Thermoplastic is among the most popular materials in many industries since it offers excellent flexibility and versatility. Our article will introduce types and 10 examples of thermoplastics, helping you decide which one is the most suitable for your products.
Let's scroll down for more details!
Read more: Thermosetting vs Thermoplastic: Which one to choose?
1. What are thermoplastics?
Thermoplastic is a flexible plastic polymer substance that softens when heated. It is made up of linearly bonded polymers and monomers. The qualities of the material are determined by the length of these chains; longer chains yield heavier molecular weights and greater durability. Thermoplastic melts when heated, enabling a variety of shapes and forms. When cooled, it solidifies and keeps its molecular structure. The material can often handle this process repetition, making it a versatile and recyclable option in many industries.
2. Types of thermoplastics and their uses
Below are the most common types of thermoplastics and their uses:
2.1. Acrylic

Acrylic thermoplastic
Acrylic is a multipurpose material well-known for its eye-catching appearance and durable impact resistance. It can be molded in a variety of colors and is frequently used as a replacement for glass in different applications, including windows, aquariums, fish tanks, and motorcycle helmet visors. Because of its weather durability, ease of maintenance, and aesthetic appearance, acrylic is also utilized in vehicle lighting and shop signage, as well as in arts and crafts projects.
2.2. ABS (acrylonitrile butadiene styrene)
ABS is a flexible, lightweight thermoplastic made up of acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene. It offers distinct degrees of impact resistance, toughness, and heat resistance and may be molded into a variety of commonplace objects and components. Tennis rackets, golf club heads, athletic equipment, musical instruments, drainpipe systems, and automobile parts are among the many products that use ABS. It is also a crucial part of the well-known kids' toy LEGO. The material is easy to customize and easily meets specific manufacturer requirements.
2.3. Polyamide or Nylon
Polyamide or Nylon is a durable material used in clothing and athletic gear. It has a strong resistance against impact, abrasion, chemical corrosion, and general wear and tear. Thus, it is present in many applications in various industries, including clothing, sports equipment, footwear, medical devices, industrial parts, and automobiles. It is frequently used to create heat-resistant textiles and is commonly employed in place of silk in a variety of goods, including parachutes, fabrics, rope, musical instrument strings, flak vests, and women's stockings.
2.4. Polypropylene (PP)

Polypropylene pipes
Polypropylene (PP) is incredibly flexible and resilient to stress and cracking, as it can withstand a high melting point. It works great for rugs, sportswear, and car parts that need to be bent into place. It is environmentally friendly because it can be reused numerous times. Compounds for a wide range of items have been made from it, such as piping systems, diapers, vehicle batteries, carpeting, rope, reusable containers, lab equipment, and stationery.
2.5. Polystyrene
Polystyrene, made by adding rubber to crystal styrene, is widely used due to its durability and impact resistance. The material is low-cost, easy to produce, and non-toxic, making it suitable for FDA grades and containers for consumable goods. In addition, polystyrene is used to make drinking cups, packaging peanuts, CD and DVD cases, and disposable kitchenware. You can find high gloss grades and flame-free versions of this material in the market.
2.6. Polyvinyl chloride
Lightweight and durable polyvinyl chloride is used to make roofing sheets, gutters, drain pipes, and vinyl siding. In addition, it is utilized in upholstery, outerwear, hoses, and electrical insulation for tubing. The material's non-flammable and weatherproof allow it to work effectively in the insert molding process. Plasticizers are frequently added for a variety of uses.
2.7. Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate is a strong, transparent and highly impact resistant thermoplastic. Because it is simple to work with, mold, and thermoform, polycarbonate often appears in the building sector. It is perfect for medicinal purposes, porch or outhouse windows, conservatory roofing, and bulletproof greenhouse panels. Thanks to its flexibility and resistance to breaking or cracking under extreme stress, polycarbonate applications also include data storage devices, construction materials, electronic components, and automotive and aircraft parts.
2.8. Polyester
Polyester is a thermoplastic that is used in a variety of industries, including apparel, mattresses, appliances, healthcare, and packaging. It provides outstanding toughness-stiffness balance, dimensional stability, and chemical resistance. Moreover, polyester materials are very stain-resistant. However, drying periods are a major concern since they can be moisture-sensitive and have poor thermal characteristics. In addition, ropes, yarns, seat belts, coated fabrics, plastic reinforcements, and conveyor belt fabrics are some more industrial uses.
2.9. Polyethylene

Polyethylene bottles
Polyethylene is a tough and high chemical and temperature resistant material. It's a popular choice for many applications, including packaging (films, bottles, geomembranes, bags, etc.), moving machine components, artificial joints, bulletproof vests, pipelines, bearings, and gears.
2.10. Polylactic acid (PLA)
Polylactic acid (PLA): PLA is a biodegradable substance that is frequently sourced from sustainable sources like sugarcane and corn starch. It is commonly utilized with fused deposition modeling techniques in 3D printing.
2.11. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE, Teflon)
Polytetrafluoroethylene or Teflon is a well-known nonstick cookware coating. Since it lowers wear and friction and the energy consumption of machines, it also works as a lubricant. The material is frequently used for electrical equipment, self-cleaning ovens, nonstick cookware, and waterproof clothing.
2.12. Cellulose acetate
Cellulose acetate is a synthetic fiber used in adhesives, eyeglass frames, and photography. It is also used to make playing cards and cigarette filters.
3. A list of 10 examples of thermoplastics
There are examples of high performance thermoplastics. Here is a list of the 10 most common ones:
- Toys (LEGO)
- Food storage containers
- Plastic grocery bags
- Drinking bottles
- Shampoo bottles
- Sports equipment
- Telephone handsets
- Toothbrushes
- Cable insulation
- Bullet-proof vests
4. Conclusion
We've introduced 10 examples of thermoplastics. In short, thermoplastic, a plastic substance that can be molded and reshaped yet also hardened when cooled, is a common material in many applications, from electronics to toys. It is versatile and frequently works well as a metal alternative. Thermoplastic can also be used with other materials to achieve a range of effects.
5. About EuroPlas thermoplastics compounds
As a leader in the masterbatch industry, EuroPlas offers a wide range of thermoplastic compounds that are flexible and of high quality. They are all-in-one materials, allowing you to process them directly without adding any material. The material can also be tailor-made based on the final product's requirements. Our engineering thermoplastics compounds can be used in automobile, electronics manufacturing, interior decoration, and renewable energy. Here are some examples of our products:
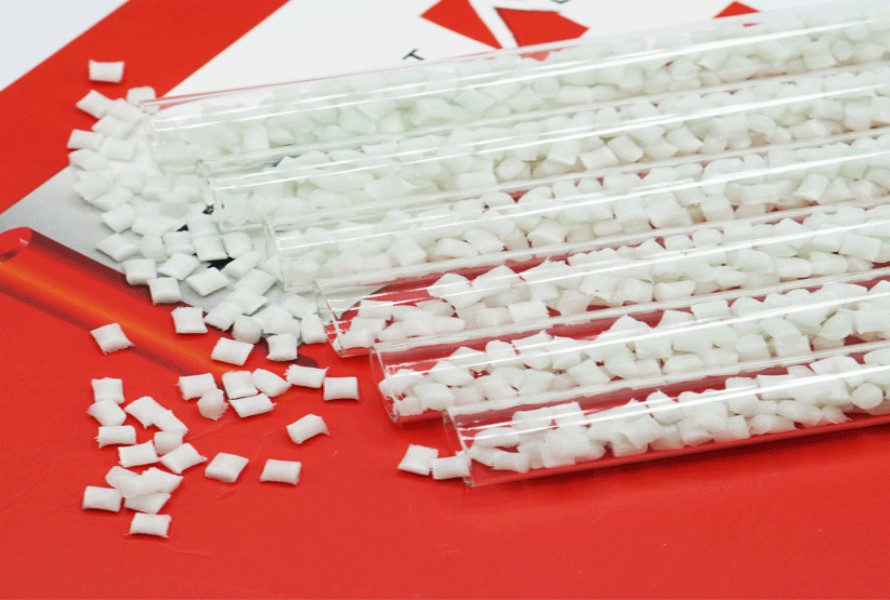 PP engineering plastic compound is a blend of PP resin and special reinforcing agents such as flame retardant additives, conductive black carbon, talc mineral, fiber/glass beads, etc. Depending on the requirements of the final product's characteristics, manufacturers will choose what reinforcements to combine.
PP engineering plastic compound is a blend of PP resin and special reinforcing agents such as flame retardant additives, conductive black carbon, talc mineral, fiber/glass beads, etc. Depending on the requirements of the final product's characteristics, manufacturers will choose what reinforcements to combine.
We have:
5.2. PA (Nylon) engineering plastic compound
 Polyamide-6 (PA6) and Polyamide-66 (PA66) are among the top choices for manufacturing thanks to their outstanding properties. The former is cheaper, easier to process, and distorts less, while the latter is stiffer and has higher temperature resistance and better abrasion resistance. EuroPlas has added other additives to the PA6 and PA66 resin to increase their performance.
Polyamide-6 (PA6) and Polyamide-66 (PA66) are among the top choices for manufacturing thanks to their outstanding properties. The former is cheaper, easier to process, and distorts less, while the latter is stiffer and has higher temperature resistance and better abrasion resistance. EuroPlas has added other additives to the PA6 and PA66 resin to increase their performance.
- PA6, PA66 blend compound: PA6, PA66 Blend compound combines PA6/PA66 resin, elastomer, and impact strength modifiers, giving it resiliency and strong mechanical properties. This material from EuroPlas will help you produce mechanically strong and highly precise final products. Its application includes roller bearings, carburetors, control valves, exhaust gas, and other gear-related components.
- PA66, PA6 Glass fiber compound: PA resin is mixed with glass fiber reinforced, providing the PA66 and PA6 Glass fiber compound with toughness, mechanical strength, high heat deflection temperature, chemical resistance, and wear resistance. With 30-50% of glass fiber, EuroPlas PA66, PA6 Glass fiber compound is ideal for producing drive belts, bearings, gears, carburetor components, household electrical components, and computer details.
5.3. Polycarbonate Engineering Plastic Compound
 Polycarbonate engineering plastic compound is mixed between the polycarbonate base, reinforcing agents, and additives. Its purpose is to create a material meeting the property requirements of the final products. The end products can achieve special properties thanks to the compound. Engineering plastic is commonly seen in electronics and automobile manufacturing, interior design, and renewable energy.
Polycarbonate engineering plastic compound is mixed between the polycarbonate base, reinforcing agents, and additives. Its purpose is to create a material meeting the property requirements of the final products. The end products can achieve special properties thanks to the compound. Engineering plastic is commonly seen in electronics and automobile manufacturing, interior design, and renewable energy.
EuroPlas Polycarbonate engineering plastic compound includes:
- PC glass fiber compound: a mixture of polycarbonate resin and glass fiber with rigidity, heat, and impact resistance.
- PC flame retardant compound perfectly combines polycarbonate resin and halogen flame retardant. It's lightweight, transparent, durable, impact-resistant, and high-temperature resistant.
5.4. ABS Plastic Products
 ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) is a thermoplastic polymer known for its toughness, heat resistance, and impact resistance. ABS is commonly used in a wide range of applications, such as electronic housings, automotive parts, and toys, due to its mechanical properties and ease of processing.
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) is a thermoplastic polymer known for its toughness, heat resistance, and impact resistance. ABS is commonly used in a wide range of applications, such as electronic housings, automotive parts, and toys, due to its mechanical properties and ease of processing.
- ABS Antistatic compound: It's the combination of ABS resin and antistatic additive. It helps prevent surface static, thus minimizing the risk of electrostatic discharge and ensuring safety during processing and product use.
- ABS Glass Fiber Compound: It's a combination of ABS resin, glass fiber, and suitable additives. It can increase the stiffness, heat deflection temperature (HDT), and softening point (VICAT) of end-products.
- ABS flame retardant compound: It is made of ABS resin and flame retardant additives, which are in different fire resistance levels according to UL94 standards: V0, V1, and V2. It's well-known for its ability to prevent fire spread on plastic surfaces.
Contact EuroPlas right now for more detail!