly used in clear PET boxes, which provide storage usage in the refrigerator.
- Electrical Insulation: Applications of PET in electronics are mechanical strength products and electrical parts. There are insulation films, capacitor film and flexible printed circuits, notably PET films are applied in solar panels to enhance efficiency and durability.
- 3D Printing: PET is one of the most preferred materials used in 3D printing applications. It exhibits high tensile strength, great flexibility, and easy printing. Creating custom parts/prototypes and even functional tools have made it an attractive material for hobbyists and professionals alike.
|
4. Which Plastic Should You Choose?
Understanding about PBT vs PET is essential to choose the most appropriate material for a given application. While both these materials come with their individual advantages, knowing some specific criterias can result in more efficient production processes at reduced costs. Below are important criterias for selection when choosing betweenPET vs PBT.

PET is the best option for applications requiring good clarity, lightweight, and moisture resistance
4.1. Operating environment
The environment in which the product will operate is critical in determining the best choice whether PBT vs PET. For each type of environment (temperatures, chemicals, or moisture exposure,ect) PET vs PBT must be compared concerning the resistances. In fact, PBT is ideal for components and industrial machinery where they perform well in environments with higher temperatures coupled with chemicals. In contrast, PET is the best option for applications requiring good clarity, lightweight, and moisture resistance, such as packaging and textiles. Therefore, a humid or chemical environment suits PBT, while moderate conditions requiring transparency and recyclability suit PET.
4.2. Functional Requirements
It is also necessary to consider the functional requirements of final products between PBT vs PET. For instance, if a product is needed to have tensile strength, rigidity, or impact resistance, PET, with better mechanical properties is the best option. On the other hand, for applications that are required to provide stability for the long term under high temperatures or stresses, like in automotive applications or electrical devices, PBT offers higher thermal resistance and moisture stability. It is therefore necessary to concentrate enough on the specific performance requirements to enable optimum choice of materials.
5. Conclusion
In conclusion, PBT vs PET are two essential materials that are very important to many industries because they present some unique benefits of application. For PBT, it does exceptionally well in high temperatures and in more chemically tougher conditions. While PET is an ideal choice for lightweight, transparent, recyclable applications. Currently, the high demand market has more and more emphasized the importance of the two materials. In the near future, as industries have to be kept on balancing between performance versus sustainability, enhancements will be implemented to improve and create recycling and green production methods in the future.
6. About EuroPlas’ Engineering Plastic Compound
EuroPlas is proud to be the world's leading supplier of high-quality plastic materials. With many years of experience, EuroPlas guarantees a comprehensive supply of high-grade engineering plastic compounds. The engineering plastic compound of EuroPlas is a combination of a series of properties such as easy processing, cost-effectiveness, heat resistance, hardness and excellent abrasion resistance. Here are some typical engineering plastic compounds that will make a difference for your project:

EuroPlas guarantees a comprehensive supply of high-grade engineering plastic compounds
-
PBT GF-FR compound: This compound is an engineering plastic comprising PBT plastic with glass fiber reinforcements, color, and flame retardant additive.
- PA6, PA66 blend compound: PA6, PA66 blend compound comprises PA6/PA66 resin, elastomer, and impact strength modifiers, so it is resilient with strong mechanical properties.
- PA66, PA6 Glass fiber compound: PA66, PA6 compound is made of PA resin and reinforced with glass beads or glass fibers.
- PC flame retardant compound: PC-FR compound is made of PC resin mixed with halogen flame retardant with different UL94 standard fireproof levels such as 5VA, 5VB, V0, V1, V2.
- PC glass fiber compound: PC-GF compound is made of PC resin mixed with glass fiber as reinforcement.
- HIPS flame retardant compound: HIPS flame retardant compound is made of HIPS resin and flame retardant with different levels of standard such as V0, V1 and V2.
- HIPS Conductive compound: This compound is made of HIPS resin and carbon black conductive as the reinforcement.
- ABS Glass fiber compound: It is a combination of ABS resin, glass fiber, and suitable additives.
- ABS Antistatic compound: The compound is a specialty ABS-based compound that has the ability to dissipate static electricity.
- ABS flame retardant compound: It is made of ABS resin and flame retardant additives which are in different fire resistance levels according to UL94 standard: V0, V1, and V2.
- PP flame retardant compound: The main components of this compound are polypropylene (PP) resin and halogen/non-halogen flame retardant with different levels of UL94-standard flame retardants: 5VA, 5VB, V0, V1, V2.
- PP conductive compound: This is a combination of PP resin and carbon black conductive.
- PP BaSO4 compound: PP BaSO4 compound reduce shrinkage and deformation in high-temperature settings and enhance formability and heat, chemical, and impact resistance.
- PP talc compound: This is a combination of talc powder and appropriate additives based on end-products' requirements.
- PP glass bead compound: PP glass bead compound is a combination of PP resin, glass beads, and other additives.
EuroPlas ensures that our product's processes are always strictly controlled to meet all high standard requirements. Contact EuroPlas today to get the best advice for your upcoming project!